if you decide to have an Ovarian cyst removal surgery in Iran, reading this article can improve your knowledge about cost of Ovarian cyst removal surgery in Iran to a great extent and help you to choose the best city and hospital to perform Ovarian cyst removal surgery in Iran.
In this article we provide you with a comprehensive description of Ovarian cyst removal surgery in Iran, the cost of Ovarian cyst removal surgery in Iran and the best gynecologists.
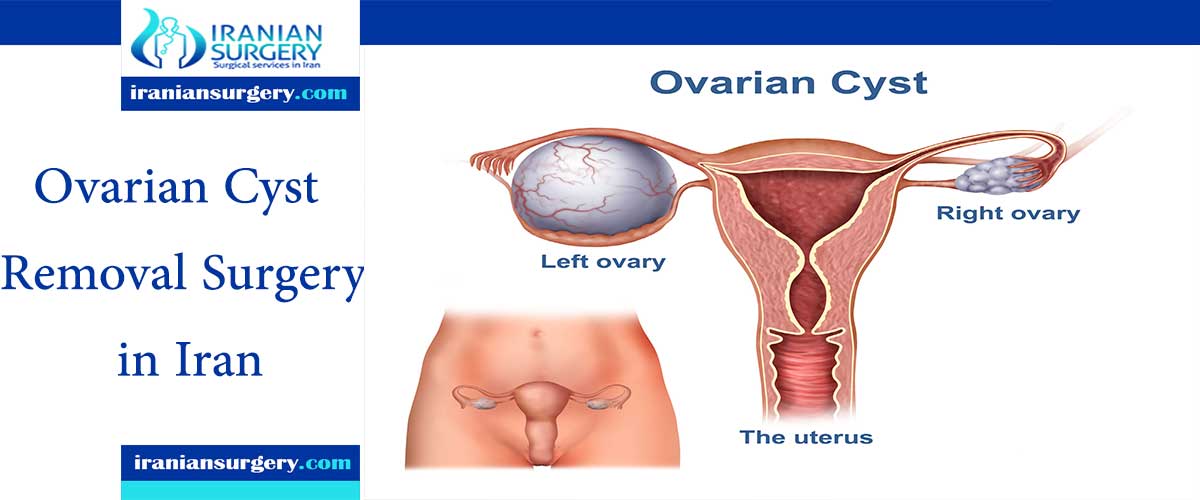
What are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can grow in or on your ovaries. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and go away on their own. But you may need surgery to remove a cyst if it’s causing you pain or discomfort or if there’s a chance it could be cancer.
Ovarian cysts are usually removed using a surgical procedure called laparoscopy (a type of keyhole surgery), but sometimes open surgery is necessary. Your procedure will be carried out by a gynecologist.
General information about ovarian cyst surgery in Iran
The following table describes general information about Ovarian cyst surgery in Iran including Ovarian cyst surgery cost in Iran, recovery time, and to name but a few.
| General Information | |
| Cost | $ 1000- 1800 |
| Anesthesia | General |
| Hospital Stay | 1-3 Days |
| Back to Work | 3 to 7 Days |
| Duration of Operation | 1-2 Hours |
| Minimum Stay in Iran | 10 Days |
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst usually only causes symptoms if it splits (ruptures), is very large or blocks the blood supply to the ovaries.
In these cases, you may have:
- Pelvic pain this can range from a dull, heavy sensation to a sudden, severe and sharp pain.
- Pain during sex
- Difficulty emptying your bowels
- A frequent need to urinate
- Heavy periods, irregular periods or lighter periods than normal
- Bloating and a swollen tummy
- Feeling very full after only eating a little
- Difficulty getting pregnant – although fertility is unaffected in most women with ovarian cysts.
An ovarian cyst may need to be removed if it is:
. Suspected of being cancerous the chances are more likely in older woman.
. Large more than 2.5 inches in diameter
. Solid rather than containing just fluid
. Causing pain
Ovarian cyst diagnosis
A cyst on your ovary can be found during a pelvic exam. Depending on its size and whether it’s fluid filled, solid or mixed, your doctor likely will recommend tests to determine its type and whether you need treatment. Possible tests include:
. Pregnancy test. A positive test might suggest that you have a corpus luteum cyst.
. Pelvic ultrasound. A wandlike device (transducer) sends and receives high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create an image of your uterus and ovaries on a video screen. Your doctor analyzes the image to confirm the presence of a cyst, help identify its location and determine whether it’s solid, filled with fluid or mixed.
. Laparoscopy. Using a laparoscope, a slim, lighted instrument inserted into your abdomen through a small incision your doctor can see your ovaries and remove the ovarian cyst. This is a surgical procedure that requires anesthesia.
. CA 125 blood test. Blood levels of a protein called cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) often are elevated in women with ovarian cancer. If your cyst is partially solid and you’re at high risk of ovarian cancer, your doctor might order this test.
