Knee Replacement Surgery Cost
Knee Replacement cost 2021
Knee replacement surgery review
How much does Knee Replacement Surgery Cost 2021? ( Zimmer BRAND )
Knee replacement Surgery cost in Iran is between $2500_4000.
Knee replacement Surgery cost in india is between $5000
Knee replacement Surgery cost in south africa is between $13000_15000.
Knee replacement Surgery cost in pakistan is between $7000_8000.
Knee replacement Surgery cost in UK is between $13000_16000.
What is a knee Replacement?
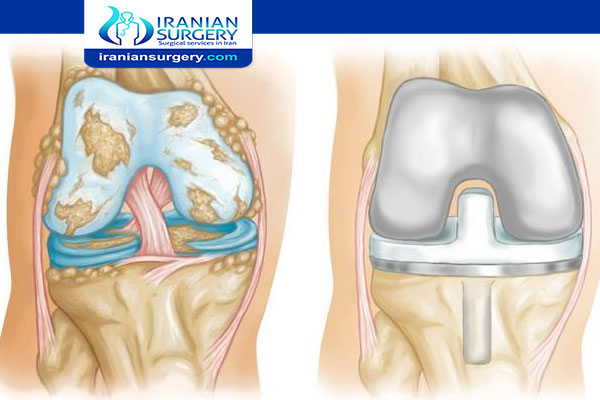
Knee replacement surgery also known as knee arthroplasty, or knee resurfacing restores the weight-bearing façade of a damaged, worn, or diseased knee joint. The aim is to remove pain and restore mobility.
The surgeon caps the ends of the bones that form the knee joint with metal or plastic components, or implants a prosthetic, shaped as a joint. This enables the knee to move properly.
Knee replacement is a kind of arthroplasty. Arthroplasty literally means “the surgical repair of a joint,” and it involves the surgical reconstruction and replacement of degenerated joints, using artificial body parts, or prosthetics.
When the articular cartilage of the knee becomes damaged or worn, it becomes painful and the knee is hard to move. Instead of sliding over each other, the bones rub and crush together.
With a prosthesis, the patient will feel less pain, and the knee will move properly.
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Total knee replacement surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Total knee replacement
Read more about : Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Read more about : Herniated disk treatment
General information about knee replacement Surgery
The following table describes general information about knee replacement Surgery including knee replacement Surgery cost in Iran, recovery time, and to name but a few.
General Information |
|
Cost | $ 2500- 4000 |
Anesthesia | General |
Hospital Stay | 2-5 Days |
Back to Work | 4-6 Weeks |
Duration of Operation | 1-3 Hours |
Minimum Stay in Iran | 3-4 Weeks |
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best orthopedic Surgeons and hospitals in Iran. The price of a total knee replacement Surgery in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined based on photos and an in-person assessment with the doctor. So if you are looking for the cost of total knee replacement Surgery in Iran, you can contact us and get free consultation from Iranian surgery.
Dr. Hamid Roshandel
Dr. Hamid Roshandel graduated from Shahid Beheshti University with a doctorate in general medicine
Orthopedic Specialty Surgery from Tehran University, Faculty of General Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University
Orthopedic specialty surgery from Tehran University
He is a member of the Iranian Association of Pelvic Surgeons and Member of the European Association of Orthopedic Surgeons.
Dr. Hamed Jafari
Specialty: Surgeon and orthopedic specialist
Knee Surgeon & member of AAOS
Knee surgeon, member of American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, knee joint replacement, cruciate ligament and meniscus by full arthroscopic method.
Dr. Hamed Jafari is an orthopedic specialist and surgeon in Shiraz. He is one of the most professional and well-known orthopedic surgeons in Shiraz and Iran.
Before knee Replacement Surgery
Why it's done
There are three common reasons for the procedure:
. Osteoarthritis: this type of arthritis is age related, caused by the normal wear and tear of the knee joint. It mostly affects patients aged over 50 years, but younger people may have it.
Osteoarthritis is caused by inflammation, breakdown, and the gradual and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. Over time, the cartilage wears down and the bones rub together. To compensate, the bones often grow thicker, but this results in more friction and more pain.
. Rheumatoid arthritis: also called inflammatory arthritis, the membrane around the knee joint to become thick and inflamed. Chronic inflammation damages the cartilage, causing soreness and stiffness.
