Risk factors for cervical cancer

What Are the Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer?
Risk factors
Risk factors for cervical cancer include:
. Many sexual partners. The greater your number of sexual partners — and the greater your partner's number of sexual partners — the greater your chance of acquiring HPV.
. Early sexual activity. Having sex at an early age increases your risk of HPV.
. Other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Having other STIs — such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and HIV/AIDS — increases your risk of HPV.
. A weakened immune system. You may be more likely to develop cervical cancer if your immune system is weakened by another health condition and you have HPV.
. Smoking. Smoking is associated with squamous cell cervical cancer.
. Exposure to miscarriage prevention drug. If your mother took a drug called diethylstilbestrol (DES) while pregnant in the 1950s, you may have an increased risk of a certain type of cervical cancer called clear cell adenocarcinoma.
Read more about : Metastatic myxofibrosarcoma treatment with the best Iranian oncologist surgeon
Read more about : Cervical cancer treatment
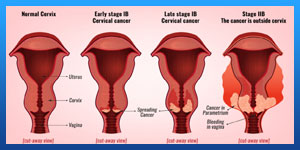
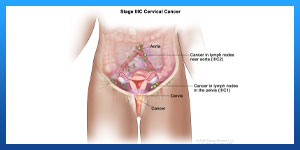
Read more about : Cervical cancer stage
Read more about : Early symptoms of Cervical cancer
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best Surgeons to treat your cervical cancer in Iran. The price of treating a cervical cancer in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by the type of treatment you have and an in-person assessment with the doctor. So if you are looking for the cost of cervical cancer treatment in Iran, you can contact us and get free consultation from Iranian surgery.
Cervical Cancer Causes
Cervical cancer begins when healthy cells in the cervix develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do.
Healthy cells grow and multiply at a set rate, eventually dying at a set time. The mutations tell the cells to grow and multiply out of control, and they don't die. The accumulating abnormal cells form a mass (tumor). Cancer cells invade nearby tissues and can break off from a tumor to spread (metastasize) elsewhere in the body.
It isn't clear what causes cervical cancer, but it's certain that HPV plays a role. HPV is very common, and most people with the virus never develop cancer. This means other factors — such as your environment or your lifestyle choices — also determine whether you'll develop cervical cancer.
Read more about : How to burst a bartholin cyst at home?
Read more about : Colorectal cancer surgery
Read more about : Anal Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Bone cancer stage
Reducing your chances of getting cervical cancer
Being at risk for getting any kind of cancer can be mentally and emotionally challenging. The good news is that cervical cancer may be preventable. It develops slowly and there are a lot of things you can do to reduce your chances of developing cancer.
A vaccine is available to protect against some of the HPV strains most likely to cause cervical cancer. It’s currently recommended for boys and girls ages 11 through 12. It’s also recommended for women up to age 45 and men up to age 21 who weren’t previously vaccinated.
If you’re within this age bracket and haven’t been vaccinated, you should talk to your doctor about vaccination.
In addition to vaccination, practicing sex with a condom or other barrier method and quitting smoking if you smoke are key steps you can take to prevent cervical cancer.
Making sure that you get regular cervical cancer screenings is also an important part of reducing your cervical cancer risk. How often should you be screened? The timing and type of screening depends on your age.
The updated recommendations for cervical cancer screening include:
. Women younger than 21 years: Cervical cancer screening isn’t recommended.
. Women ages 21 through 29: Cervical cancer screening through Pap smear alone every three years.
. Women ages 30 through 65: Three options for cervical cancer screening, including:
. Pap smear alone every three years
. High-risk HPV testing (hrHPV) alone every five years
. Both Pap smear and hrHPV every five years
. Women age 65 and older: Cervical cancer screening isn’t recommended, provided that adequate prior screening was performed.
Read more about : Brain Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Oral Cancer Treatment

