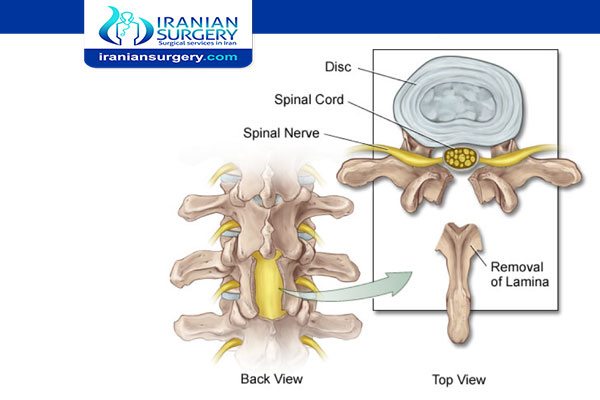
What is a Laminectomy?
how much does Laminectomy surgery cost?
Laminectomy is surgery that creates space by removing the lamina — the back part of a vertebra that covers your spinal canal. Also known as decompression surgery, laminectomy enlarges your spinal canal to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. That is, it helps ease pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots caused by injury, herniated disk, narrowing of the canal (spinal stenosis), or tumors.
This pressure is also caused by bony overgrowths within the spinal canal, which can occur in people who have arthritis in their spines. These overgrowths are sometimes referred to as bone spurs, but they're a normal side effect of the aging process in some people.
Laminectomy is generally used only when more-conservative treatments — such as medication, physical therapy or injections — have failed to relieve symptoms. Laminectomy may also be recommended if symptoms are severe or worsening dramatically.
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Total knee replacement surgery success story in Iran
General information about Laminectomy Surgery
The following table describes general information about Laminectomy surgery including Laminectomy surgery cost in Iran, recovery time, and to name but a few.
General Information |
|
Cost | $ 2500 |
Anesthesia | General |
Hospital Stay | 1-4 Days |
Back to Work | 4-6 Weeks |
Duration of Operation | 1-3 Hours |
Minimum Stay in Iran | 3-4 Weeks |
Read more about : Is a spinal fusion major surgery?
Read more about : Total knee replacement
Read more about : Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Read more about : Herniated disk treatment
Before Laminectomy Surgery
Why it's done
Why is a Laminectomy performed?
A laminectomy is often done to relieve the effects of spinal stenosis. In this condition, your spinal column narrows and puts pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This pressure can cause pain, weakness or numbness that can radiate down your arms or legs.
Because the laminectomy restores spinal canal space but does not cure you of arthritis, it more reliably relieves radiating symptoms from compressed nerves than it does back pain from spinal joints.
Spinal stenosis may be caused by:
. Shrinking of the discs of the spine and swelling of the bones and ligaments, which both occur with aging.
. Arthritis of the spine, which is more common in older adults.
. A congenital defect, or defect present at birth, such as abnormal growth of the spine.
. Paget’s disease of the bones, which is a condition in which bones grow improperly.
. Achondroplasia, which is a type of dwarfism.
. A tumor in the spine
. A traumatic injury
. A herniated or slipped disc
Depending on the location and severity, spinal stenosis can lead to:
. Pain in the neck or lower back
. Numbness, aching, or tingling that radiates from the arms into the hands
. Numbness or aching that runs down the buttocks and into the legs
. Cramping or weakness in the hands, arms, legs, or feet
. Difficulty walking
. Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel movements
Your doctor may recommend laminectomy if:
. Conservative treatment, such as medication or physical therapy, fails to improve your symptoms
. You have muscle weakness or numbness that makes standing or walking difficult
. You experience loss of bowel or bladder control
In some situations, laminectomy may be necessary as part of surgery to treat a herniated spinal disk. Your surgeon may need to remove part of the lamina to gain access to the damaged disk.
How do I prepare for a Laminectomy?
. Your healthcare provider will explain the surgery to you and offer you the chance to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
. You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the surgery. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
. In addition to a complete health history, your healthcare provider may do a physical exam to make sure that you are in good health before undergoing the procedure. You may have blood tests or other diagnostic tests.
. Tell your healthcare provider if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medicines, latex, tape, and anesthesia medicines (local and general).
. Tell your healthcare provider of all prescribed and over-the-counter medicines and herbal supplements that you are taking.
. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any blood-thinning (anticoagulant) medicines, aspirin, or other medicines that affect blood clotting. You may be told to stop these medicines before the procedure.
. If you are pregnant or think you could be, tell your healthcare provider.
. Follow any directions you are given for not eating or drinking before the surgery.
. You may get a sedative before the surgery to help you relax.
. You may meet with a physical therapist before your surgery to discuss rehabilitation.
. Certain activities may be limited after your surgery. Arrange for someone to help you for a few days with the household activities and driving.
. Based on your health condition, your healthcare provider may have other instructions for you.
Before laminectomy, a doctor may ask a person to:
. Avoid smoking
. Get a back brace and other supportive devices for use in the home
. Place clothes, food, utensils, and other necessary items in easily accessible places
Risks and Complications
What are the risks and complications of a laminectomy?
As with any surgical procedure, complications can occur. Some possible complications may include:
. Bleeding
. An infection in the surgical site or vertebral bones
. Blood clots in the legs or lungs
. Wound pain
. Risks linked to the use of general anesthesia
. Damage to a spinal nerve
. Difficulty breathing
. Unsuccessful treatment, which can lead to pain that persists after surgery
. A return of back pain, particularly after spinal fusion
. A heart attack
. A stroke
. A cerebrospinal fluid leak because of a tear of the dura mater, which is the membrane that surrounds the spinal cord
. Nerve or blood vessels in the area of surgery may be injured. This can cause weakness or numbness. The pain may not be eased by the surgery or may become worse, although this is rare.
