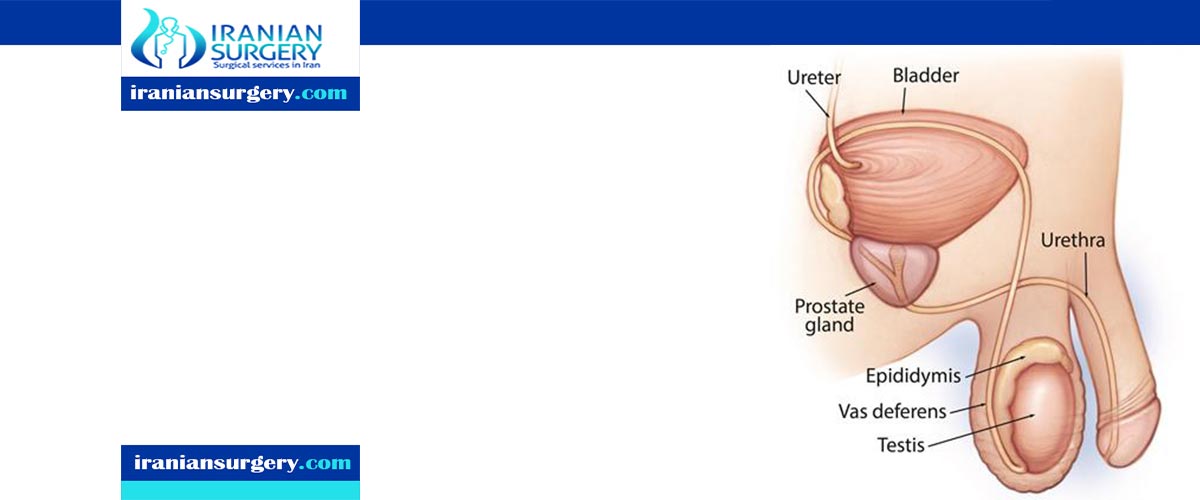
Tests for Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is usually found as a result of symptoms that a person is having. It can also be found when tests are done for another condition. The next step is an exam by a doctor.
The doctor will feel the testicles for swelling or tenderness and for the size and location of any lumps. The doctor will also examine your belly (abdomen), lymph nodes, and other parts of your body carefully to look for signs of cancer spread. Often the results of the exam are normal other than the changes in the testicles. If a lump or other sign of testicular cancer is found, testing will be needed to look for the cause.
Read more about : Disadvantages of having one testicle
Read more about : Testicular Cancer Survival Rates
Read more about : Phalloplasty surgery
Read more about : Penile implant
Diagnosis
In some cases men discover testicular cancer themselves, either unintentionally or while doing a testicular self-examination to check for lumps. In other cases, your doctor may detect a lump during a routine physical exam.
To determine whether a lump is testicular cancer, your doctor may recommend:
- A testicular ultrasound test uses sound waves to create an image of the scrotum and testicles. During an ultrasound you lie on your back with your legs spread. Your doctor then applies a clear gel to your scrotum. A hand-held probe is moved over your scrotum to make the ultrasound image.
An ultrasound test can help your doctor determine the nature of any testicular lumps, such as whether the lumps are solid or fluid-filled. An ultrasound also tells your doctor whether lumps are inside or outside of the testicle.
- Blood tests.Your doctor may order tests to determine the levels of tumor markers in your blood. Tumor markers are substances that occur normally in your blood, but the levels of these substances may be elevated in certain situations, including testicular cancer. A high level of a tumor marker in your blood doesn’t mean you have cancer, but it may help your doctor in determining your diagnosis.
- Surgery to remove a testicle (radical inguinal orchiectomy).If it’s determined that the lump on your testicle may be cancerous, surgery to remove the testicle may be recommended. Your removed testicle will be analyzed to determine if the lump is cancerous and, if so, what type of cancer.
Read more about : Arachnoid cyst size 3 cm
Other tests
In almost all cases, you’ll need further tests to check whether testicular cancer has spread.
When cancer of the testicle spreads, it most commonly affects the lymph nodes in the back of the abdomen or the lungs.
You may need to have a chest X-ray to check for signs of a tumour.
You’ll also need a scan of your entire body. This is usually a CT scan to check for signs of the cancer spreading.
In some cases, a different type of scan known as an MRI scan may be used.
Sources:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/testicular-cancer/diagnosis/
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/testicular-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/detection.html