Stage 2 breast cancer
Breast Cancer Treatment Stage 1 and 2
What is the survival rate of stage 2 breast cancer?
Breast cancer stages range from 0-4. Each stage has different symptoms and treatment options.
Breast cancer has four stages, and a doctor uses the TNM staging system to identify which of these four stages the breast cancer has reached.
Read more about : Metastatic myxofibrosarcoma treatment with the best Iranian oncologist surgeon
The letters TNM mean the following:
. T stands for tumor and indicates how much of the breast tissue is involved.
. N stands for nodes and indicates whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
. M stands for metastasis and indicates whether cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
The TNM staging system also uses numbers. The numbers from 0-4 determine how advanced the cancer is.
The system is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). This means all cancer doctors describe and classify the stages of cancer in the same way.
To determine which stage a person’s breast cancer has reached, a doctor will perform tests. Tests include blood tests, CT and PET scans, MRI’s, X-rays, including a mammogram, and ultrasounds.
Read more about : Treatment For Breast Cancer Stage 1
Read more about : Early stage breast cancer treatment
Stage 2 breast cancer
Stage 2 breast cancer also has subcategories known as 2A and 2B.
Stage 2A breast cancer is an invasive cancer where:
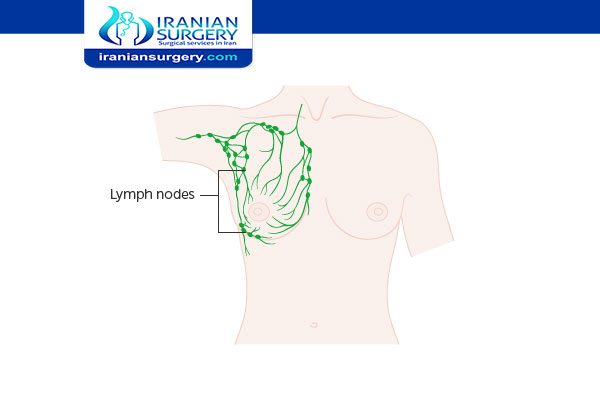
. There is no tumor growth in the breast itself, but cancerous masses that are over 2 mm in diameter are growing in up to three axillary lymph nodes (in and around the armpit) or lymph nodes near the breastbone.
. There is a tumor in the breast that is under 2 cm in diameter that has spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
. The tumor is 2–5 cm in diameter but has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage 2B breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
. A tumor that measures 2–5 cm in diameter is growing in the lymph nodes alongside clusters of cancerous cells. These cancerous cells form groups between 0.2 mm–2 mm in size.
. There is a tumor that is 2–5 cm in diameter, and cancerous cells have spread to one to three axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes by the breastbone.
. The tumor is larger than 5 cm, but cancerous cells have not spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Read more about : Cervical cancer treatment
Read more about : Risk factors of cervical cancer
Treatment for stage 2 breast cancer
The most common type of treatment for stage 2 breast cancer is surgery.
. Surgery
In most cases, treatment involves removing the cancer.
A person with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer may undergo a lumpectomy or mastectomy. The doctors and the individual can decide based on the size and location of the tumor.
. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy targets any remaining cancer cells in the chest and lymph nodes. It’s often recommended after surgery.
. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic therapy to kill cancer cells throughout the body. These powerful drugs are delivered intravenously (into a vein) over the course of many weeks or months.
There are a variety of chemotherapy drugs used to treat breast cancer, including:
. Docetaxel (Taxotere)
. Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
. Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
You may receive a combination of several chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy is particularly important for TNBC. Herceptin is given along with chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancers.
Your doctor may also recommend other HER2-targeted therapies, such as Perjeta or Nerlynx.
. Hormone treatment
After all other treatment is complete, you may benefit from continued treatment for hormone-positive breast cancers.
Oral medications such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors may be prescribed for five or more years.
. Combination therapy
A doctor may recommend a combination of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy (if the cancer is hormone receptive) to people with stage 2A or 2B breast cancer.
Stage 3 breast cancer
The subcategories for stage 3 breast cancer are 3A, 3B, and 3C.
3A breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
. There is no tumor in the breast, or a tumor of any size is growing alongside cancer found in four to nine axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes by the breastbone.
. A person has a tumor greater than 5 cm, as well as clusters of breast cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are between 0.2–2 mm in diameter.
. The tumor is larger than 5 cm, and cancer has also spread to one to three axillary lymph nodes or the lymph nodes near the breastbone.
Stage 3B breast cancer is invasive breast cancer where:
. A tumor of any size has spread into the chest wall or skin of the breast, causing swelling or an ulcer to develop. It could also have spread to up to nine axillary lymph nodes or may have spread to lymph nodes by the breastbone.
If cancer spreads to the skin of the breast, a person may have inflammatory cancer.
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include:
. The skin of the breast turning red
. Swelling of the breast
. The breast feeling unnaturally warm
Stage 3C breast cancer is an invasive breast cancer where:
. There is no actual tumor in the breast, or the tumor may be any size and has spread into the wall of the chest or the skin of the breast. Cancer may also be present in 10 or more axillary lymph nodes.
. Cancer has spread to a person’s lymph nodes above or below the collarbone or axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes located close the breastbone.
Treatment for stage 3 breast cancer
Treatment for people with stage 3 breast cancer includes chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation. Typically, doctors administer the chemotherapy before performing the surgery in an attempt to shrink a tumor.
People with stage 3 breast cancer will probably need radiation therapy to kill off any remaining cancer cells. Doctors may also recommend hormone therapy, as well as additional targeted therapies, if necessary.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best Surgeons to treat your Breast cancer in Iran. The price of treating a Breast cancer in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by the type of treatment you have and an in-person assessment with the doctor. So if you are looking for the cost of Breast cancer treatment in Iran, you can contact us and get free consultation from Iranian surgery.
Breast cancer treatment considerations
The stages of breast cancer give a doctor an indication of how developed the breast cancer is and the kind of treatment options that may be effective.
There are, however, other factors that doctor’s take into consideration when determining how successful a specific type of breast cancer treatment might be.
These include:
. Age: Those under 40 tend to have more aggressive breast cancers.
. Pregnancy: Doctors may delay chemotherapy until the second or third trimester and delay hormone and radiation therapy until after the baby is born.
. How fast cancer grows and spreads: More aggressive cancers require more aggressive treatments.
. Family history: People whose close relatives have experienced breast cancer are more likely to experience it themselves.
. Genetic mutation status: If someone tests positive for the breast cancer genes known as BRCA1 (Breast Cancer gene one) and BRCA2 (Breast Cancer gene two), their risk of developing breast cancer increases significantly. Some people may require tests for other genes associated with breast cancer.
Outlook
A person’s outlook depends on early diagnosis and the stage of their cancer. The earlier a person receives treatment, the better the prognosis.
People should routinely check for any signs of breast cancer by performing monthly breast exams and should talk to their doctor about having regular mammograms.
Some people may need to begin screening earlier than others depending on their risk factors. Discuss this with the doctor. Other people may be candidates to start screening later, but it is a good idea to share the decision making with a doctor who will be able to advise on the best way forward.
Treatment depends on many factors, including the stage of breast cancer, family history, genetics and a person’s personal preferences. Doctors will tailor treatment to each individual and will adjust it depending on how well a person responds initially.