Elevated CA 125 levels can also occur in noncancerous conditions, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Before ovarian cyst removal surgery
Complications of ovarian cyst removal
Complications are when more serious, unexpected problems occur during or after your procedure.
Most women recover well after ovarian cyst removal. Keyhole surgery causes fewer complications and has a shorter recovery time than open surgery.
Possible complications of any type of surgery include bleeding or a blood clot, usually in a vein in your leg (deep vein thrombosis – DVT). You could also develop an infection.
Ovarian cyst removal can cause damage to other organs, such as your bowel, ureters or bladder, but this is unusual.
Your gynecologist will try to preserve your ovaries so you can still have children, but this may not always be possible. Before your procedure, your gynecologist should discuss with you the chance of losing an ovary during the operation.
You should contact the hospital where you had your surgery if you develop any of the following symptoms:
. Tummy pain that’s getting worse
. A high temperature, especially if you’ve also lost your appetite or are sick
. Red or painful skin around your scars
. Burning or stinging when you pass urine more often, or not being able to pass it at all.
. Pain, swelling, redness or a feeling of heat on your legs.
Preparing for ovarian cyst removal
You will get some information from your hospital explaining how to prepare for your operation. If you smoke, for example, you’ll be asked to stop smoking. Smoking increases your risk of getting an infection after surgery, which can slow down your recovery. It can also lead to complications.
Ovarian cysts are usually removed by keyhole surgery as a day-case procedure. This means you can probably go home on the same day, although sometimes an overnight stay is needed.
Before you go in, make arrangements to have a friend or family member take you home from hospital after your procedure. And make sure there can be someone at home with you for the first 24 hours.
The operation is done under general anesthesia, so you’ll be asleep while it’s going on. You’ll be asked to follow fasting instructions. This usually means not eating or drinking anything other than clear fluids for about six hours before your surgery. You can usually drink water up to two hours before your surgery, but not after that. It’s important to follow any advice your hospital gives you.
You may be asked to wear compression stockings to help prevent blood clots forming in the veins in your legs.
Your gynecologist will discuss with you what will happen before, during and after your procedure, including any pain you might have. If you’re unsure about anything, don’t be afraid to ask. No question is too small. It’s important that you feel fully informed so you feel happy to give your consent for the procedure to go ahead. You may be asked to do this by signing a consent form.
Ovarian cyst treatment
Treatment depends on your age, the type and size of your cyst, and your symptoms. Your doctor might suggest:
. Watchful waiting. In many cases you can wait and be re-examined to see if the cyst goes away within a few months. This is typically an option regardless of your age if you have no symptoms and an ultrasound shows you have a simple, small, fluid-filled cyst.
Your doctor will likely recommend that you get follow-up pelvic ultrasounds at intervals to see if your cyst changes in size.
. Medication. Your doctor might recommend hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, to keep ovarian cysts from recurring. However, birth control pills won’t shrink an existing cyst.
. Surgery. Your doctor might suggest removing a cyst that is large, doesn’t look like a functional cyst, is growing, continues through two or three menstrual cycles, or causes pain.
Some cysts can be removed without removing the ovary (ovarian cystectomy). In some cases, your doctor might suggest removing the affected ovary and leaving the other intact (oophorectomy).
If a cystic mass is cancerous, your doctor will likely refer you to a gynecologic cancer specialist. You might need to have your uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes removed (total hysterectomy) and possibly chemotherapy or radiation. Your doctor is also likely to recommend surgery when an ovarian cyst develops after menopause.
During ovarian cyst removal surgery
What happens during ovarian cyst removal?
Ovarian cyst removal is usually done through keyhole surgery, but sometimes a larger cut is needed (open surgery). Your gynecologist will discuss with you which type of operation will be best in your circumstances. The procedure will usually take between 1-2 hours.
Simple or small cysts can usually be removed by keyhole surgery. If you’re having keyhole surgery, your gynecologist will make two or three small cuts (between 5mm and 1cm long). One will be near your belly button and two will be lower down, usually one on each side. They’ll pass small instruments and a tube-like telescopic camera (called a laparoscope) through the cuts. This procedure is known as laparoscopy. Your gynecologist will then examine your ovaries and remove the cyst. The cuts on your skin are closed with glue or stitches.
In some situations, your gynecologist may need to carry out open surgery. This is when a single, larger cut is made in your lower abdomen (tummy) to reach your ovary. Your gynecologist may recommend you have open surgery if the cyst is very large or there’s a chance it may be cancerous. Or they might have to change a laparoscopy to open surgery during the procedure to remove your cyst safely.
Under some circumstances, your whole ovary may need to be removed during the procedure.
