LDH
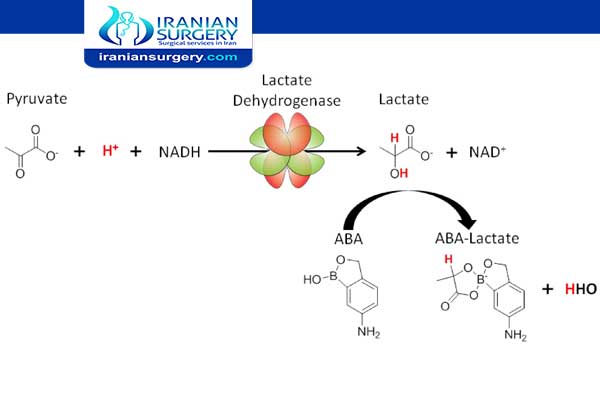
What is being tested?
What are the types of LDH isoenzymes?
What do the test results mean?
What is a normal LDH level?
Does high LDH mean cancer?
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LD)
What is being tested?
Lactate dehydrogenase (LD or LDH) is an enzyme involved in energy production that is found in almost all of the body’s cells, with the highest levels found in the cells of the heart, liver, muscles, kidneys, lungs, and in blood cells; bacteria also produce LD. This test measures the level of LD in the blood or sometimes other body fluids. Only a small amount of LD is usually detectable in the fluid portion of the blood.
What are the types of LDH isoenzymes?
There are five different forms of LDH that are called isoenzymes. They are distinguished by slight differences in their structure. The isoenzymes of LDH are LDH-1, LDH-2, LDH-3, LDH-4, and LDH-5.
Different LDH isoenzymes are found in different body tissues. The areas of highest concentration for each type of isoenzyme are:
- LDH-1: heart and red blood cells
- LDH-2: heart and red blood cells
- LDH-3: lymph tissue, lungs, platelets, pancreas
- LDH-4: liver and skeletal muscle
- LDH-5: liver and skeletal muscle
Read more about : Cervical Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Stages of fissure healing
Read more about : How to pop a bartholin cyst yourself?
Read more about : Foods that cure fissures
What do the test results mean?
Typical ranges for LDH levels
LDH levels vary based on age and the individual laboratory. Infants and young children will have much higher normal LDH levels than older children or adults. LDH is often reported in units per liter (U/L). In general, normal ranges for LDH levels in the blood are as follows:
| Age | Normal LDH level |
| 0 to 10 days | 290–2000 U/L |
| 10 days to 2 years | 180–430 U/L |
| 2 to 12 years | 110–295 U/L |
| Older than 12 years | 100–190 U/L |
Read more about : Colorectal cancer surgery
Read more about : Anal Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Bone cancer stage
High LDH levels
High levels of LDH indicate some form of tissue damage. High levels of more than one isoenzyme may indicate more than one cause of tissue damage. For example, a patient with pneumonia could also have a heart attack. Extremely high levels of LDH could indicate severe disease or multiple organ failure.
Because LDH is in so many tissues throughout the body, LDH levels alone won’t be enough to determine the location and cause of tissue damage. A diagnosis will also require the use of other tests and images in addition to measuring the levels of LDH. For example, high LDH-4 and LDH-5 may mean either liver damage or muscle damage, but liver disease can’t be confirmed without a full liver panel.
Before the discovery of other blood markers for heart injury, LDH was used to monitor people with heart attacks. Now, troponin, a protein produced more specifically in heart cells, is often a more accurate indicator of a heart attack.
Once your doctor diagnoses your particular condition, they may measure your LDH levels regularly to track the progress of your treatment.
LDH levels are also often used during the treatment of certain cancers to predict outcomes and monitor the body’s response to medications.
Read more about: Cancer treatment in Iran
Read more about: Does colorectal cancer occur in old people?
Read more about: FSH,PRL,BHCG.TITER
Read more about: LDL-CHOL
Low LDH levels
LDH deficiency affects how the body breaks down sugar for use as energy in cells, particularly muscle cells. It’s very rare for a person to have low LDH levels.
Two types of genetic mutations cause low LDH levels. People with the first type will experience fatigue and muscle pain, especially during exercise. While those with the second type may have no symptoms at all. You may also have low LDH levels if you’ve consumed a large amount of ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
Read more about: cervical cancer risk factors
Read more about: cervical cancer symptoms
What is a normal LDH level?
Normal LDH levels range from 140 units per liter (U/L) to 280 U/L or 2.34 microkatals/L to 4.68 microkatals/L.
Does high LDH mean cancer?
High levels of LDH indicate some form of tissue damage. High levels of more than one isoenzyme may indicate more than one cause of tissue damage. For example, a patient with pneumonia could also have a heart attack. Extremely high levels of LDH could indicate severe disease or multiple organ failure. There is increasing evidence to suggest that high levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the blood could be a good indicator of cancer development and progression. LDH levels become elevated when cells and tissues are damaged, and are particularly high during active tumor progression into various internal organs. However, a direct link between early LDH levels and cancer survival has not yet been fully investigated.
Read more about: Childhood cancer treatment facts
Read more about: kidney cancer symptoms
Read more about: HDL-CHOL
What causes high LDH levels in blood?
Although LDH is abundant in tissue cells, blood levels of the enzyme are normally low. However, when tissues are damaged by injury or disease, they release more LDH into the bloodstream. Conditions that can cause increased LDH in the blood include liver disease, heart attack, anemia, muscle trauma, bone fractures, cancers, and infections such as meningitis, encephalitis, and HIV.
Read more about: Bladder cancer symptoms in men
What is considered a high LDH level?
High levels of LDH indicate some form of tissue damage. High levels of more than one isoenzyme may indicate more than one cause of tissue damage. For example, a patient with pneumonia could also have a heart attack. Extremely high levels of LDH could indicate severe disease or multiple organ failure.
Because LDH is in so many tissues throughout the body, LDH levels alone won’t be enough to determine the location and cause of tissue damage. A diagnosis will also require the use of other tests and images in addition to measuring the levels of LDH. For example, high LDH-4 and LDH-5 may mean either liver damage or muscle damage, but liver disease can’t be confirmed without a full liver panel.
Before the discovery of other blood markers for heart injury, LDH was used to monitor people with heart attacks. Now, troponin, a protein produced more specifically in heart cells, is often a more accurate indicator of a heart attack.
Once your doctor diagnoses your particular condition, they may measure your LDH levels regularly to track the progress of your treatment.
LDH levels are also often used during the treatment of certain cancers to predict outcomes and monitor the body’s response to medications.
Read more about: Rectal Cancer Staging
Read more about: Bone cancer causes
Read more about: Ovarian Cancer Treatment