. Post-traumatic arthritis: this type of arthritis is due to a severe knee injury. When the bones around the knee break or the ligaments tear, this will affect the knee cartilage.
Read more about : Cycling after knee arthroscopy
Read more about : Best way to sleep with compression fracture
Anatomy of the knee
Joints are the areas where 2 or more bones meet. Most joints are mobile, allowing the bones to move. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles (located on the front of the thighs), which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles (located on the back of the thighs), which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of connective tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments of the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia (shin bone).
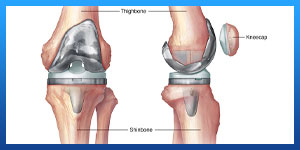
The knee consists of the following:
. Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
. Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
. Patella. This is the kneecap.
. Cartilage. A type of tissue that covers the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce the friction of movement within a joint.
. Synovial membrane. A tissue that lines the joint and seals it into a joint capsule. The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid (a clear, sticky fluid) around the joint to lubricate it.
. Ligament. A type of tough, elastic connective tissue that surrounds the joint to give support and limits the joint's movement.
. Tendon. A type of tough connective tissue that connects muscles to bones and helps to control movement of the joint.
. Meniscus. A curved part of cartilage in the knees and other joints that acts as a shock absorber, increases contact area, and deepens the knee joint.
Read more about : Knee Ligament Repair
Read more about : Hip replacement
Preparing for surgery
. Knee arthroplasty involves major surgery, so pre-operative preparation, medical consultations, and physical evaluations usually begin a month before the set date of the operation.
. Preparatory and diagnostic tests will include checking blood count, seeing how the blood clots, carrying out electrocardiograms (ECGs), and urine tests.
. Surgery is usually performed either under general, spinal, or epidural anesthetic.
. Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
. You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
. In addition to a complete medical history, your doctor may perform a complete physical examination to ensure you are in good health before undergoing the procedure. You may undergo blood tests or other diagnostic tests.
. Notify your doctor if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medications, latex, tape, and anesthetic agents (local and general).
. Notify your doctor of all medications (prescribed and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking.
. Notify your doctor if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any anticoagulant (blood-thinning) medications, aspirin, or other medications that affect blood clotting. It may be necessary for you to stop these medications prior to the procedure.
. If you are pregnant or suspect that you are pregnant, you should notify your doctor.
. You will be asked to fast for eight hours before the procedure, generally after midnight.
. You may receive a sedative prior to the procedure to help you relax.
. You may meet with a physical therapist prior to your surgery to discuss rehabilitation.
. Arrange for someone to help around the house for a week or two after you are discharged from the hospital.
. Based on your medical condition, your doctor may request other specific preparation.
Read more about : Gastric Sleeve VS. Gastric Bypass
Read more about : Open heart surgery
Who is a good candidate for knee replacement?
Knee surgery may be suitable for patients who experience:
. Severe knee pain or stiffness that prevents them from carrying out everyday tasks and activities, such as walking, going upstairs, getting in and out of cars, getting up from a chair.
. Moderate but continuous knee pain that continues while sleeping or resting.
. Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that does not improve after taking medications or resting.
. Knee deformity, where there is a noticeable arch on the inside or outside of the knee.
. Depression, resulting from an inability to carry out daily or social activities.
If the other available treatment options have not worked, surgery may be the best option.
Advantages
There are several possible advantages of knee replacement surgery. These include:
. Freedom from pain
. Improved mobility
. Improved quality of life because everyday activities and exercise are easier.
Disadvantages
Possible disadvantages of knee replacement surgery can include replacement joints wearing out over time, difficulties with some movements and numbness.
We now know that knee replacements aren't so likely to be effective in the early stages of arthritis. We can be much more confident of a good outcome where the arthritis is more advanced.
The possible disadvantages of knee replacement surgery include:
. A replacement knee can never be quite as good as a natural knee – most people rate the artificial joint about three-quarters normal.
. Most knee replacements aren’t designed to bend as far as your natural knee. Although it’s usually possible to kneel, some people find it uncomfortable to put weight on the scar at the front of the knee.
. You may also be aware of some clicking or clunking in the knee replacement.
. You may have some numbness at the outer edge of the scar to begin with. This usually improves over about two years but it’s unlikely that the feeling will completely return to normal.
. A replacement knee joint may wear out after a time or may become loose.
