Can you fix a paralyzed vocal cord?
How long do vocal cord injections last?
Is vocal cord injection painful?
How long do vocal cord injections last?
How do you control vocal cord dysfunction?
How do I lubricate my vocal cords?
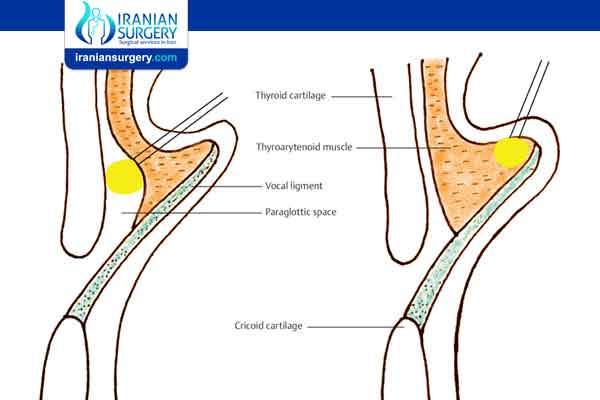
A vocal cord injection is a procedure in which a filling agent is injected into your vocal cord to augment your vocal cord.
This procedure is used to repair vocal cord paralysis or immobility, age-related voice changes and vocal cord scars.
Read more about: Fat augmentation of vocal cord
Before the procedure
Medications: For 10 days before the injection, do not take aspirin or medicines that contain:
- Vitamin E
- Multivitamins
- Herbs
- Anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen
These medicines can cause bleeding. Instead, use acetaminophen (Tylenol) as needed for pain.
Blood thinners: If you are using medicines that thin your blood to treat another condition, such as high cholesterol, please contact your primary care doctor. You will need to discuss when to stop and restart these medicines.
Eating and drinking: Please do not eat or drink anything three hours before the injection, including water or coffee. If you need to take medicine, take it with a small sip of water.
Allergies: Be sure to tell the nurse or doctor if you have any allergies to numbing medications, such as Lidocaine.
Read more about: Vocal cord injection technique
During the procedure
The injection is done in one of two ways:
- Through the mouth. The doctor will numb the back of your mouth with a numbing medication, which controls the gag reflex. After your vocal cords are numbed, and the material is injected.
- Through the skin of the neck. A small camera will be placed in the nose and used to view the voice box. Numbing medication is given and a thin needle is placed through the neck to place the material.
After the procedure
- Avoid food and drink. Do not eat or drink for at least one hour. This will give the numbing medicine time to wear off. Your regular diet can resume after one hour.
- Bloody mucous. Blood-tinged mucous is normal.
- Don’t cough. Do not cough or clear the throat. This irritates the tissue.
- Do not smoke. Smoking will irritate your throat.
Read more about: Laryngoscopy surgery

Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and lifestyle, listen to your voice, and ask you how long you’ve had voice problems. To further evaluate your voice problems, the following tests may be performed:
- Your doctor will look at your vocal cords using a mirror or a thin, flexible tube (known as a laryngoscope or endoscope) or both. You may also have a test called videostrobolaryngoscopy that’s done using a special scope that contains a tiny camera at its tip or a larger camera connected to the scope’s viewing piece.
These special high-magnification endoscopes allow your doctor to view your vocal cords directly or on a video monitor to determine the movement and position of the vocal cords and whether one or both vocal cords are affected.
- Laryngeal electromyography.This test measures the electric currents in your voice box muscles. To obtain these measurements, your doctor typically inserts small needles into your vocal cord muscles through the skin of the neck.
This test doesn’t usually provide information that might change the course of treatment, but it may give your doctor information about how well you may recover. This test is most useful for predicting how you’ll recover when it’s done between six weeks and six months after your symptoms began.
- Blood tests and scans.Because a number of diseases may cause a nerve to be injured, you may need additional tests to identify the cause of the paralysis. Tests may include blood work, X-rays, MRI or CT scans.
Can you fix a paralyzed vocal cord?
This allows your unimpaired vocal cord to better vibrate against its paralyzed partner. Replacing the damaged nerve (reinnervation). In this surgery, a healthy nerve is moved from a different area of the neck to replace the damaged vocal cord. Some doctors combine this surgery with a bulk injection.
Read more about: Laryngoscopy surgery
How long do vocal cord injections last?
Long term clinical results show that persistent medialization after CaHA injection may be present up to 2 years and more, with an average duration of 18 months . Bovine-based gelatin products, such as Gelfoam and Surgifoam, can be used for temporary vocal fold injection augmentation.
Is vocal cord injection painful?
Most patients experienced mild to moderate pain with increasing heart rate during the procedure. Pain remained or increased 20 minutes after the procedure and improved but persisted for 1 day. Sensory and affective discomfort was endorsed by the majority. A minority of patients experienced bruising and changes in swallowing with diet modification for 3 days after the procedure. Sixteen percent had discomfort after 1 week.
How long do vocal cord injections last?
