Posterior colpotomy procedure
Overview
The colpotomy method of tubal ligation was once the preferred female sterilization technique. But now, doctors usually use laparoscopy or laparotomy since these abdominal tubal ligation procedures do not have as many risks as a colpotomy.
The Procedure
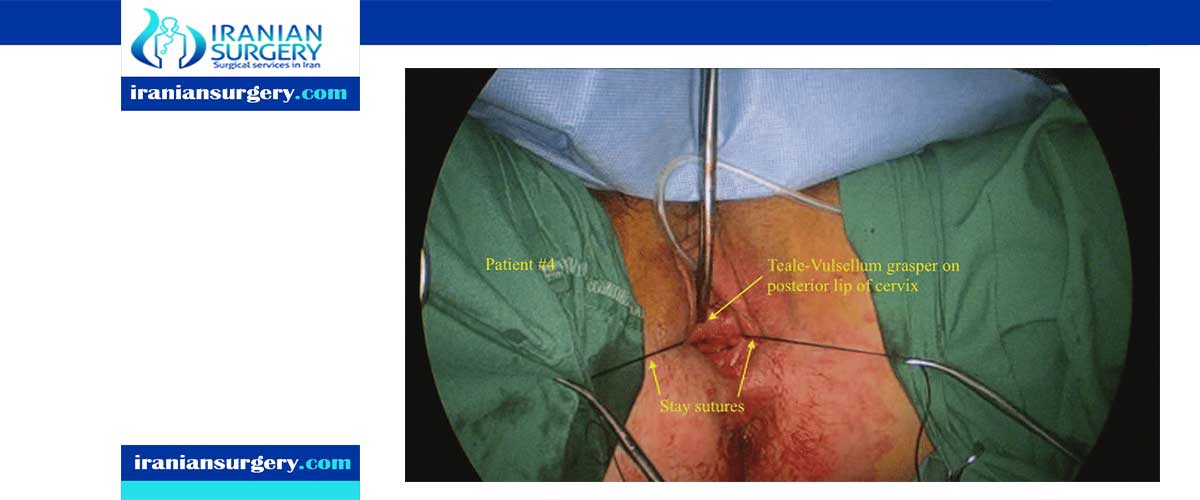
A colpotomy is a type of incision that can be used during a vaginal sterilization procedure (the other type of procedure is called a culdoscopy). During a colpotomy tubal ligation, your doctor makes an incision into the posterior vaginal fornix (the fancy medical word for the back of the vagina). This incision can be made horizontally (side to side) or vertically (up to down). Your surgeon will then insert an intrauterine sound through the incision and into the peritoneal cavity (the space within the abdomen that contains the intestines, the stomach, and the liver).
The intrauterine sound is just a medical instrument that is designed to help probe and open passages within the body—it helps your surgeon to correctly position the uterus and bring the fallopian tubes into view. Some surgeons may use an endoscope (a small, telescope-like medical instrument with a light). Your surgeon will then take your fallopian tubes out through the incision and into the vagina. Your fallopian tubes are then closed/ligated—they can be tied, clipped, and/or sealed shut. Finally, your doctor will put the fallopian tubes back into place, and your incision is stitched shut.
What to Expect Post-Procedure
You can expect that your recovery from a colpotomy will take a few days. Your doctor will probably advise you to wait to have sexual intercourse until your incision has completely healed—this usually takes several weeks. Once you have healed from you colpotomy, you will not have any visible scars.
Pros
A major advantage of having a colpotomy during your tubal ligation is that there are no incisions in your abdomen. This type of tubal ligation can also offer additional benefits. A colpotomy tubal ligation can be a safer option for women who:
- Are obese
- Have a retroverted uterus (a uterus that tilts back instead of front)
- Have a history of abdominal wall/hernia repairs
Cons
There are not as many surgeons in the United States who are trained to perform a colpotomy as a tubal ligation procedure. Research is now showing that this method may be safer than originally thought. But many surgeons prefer to do abdominal tubal ligations because the complication rates associated with colpotomy tubal ligations appear to be twice as high, and the effectiveness rates may be slightly lower. Colpotomy tubal ligations have also been linked to higher infection rates. Some surgeons will provide you with antibiotics to take after a colpotomy to help prevent infection. A colpotomy may also be more difficult to perform because it requires a woman to be in a lithotomy position (your legs are in stirrups) while under local anesthesia.
Technique, tips, and tricks
Posterior colpotomy allows the removal of fibroids during laparoscopic myomectomy without the need to enlarge the abdominal incisions and without the use of intracorporeal power morcellation. Instead, tissue is extracted transvaginally. The incision is hidden in a natural orifice, the vagina.
A colpotomy is a type of incision that is made in the back wall of the vagina. During a tubal ligation, your doctor can use a colpotomy (also known as a vaginotomy) as one of the ways to reach your fallopian tubes. A tubal ligation that uses a colpotomy incision is considered to be minimally invasive surgery.