Most knee replacements will last for 15 years or more, so younger patients are more likely to need a repeat knee operation at some point in later life. The chances of needing repeat surgery are increased if:
. You’re overweight
. You do heavy manual work.
. You run or play vigorous sports.
Although your knee can be replaced again if necessary, revision surgery is more complicated and the benefits tend to lessen with each revision.
Read more about : Spinal Fusion Surgery
Read more about : Knee arthroscopy orthobullets
Risks and Complications
What are the risks of undergoing a knee replacement surgery?
Risks of knee replacement surgery include:
. Blood clots in the legs or lungs
. Pulmonary embolism, which can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and even shock.
. A fracture during or after surgery
. Urinary tract infection
. Nausea and vomiting
. Chronic knee pain and stiffness
. Bleeding in the knee joint
. Blood vessel injury
. Heart attack
. Stroke
. Infection of the knee which can require reoperation.
. The risks of anesthesia include potential heart, lung, kidney, and liver damage
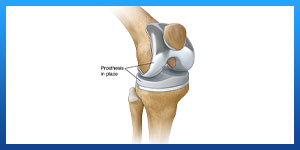 Other common complications include:
Other common complications include:
. Allergic reaction to the bone cement
. Excess bone forming around the artificial knee joint, leading to restricted movement in the knee.
. Excess scar tissue restricts movement of the knee
. Instability of the kneecap, resulting in painful dislocation to the outer side of the knee.
. Ligament, artery, or nerve damage around the knee joint
. Dislocated kneecap
. Wearing down of implant surfaces, causing components to loosen
Further surgery may be necessary if the replacement becomes loose or wears out, if there is a serious infection, or if the person has a fall.
Read more about Virgin tightening surgery before and after
Read more about Ovarian cyst size chart
During knee Replacement Surgery
Treatment
Types of knee replacement surgery
Knee replacement can be total or partial.
. Total knee replacement (TKR): Surgery involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint. It is the most common procedure.
Surgery lasts between 1 and 3 hours. The individual will have less pain and better mobility, but there will be scar tissue, which can make it difficult to move and bend the knees.
. Partial knee replacement (PKR): Partial replacement replaces only one side of the knee joint. Less bone is removed, so the incision is smaller, but it does not last as long as a total replacement.
PKR is suitable for people with damage to only one part of the knee. Post-operative rehabilitation is more straightforward, there is less blood loss and a lower risk of infection and blood clots.
The hospital stay and recovery period are normally shorter, and there is a higher chance of more natural movement.
During the procedure
Knee replacement requires a stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor's practices.
Knee replacement surgery is most often performed while you are asleep under general anesthesia. Your anesthesiologist will discuss this with you in advance.
Generally, knee replacement surgery follows this process:
- You will be asked to remove clothing and will be given a gown to wear.
- An intravenous (IV) line may be started in your arm or hand.
- You will be positioned on the operating table.
- A urinary catheter may be inserted.
- If there is excessive hair at the surgical site, it may be clipped off.
- The anesthesiologist will continuously monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen level during the surgery.
- The skin over the surgical site will be cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
- The doctor will make an incision in the knee area.
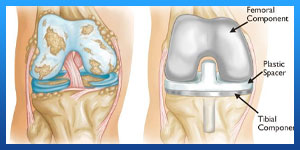
- The doctor will remove the damaged surfaces of the knee joint and resurface the knee joint with the prosthesis. The knee prosthesis is made up of metal and plastic. The most common type of artificial knee prosthesis is a cemented prosthesis. Uncemented prostheses are not commonly used anymore. A cemented prosthesis attaches to the bone with surgical cement. An uncemented prosthesis attaches to the bone with a porous surface onto which the bone grows to attach to the prosthesis. Sometimes, a combination of the 2 types is used to replace a knee.
The prosthesis is generally comprised of 3 components: the tibial component (to resurface the top of the tibia, or shin bone); the femoral [thigh bone] component (to resurface the end of the thighbone; and the patellar component (to resurface the bottom of the kneecap that rubs against the thighbone).
- The incision will be closed with stitches or surgical staples.
- A drain may be placed in the incision site to remove fluid.
- A sterile bandage or dressing will be applied
Read more about Cancer treatment in Iran
Read more about side effects of having only one testicle
Read more about rectal bleeding
Read more about Laser Eye Surgery in Iran
Alternatives to surgery
Most doctors recommend non-surgical (conservative) treatments before considering a knee replacement. These include:
. Diet
Losing weight will reduce the strain on your knee.