- Gelfoam
Lasts 4-6 weeks
- Radiesse Voice Gel:
Lasts 2-3 months.
- Radiesse (calcium hydroxyapatite in carboxymethylcellulose carrier
Lasts 4-6 months
The persistence of the injection likely depends on many factors including location of injection, size of needle hole (may partially extruded), recipient bed (e.g. irradiated or scarred) and other unknowns.
A single injection may occasionally last for years and may reflect either the persistence of collagen, ingrowth of new collagen, repositioning of the vocal cord by placement of the collagen, or continued reinnervation with adaptation improving glottic closure.
- Human derived collagen (Cosmoplast, Cosmoderm)
Lasts 4-6 months
- Micronized Alloderm (Cymetra)
Lasts 2-12 months
- Hyaluronic acid gels (Restylane, Perlane)
Lasts 4-6 months
Read more about: Injection laryngoplasty recovery
How do you control vocal cord dysfunction?
VCD is different than many other breathing problems because medicines are not the main treatment to control or prevent VCD.
- The main treatment for VCD is speech therapy techniques that help you learn to control your vocal cords.
- Speech therapy techniques are usually taught by a speech therapist or psychologist who is trained and experienced in treating VCD.
- The techniques you will learn will help to improve your ability to relax your throat muscles.
- You may have to meet with a therapist at least three to four times to learn these techniques.
- Learning these techniques takes regular practice. You will need to practice them even when you are not having VCD, so you can be ready to control the symptoms before they become severe.
- Strong emotions and stress can trigger VCD, so it is important to learn to manage your stress. Relaxation techniques, biofeedback, and psychotherapy have been shown to be helpful in controlling VCD.
- If you have asthma and VCD, it is important that your asthma is under good control.
- If your VCD is triggered by post-nasal drip or acid reflux (GERD), it is important to talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do to control these.
Read more about: Fat injection thyroplasty permanent
How do I lubricate my vocal cords?
- Drink water to keep your body well hydrated, and avoid alcohol and caffeine. Your vocal cords vibrate very fast, and having a proper water balance helps keep them lubricated. Important note: Foods containing large amounts of water are excellent hydration-conscious snacks, including apples, pears, watermelon, peaches, melons, grapes, plums, bell peppers and applesauce.
- Allow yourself several “vocal naps” every day, especially during periods of extended use. For instance, teachers should avoid speaking during the breaks between classes and find quiet ways to spend the lunch hour rather than talking in a noisy staff room with colleagues.
- Don’t smoke, or if you already do, quit. Smoking raises the risk of throat cancer tremendously, and inhaling smoke (even secondhand smoke) can irritate the vocal cords.
- Don’t abuse or misuse your voice. Avoid yelling or screaming, and try not to talk loudly in noisy areas. If your throat feels dry or tired, or your voice is getting hoarse, reduce your voice use. The hoarseness is a warning sign that your vocal cords are irritated.
- Keep your throat and neck muscles relaxed even when singing high notes and low notes. Some singers tilt their heads up when singing high notes and down when singing low notes. “The high notes are on the ceiling and the low notes are on the floor,” Rosenberg says. “Over time, you’ll pay for that”—not just with strained vocal muscles but also by causing future limits on the vocal range.
- Pay attention to how you speak every day. Even performers who have good singing habits can cause damage when they speak. Many skilled singers don’t continue their healthy habits when they speak
- Don’t clear your throat too often. When you clear your throat, it’s like slamming your vocal cords together. Doing it too much can injure them and make you hoarse. Try a sip of water or swallow to quench the urge to clear. If you feel like you have to clear your throat a lot, get checked by a doctor for such things as acid reflux disease, or allergy and sinus conditions.
- When you’re sick, spare your voice. Don’t talk when you’re hoarse due to a cold or infection. Listen to what your voice is telling you.
- When you have to speak publicly, to large groups or outdoors, think about using amplification to avoid straining your voice.
- Humidify your home and work areas. Remember, moist is good for the voice.
Read more about: Fat injection laryngoplasty
VCD symptoms
If an acute episode is mild, you may not have any symptoms.
When you do have symptoms, most of them are caused by inhaled air moving through a smaller area than usual. They come on suddenly and can mimic an asthma attack.
Symptoms for vocal cord dysfunction include:
- shortness of breath
- feeling you’re suffocating, also called air hunger
- wheezing, especially during inhalation
- stridor, which is a high-pitched sound during inhalation
- chronic coughing
- chronic throat clearing
- throat tightness or choking feeling
- hoarseness or weak voice
- chest tightness or chest pain
These symptoms can be frightening, especially when they come on suddenly. Some people feel anxious, panicky, and afraid when they get them. This can make it even harder for you to breathe.
In someone with asthma, similar symptoms can mean they’re having a severe attack that can be life-threatening and needs immediate treatment. One important difference between them is that wheezing is heard when you exhale with asthma, but it’s heard when you inhale with VCD.
Read more about: Fat augmentation of vocal cord