Testicular Cancer Age
Can you get testicular cancer at any age?
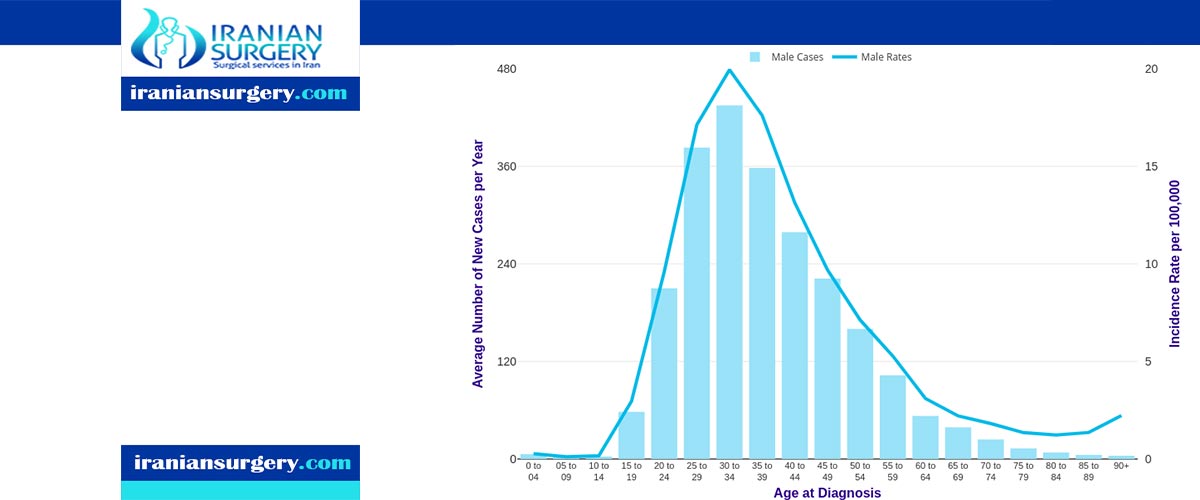
Testicular cancer occurs in the testicles (testes), which are located inside the scrotum, a loose bag of skin underneath the penis. The testicles produce male sex hormones and sperm for reproduction. Though it can affect a man or boy at any age, it is most often found in men age 15 to 44 years.
Read more about : Donating a testicle pros and cons
Read more about : Disadvantages of having one testicle
Read more about : Testicular Cancer Survival Rates
Read more about : Phalloplasty surgery
Read more about : Penile implant
Read more about : Chances of getting pregnant with one testicle
Testicular Cancer: Symptoms and Signs
What is usually the first sign of testicular cancer?
People with testicular cancer may experience a variety of symptoms or signs. Sometimes, men with testicular cancer do not have any of these changes. Or, the cause of a symptom may be a different medical condition that is not cancer. So, having these symptoms does not mean that a man definitely has cancer.
Usually, an enlarged testicle or a small lump or area of hardness are the first signs of testicular cancer. Any lump, enlargement, hardness, pain, or tenderness should be evaluated by a doctor as soon as possible. Other symptoms of testicular cancer usually do not appear until after the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms of testicular cancer may include:
. A painless lump or swelling on either testicle. If found early, a testicular tumor may be about the size of a pea or a marble, but it can grow much larger.
. Pain, discomfort, or numbness in a testicle or the scrotum, with or without swelling.
. Change in the way a testicle feels or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum. For example, 1 testicle may become firmer than the other testicle. Or testicular cancer may cause the testicle to grow bigger or to become smaller.
. Dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin
. Sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum
. Breast tenderness or growth. Although rare, some testicular tumors make hormones that cause breast tenderness or growth of breast tissue, a condition called gynecomastia.
. Lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and bloody sputum or phlegm can be symptoms of later-stage testicular cancer.
. Swelling of 1 or both legs or shortness of breath from a blood clot can be symptoms of testicular cancer. A blood clot in a large vein is called deep venous thrombosis or DVT. A blood clot in an artery in the lung is called a pulmonary embolism and causes shortness of breath. For some young or middle-aged men, developing a blood clot may be the first sign of testicular cancer.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best Surgeons and hospitals to treat your Testicular cancer in Iran. The price of treating a Testicular cancer in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by the type of treatment you have and an in-person assessment with the doctor. So if you are looking for the cost of Testicular cancer treatment in Iran, you can contact us and get free consultation from Iranian surgery.
Read more about : Cancer treatment in Iran
Many symptoms and signs of testicular cancer are similar to those caused by noncancerous conditions. These are discussed below:
. Change in size or a lump in a testicle
. A cyst called a spermatocele that develops in the epididymis. The epididymis is a small organ attached to the testicle that is made up of coiled tubes that carry sperm away from the testicle.
. An enlargement of the blood vessels from the testicle called a varicocele.
. A buildup of fluid in the membrane around the testicle called a hydrocele.
. An opening in the abdominal muscle called a hernia.
. Pain
. Infection. Infection of the testicle is called orchitis. Infection of the epididymis is called epididymitis. If infection is suspected, a patient may be given a prescription for antibiotics. If antibiotics do not solve the problem, tests for testicular cancer are often needed.
. Injury
. Twisting
If you are concerned about any changes you experience, please talk with your doctor. Your doctor will ask how long and how often you’ve been experiencing the symptom(s), in addition to other questions. This is to help figure out the cause of the problem, called a diagnosis.
If cancer is diagnosed, relieving symptoms remains an important part of cancer care and treatment. This may be called palliative care or supportive care. It is often started soon after diagnosis and continued throughout treatment. Be sure to talk with your health care team about the symptoms you experience, including any new symptoms or a change in symptoms.
Testicular Cancer Survival Rates
Is testicular cancer deadly?
Survival for testicular cancer is very high. Nearly all men survive their disease. Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed. They can’t tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they can’t predict what will happen in any particular person’s case.
Survival by stage
The figures below are for 4 stages of testicular cancer. Your doctor may use a different system that only has 3 stages.
. Stage 1
Almost all men survive their cancer for five years or more after diagnosis.
Stage 1 means the cancer is only in the testes.
. Stage 2
Almost 95 out of 100 men (almost 95%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Stage 2 means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
. Stage 3
More than 80 out of 100 men (more than 80%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Stage 3 means the cancer has spread to lymph nodes further away from the testicles: for example, in the armpit or neck.
. Stage 4
Around 80 out of 100 men (around 80%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Stage 4 is now classed as a stage 3C cancer. It means the cancer has spread to other organs in the body, such as the lungs. This is called metastatic cancer.
Read more about : What to eat after hemorrhoid surgery?
Read more about : How to sleep after meniscus surgery?
Read more about : Hair transplant growth chart
Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/testicular-cancer-care/symptoms-causes/syc-20352986