After ovarian cyst removal surgery
After your laparoscopy, your nurse will make sure you’re not in pain and let you rest for a few hours. They’ll offer you something to eat and drink. You’ll usually be able to go later that day when you feel ready. Someone should drive you home and a friend or relative should stay with you overnight.
Your nurse will give you some advice about caring for your healing wounds before you go home. They’ll probably want to check that you can pass urine OK before you go home and may also give you some painkillers to take. You may be given a date for a follow-up appointment.
Having a general anesthetic affects everyone differently. You may find that you’re not so coordinated or that it’s difficult to think clearly. This should pass within 24 hours. In the meantime, don’t drive, drink alcohol, operate machinery or sign anything important. Always follow any advice you’re given by your gynecologist or the hospital.
If your gynecologist used dissolvable stitches, these will disappear on their own. Other stitches may need to be removed by the practice nurse at your GP surgery. This will usually be around five to seven days after your operation.
Side-effects of ovarian cyst removal
After your surgery, you may have some side-effects. These should be mostly temporary and may include:
. Pain or discomfort in your lower tummy for a few days after your operation
. Some pain in your shoulders
. A small amount of vaginal bleeding for up to 48 hours
. Feeling more tired than usual for a few days
Recovering from ovarian cyst removal
It takes time for your body to heal after surgery. Everyone is different. You may feel tired, and need to take a daytime nap for a few days after you get home.
But it’s also important for your recovery that you get up and about. Try taking a couple of short walks (10–15 minutes) in the first few days then building up gradually. By a week after surgery, most women can walk slowly and steadily for up to 60 minutes. After about two weeks, they are back to their normal levels of exercise. You should avoid heavy lifting for four weeks.
You’ll probably be able to go back to work a week after the procedure, but this may depend on the type of work you do. It may take a week or so more. The time it takes to recover will also be affected by whether you had keyhole or open surgery. Recovery from open surgery takes longer. If you have any questions about your recovery or when you can get back to particular activities, ask your gynecologist. It’s important to follow their advice.
If you need pain relief, you can take over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. Always read the patient information that comes with your medicine and if you have any questions, ask your pharmacist.
Read more about: Ovarian Cyst Size Chart
Read more about: Ovarian tumor removal recovery time
Read more about: Virgin tightening surgery before and after
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best hospital and doctors in Iran. The price of Ovarian cyst surgery in Iran can vary according to each disease and types of surgery. So, if you are looking for the cost of Ovarian cyst surgery in Iran, you can contact us and get free consultation from Iranian surgery.


10 Responses
Ovarian Cyst Is Just One Type? Is Ovarian Cyst Dangerous?
The ovarian cysts are of different types and are often safe and treated after a while. But in cases where they are dangerous and malignant, you need to see a doctor and use medical treatment.
greetings
I have fibroid cyst and have long-term bleeding. Doctors have prescribed medroxy progesterone tablets but what do I still have to do with Spotting every day?
It is better to see a gynecologist.
It was a miscarriage and following a scan the cyst was picked up. Before that she had no idea. Yesterday they were told cyst will be drained and removed and her ovary is well.
glad to hear that, if you need more information you can check what to expect after ovarian cyst surgery? article as well . thank you
hey there, moin moin. I have a question about cyst removal surgery.my wife is a 32 year old healthy woman (she smokes time to. Time. though) and she has a ovarian cyst which her doctor said that she needs a removal surgery, would it be possible for ya to give us a short explain for it?
hey there, hope you doing fine. you need to ask your surgeon the question as he has seen the results and tests but in general its Laparoscopy. Using a laparoscope — a slim, lighted instrument inserted into your abdomen through a small incision — your doctor can see your ovaries and remove the ovarian cyst. This is a surgical procedure that requires anesthesia
Margarita Nickolovana hier wit cist in my overies. The dr already examined me and im sur of wat I have. I need to kno mor. can you give me instrucher? do i need surgery or no? i never had cist befor. and i fear fear for life for my childs if i die. i want best dr if I nees surgery.
Dear Margarita, the Iranian Surgery team is happy to help you. You have already visited a gynecologist, She/He should tell you whether you need to have your cyst removed by surgery or not. Ovarian Cyst Removal Surgery is one of the most common gynecological diseases. The two lower organs of the uterus are the ovaries, which are responsible for producing the hormone estrogen. The most common of these is the follicle. A high percentage of women develop this complication and are unaware of its existence. In some cases, these cysts go away on their own and have no symptoms, and sometimes treatment is needed in various forms. Normally, premenopausal cysts do not require surgery due to the menstrual cycle. Surgery is generally recommended when cancerous cysts are suspected. Which large or stable type is removed by this device. Two types of surgery are used to remove ovarian cysts: Laparoscopy and Laparotomy.
With any surgery, there is a risk but not treating a serious problem or something that could become serious is a higher risk.