There may be other risks depending on your specific health condition. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before the surgery.
Read more about : Cycling after knee arthroscopy
Read more about : Heart attack
During Laminectomy Surgery
Treatment
Medical Treatment
Some medical treatments for pain may include:
. Changes in activity
. Medicines, such as muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory medicines, and pain relievers.
. Spinal injections
. Physical rehabilitation, physical therapy, or both
. Occupational therapy
. Weight loss (if overweight)
. Smoking cessation
. Assistive devices, such as mechanical back supports
If medical treatments no longer work, surgery may be a choice.
How is a Laminectomy Performed?
During laminectomy surgery
A laminectomy may be done while you are asleep under general anesthesia. Or it may be done while you are awake under spinal anesthesia. If spinal anesthesia is used, you will have no feeling from your waist down. Newer techniques are being developed that may allow a laminectomy to be done under local anesthesia as an outpatient. Your doctor will discuss this with you in advance.
A laminectomy usually takes one to three hours.
Some people can go home on the same day as their procedure, while others may need to stay in the hospital for 1–4 days.
Generally, a laminectomy follows this process:
- You will be asked to remove clothing and will be given a gown to wear.
- An IV (intravenous) line may be started in your arm or hand.
- Once you are under anesthesia, a urinary drainage catheter may be inserted.
- If the surgical site is covered with extra hair, the hair may be clipped off.
- You will be positioned either on your side or belly on the operating table.
- The anesthesiologist will continuously watch your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen level during the surgery.
- The healthcare staff will clean the skin over the surgical site with an antiseptic solution.
- The surgeon will make a cut (incision) over the selected vertebra.
- The surgeon will spread the muscles apart.
- The surgeon removes the bony arch of the posterior part of the vertebra (lamina) to ease the pressure on the nerves in the area. This may involve removing bone spurs or growths, or removing all or part of a disk.
- In some cases, spinal fusion may be done at the same time. During a spinal fusion, the surgeon will connect 2 or more bones in your spine.
- The incision will be closed with stitches or surgical staples.
- A sterile bandage or dressing will be applied.
Read more about : Knee Ligament Repair
Read more about : Hip replacement
Types of laminectomy
Different types of laminectomy include:
. Cervical laminectomy: This is a procedure that a surgeon performs on a cervical vertebra in the neck.
. Lumbar laminectomy: This involves the vertebrae in the lower back. This procedure can help relieve pain in the lower back, buttocks, and legs.
. Sacral laminectomy: This procedure removes the lamina on the fused sacral vertebrae.
. Laminectomy: where a section of bone is removed from 1 of your vertebrae (spinal bones) to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
. Discectomy: where a section of a damaged disc is removed to relieve pressure on a nerve.
After Laminectomy Surgery
After Laminectomy
What happens after a Laminectomy?
When you wake up after surgery, your doctor will probably ask you to get up and walk around a bit (unless you had a spinal fusion). You’ll probably stay in the hospital for 1–4 days, but this procedure can sometimes be done on an outpatient basis.
During the next few weeks, a person should get plenty of rest and avoid:
. Bending over or twisting the spine
. Driving or operating heavy machinery
. Lifting, pulling, or pushing heavy objects
. Engaging in any strenuous exercise
While you’re recovering, you should:
. Be careful when climbing stairs
. Gradually increase your activities, such as walking
. Schedule and go to all follow-up appointments
During the recovery process, a person should remember to take any prescription medication as their doctor indicates.
Your doctor may recommend physical therapy after a laminectomy to improve your strength and flexibility.
A doctor or nurse will explain how to take care of the incision while it heals. Following these care tips can help the incision heal faster and prevent infections.
While showering, you shouldn’t scrub over the incision site. Don’t apply any lotions or creams near the incision. Avoid bathtubs, hot tubs, and swimming pools until your doctor says otherwise. These can all increase your risk of infection.
Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to take care of your wound.
Call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
. Swelling on or near the incision site
. Draining, heat, or redness at the incision site
. Difficulty breathing
. Chest pain
. A fever of 100ºF or higher
. Tenderness or swelling in the legs
. Difficulty urinating
. A loss of bowel or urinary control
Recovery time
Recovery will depend on a person’s fitness and activity levels before the surgery.
It usually takes around 4–6 weeks for a person to return to their normal level of mobility and function. However, this will depend on the severity of the condition and symptoms before the operation.
It may take up to 6 weeks for the general pain and tiredness following surgery to disappear completely.
Most people will feel ready to drive around 2–3 weeks after the operation. Many people are able to return to work after 4–6 weeks. However, if a person’s job involves a lot of driving, lifting heavy items, or engaging in other strenuous activities, they may need to be off work for up to 12 weeks.
Results
Most people report measurable improvement in their symptoms after laminectomy, particularly a decrease in pain that radiates down the leg or arm. But this benefit may lessen over time if you have a particularly aggressive form of arthritis. Laminectomy is less likely to improve pain in the back itself.
Laminectomy Surgery Cost
How much does Laminectomy surgery cost in Iran?
The cost of Laminectomy surgery in Iran is about $ 2500.
Overall Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. other countries
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in the USA
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 150 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in the USA.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in the UK
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 170 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in the UK.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in India
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 60 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in India.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Mexico
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 70 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Mexico.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Canada
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 230 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Canada.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Australia
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 180 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Australia.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Turkey
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 90 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Turkey.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Russia
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 210 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Russia.
Laminectomy Surgery cost in Iran vs. Laminectomy Surgery cost in Pakistan
The average cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Iran is 80 percent less than the cost of Laminectomy Surgery in Pakistan.