How can you see the success rate during the first few weeks or months?
How long does it take to recover from a laminectomy?
Does laminectomy weaken the spine?
Can spinal stenosis come back after surgery?
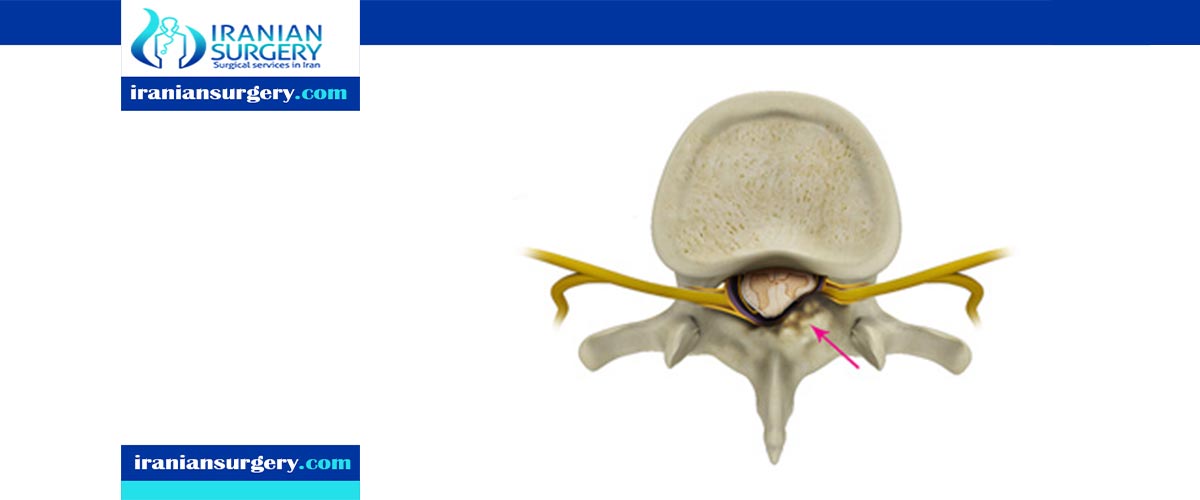
Laminectomy
Laminectomy is the traditional operating method for the decompression of spinal canal stenosis. New partial decompression processes have been suggested in the treatment of lumbar stenosis. The benefit of a micro surgical approach is the chance of an extensive bilateral decompression of the spinal canal or foramen at one or numerous levels, through a minimal para-spinal muscular separation.
Spinal stenosis is one of the most common age-related back problems. And it isn’t pleasant. It usually results from years of osteoarthritis, a thickening of the body’s ligaments that connect the bones to the spine and a deterioration of the cushioning between disks in the vertebrae all of which cause the spinal canal to narrow. As a result, nerves that travel down to the legs can become pinched near the bottom of the spine, causing pain and an inability to walk properly.
The condition affects 8 to 11 percent of Americans, mostly those over age 50, according to the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons.
The telltale symptoms of spinal stenosis are numbness, weakness and cramping or pain in the legs, thighs or feet, which interferes with the ability to walk. While symptoms of spinal stenosis start slowly and tend to worsen over time, leg pain can become so severe that sufferers find themselves unable to stand or walk for more than a few minutes.
Spinal stenosis doesn’t really cause back pain but pain that radiates down into buttocks and lower legs. The narrowing of the spinal canal reduces blood flow to nerves in the lower back. The pain often diminishes or disappears altogether when a patient is sitting or lying down unlike a pinched nerve caused by a bulging disk, which may hurt all the time.
Read more about : Total knee replacement
Read more about : Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Read more about : Herniated disk treatment
Read more about : Laminectomy Complications
Read more about : Laminectomy And Discectomy
How can you see the success rate during the first few weeks or months?
During the first few weeks or months at home, exercises and activity restrictions must be followed. The at-home exercises are usually provided by the treating physical therapist. A few at-home procedures post-surgery are:
- Pain management. Pain management includes the use of medications as well as limiting and modifying activities to prevent excessive pain. Medications may include:
- Pain-relieving medications. Pain-relieving medication such as opioids may be given for a few weeks to manage post-surgical pain. These medications are advised to be used for short-term with gradual tapering of dosage to prevent addiction. It is important to note that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not advised after a laminectomy surgery because these may delay bone healing.
- Stool-softeners. Stool-softeners may be required in the initial weeks after surgery to prevent constipation from stress, fear of pain, and medications (such as opioids). Stool softeners allow easy passage of bowels without excessive straining.
- Incision care. It is advised to avoid activities such as bathing, swimming, and hot-tubs until the incision site has completely healed. Proper care of the incision can prevent rupture of sutures, infection, or other complications. If suture removal is required, this may be done 1 to 2 weeks after surgery at the surgeon’s office. Absorbable sutures usually dissolve within a week.
- Physical therapy. It is necessary to continue with the physical therapy program and follow the prescribed exercises as instructed. Vigorous activities such as running or lifting heavy weights (typically over 5 pounds) are not advised.
- Activity modification. It is advised to modify daily activities to reduce the risk of injuring the treated segments of the spine. A grabber tool or reaching aid may be used to pick things up from the floor and/or a long-handled bath brush may be used to avoid bending while taking a shower.
- Compression stockings. Compression stockings may be advised to prevent blood-clot formation and to improve blood circulation.
Read more about: Is a Laminectomy a Major Surgery
Read more about: Laminectomy Surgery Position
laminectomy success rate
Laminectomy enlarges your spinal canal to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, and has about an 80 percent success rate at improving walking abilities. There is no cure for spinal stenosis, but there are treatments to help relieve symptoms. successful results of surgery were achieved in 86.7% of patients with lumbar stenosis, 77.6% of patients with lumbar stenosis with herniated disc, and 63.6% of patients with lateral recess stenosis. Successful results of surgery for lumbar stenosis declined to 69.6% by 1 year postoperatively.
Is a laminectomy a major surgery?
Laminectomy is a common but major surgery with significant risks and potential complications. You may have less invasive treatment options available. Consider getting a second opinion about all of your treatment choices before having a laminectomy.
How long does it take to recover from a laminectomy?
It depends on the extent of your surgery and your situation. After a minor (decompressive) laminectomy, you can usually able do desk work and light housekeeping within a few days to a few weeks. If you also had spinal fusion, your recovery time will likely be longer, 2-4 months. You may not be able to lift and bend for 2-3 months. Start light walking for exercise and physical therapy exercises as soon as your doctor says you're ready. This will help speed your recovery. You may not know if your back pain is better until 6 weeks or more after the surgery.
Read more about: Laminectomy Surgery Back Pain
Read more about: Cervical Laminectomy
Does laminectomy weaken the spine?
A well-known complication of lumbar laminectomy is excessive shear displacement in the intervertebral joint, leading to postoperative spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. In most cases, the degree of bone, ligament or facet joint removal will not significantly affect the strength of the spine. However, depending on the amount of tissue removal and whether the spine has been weakened by arthritis, degenerative changes or previous surgery, the strength of the spine may be compromised.
Can spinal stenosis come back after surgery?
Years after decompression (lumbar laminectomy), lumbar stenosis can come back (the bone can grow back) at the same level, or a new level can become stenotic and cause back pain or leg pain. Pain that is relieved right after surgery but then returns abruptly is often due to a recurrent lumbar disc herniation.
Read more about: Laminectomy Surgery Recovery Time
Read more about: Laminectomy Surgery Procedure
Read more about: Laminectomy surgery