Rectal Cancer Staging
Stages of Rectal Cancer
No matter where it starts, cancer can spread, or metastasize, through tissue, the lymph system, or the bloodstream to reach other parts of the body.
Staging cancer indicates how far the cancer has progressed, which can help your doctor decide the best treatment.
The following stages are used for rectal cancer:
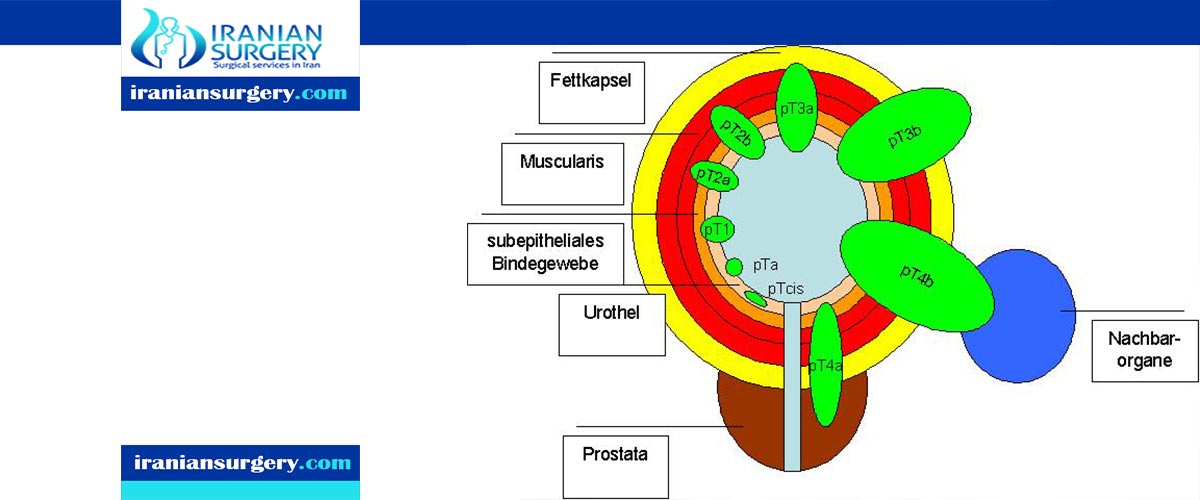
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ)
In stage 0 rectal cancer, abnormal cells are found in the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
Read more about : Colon cancer stage 4
 Stage I
Stage I
In stage I rectal cancer, cancer has formed in the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall and has spread to the submucosa (layer of tissue next to the mucosa) or to the muscle layer of the rectum wall.
Read more about : Colon cancer treatment
Stage II
Stage II rectal cancer is divided into stages IIA, IIB, and IIC.
. Stage IIA: Cancer has spread through the muscle layer of the rectum wall to the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall.
. Stage IIB: Cancer has spread through the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall to the tissue that lines the organs in the abdomen (visceral peritoneum).
. Stage IIC: Cancer has spread through the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall to nearby organs.
Stage III
Stage III rectal cancer is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
In stage IIIA, cancer has spread:
Read more about : Stage 3 rectal cancer survival rate by age
. Through the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall to the submucosa (layer of tissue next to the mucosa) or to the muscle layer of the rectum wall. Cancer has spread to one to three nearby lymph nodes or cancer cells have formed in tissue near the lymph nodes; or
. Through the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall to the submucosa (layer of tissue next to the mucosa). Cancer has spread to four to six nearby lymph nodes.
Read more about : Cancer treatment
In stage IIIB, cancer has spread:
. Through the muscle layer of the rectum wall to the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall or has spread through the serosa to the tissue that lines the organs in the abdomen (visceral peritoneum). Cancer has spread to one to three nearby lymph nodes or cancer cells have formed in tissue near the lymph nodes; or
. To the muscle layer or to the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall. Cancer has spread to four to six nearby lymph nodes; or
. Through the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall to the submucosa (layer of tissue next to the mucosa) or to the muscle layer of the rectum wall. Cancer has spread to seven or more nearby lymph nodes.
Read more about : Colorectal cancer staging
In stage IIIC, cancer has spread:
. Through the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall to the tissue that lines the organs in the abdomen (visceral peritoneum). Cancer has spread to four to six nearby lymph nodes; or
. Through the muscle layer of the rectum wall to the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall or has spread through the serosa to the tissue that lines the organs in the abdomen (visceral peritoneum). Cancer has spread to seven or more nearby lymph nodes; or
. Through the serosa (outermost layer) of the rectum wall to nearby organs. Cancer has spread to one or more nearby lymph nodes or cancer cells have formed in tissue near the lymph nodes.
Stage IV
Stage IV rectal cancer is divided into stages IVA, IVB, and IVC.
. Stage IVA: Cancer has spread to one area or organ that is not near the rectum, such as the liver, lung, ovary, or a distant lymph node.
. Stage IVB: Cancer has spread to more than one area or organ that is not near the rectum, such as the liver, lung, ovary, or a distant lymph node.
. Stage IVC: Cancer has spread to the tissue that lines the wall of the abdomen and may have spread to other areas or organs.
Read more about : Chemotherapy
Read more about : Radiation therapy