. Exercise
Even though this may be difficult because of the pain, there's usually some form of non-impact exercise (for example swimming or cycling) that you can start gently and which will improve the strength and flexibility of your knee.
. Drugs
Painkillers can reduce the pain in your joint, while non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help if your knee is swollen.
Generally these don’t provide such good results as a new knee joint but they may allow you to delay having a knee replacement operation for some years.
Alternatives to knee replacement surgery
Depending on how severe the damage is, a number of alternative procedures may be possible. However, knee replacement surgery tends to have better long-term results.
. Kneecap replacement can be done when only the kneecap is damaged. It is a short surgical procedure with a fast recovery time.
. Mini-incision surgery (MIS) involves a small cut in front of the knee, through which specialized instruments are inserted to maneuver around the tissue. The procedure is less harmful to the joint, and the recovery time is quicker and less painful.
. Image-guided surgery uses computerized images and infrared beacons to perform the surgery while the surgeon works from another, the operating theater.
. Arthroscopic washout and debridement involves the insertion of an arthroscope, a tiny telescope, through small incisions in the knee. The surgeon washes out the knee with saline solution clears away small fragments of bone. This is not advisable for patients with severe arthritis.
. Osteotomy is an open operation in which the shin bone is cut and re-aligned. After this, the patient will no longer bear their body weight on one part of the knee. It may be used for younger patients with limited arthritis, to postpone a knee replacement.
. Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) introduces new cartilage from the patient´s own cells into the damaged area. The cells are matured artificially in a test tube. This procedure is more common in cases of accidental injury.
After knee Replacement Surgery
Recovery
A patient who has knee replacement surgery will be hospitalized for 2 to 5 days, depending on how well they follow and respond to rehabilitation.
There will be pain, but a day after the procedure medical staff will encourage patients to get up and try to walk about, usually with some kind of walking aid. It is important to follow the instructions for rehabilitation.
Physical therapy sessions aim to strengthen the knee. These may be painful, but they significantly reduce the risk of future complications.
Patients who do not have help at home may need to stay in the hospital for longer.
Recovering at home
According to the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons (AAHKS), it can take up to 3 months to recover completely from a knee replacement surgical procedure.
Patients can normally drive again and return to work after 4 to 6 weeks. Physical therapy may be provided for 3 months.
Patients must comply with the instructions given by doctors, nurses and the physical therapist.
The patient may be asked:
. To take iron supplements to aid wound healing and muscle strength
. Not to bend down and lift heavy things, at least for the first few weeks
. Not to stay standing still for long periods, as the ankles might swell
. To use crutches, a walking stick, or a walker until the knee is strong enough to take your body weight.
. To use all medications according to the instructions
. To carry out the recommended exercises to encourage proper mobility
. To keep the affected leg raised on a footstool when sitting
. To avoid soaking the wound until the scar is completely healed, because of the risk of infection.
. To monitor for any signs and symptoms of infections, blood clots or pulmonary embolism.
. Precautions should be taken to avoid a fall, as this might mean further surgery.
Useful measures include:
. Ensuring there is a secure handrail and using a stable, nonslip bench or chair in the shower.
. Where possible, sleeping downstairs
. Securing any loose carpets and removing wrinkly mats around the house
. Removing or securing any trip hazards, such as loose wires
Most people can resume normal activities 6 weeks after the operation, but there may be some pain and swelling for up to 3 months, and scar tissue and muscles will still be healing for the next 2 years.
Items that may help at home include:
. A raised toilet seat
. A reaching stick for picking up items from the floor
. A long-handled shoe horn
Patients who have undergone knee replacement surgery can expect to participate in moderate and low-impact exercise activities, such as walking, swimming, and biking, but they should avoid extreme sports.
Looking after your knee replacement
Your new knee will continue to improve for as much as two years after your operation as the scar tissue heals and you exercise your muscles. You'll need to look after yourself and pay attention to any of the following problems:
. Stiffness – Sometimes the knee can become very stiff in the weeks after the operation for no obvious reason. Try placing your foot on the first or second step of the stairs, hold on to the banister and lean into your knee. This should help to improve movement and flexibility in your knee. It’s very important to continue with the exercises you were working on in the hospital. If the stiffness doesn’t improve after about six weeks your surgeon may need to move or manipulate your knee. This will be done under anesthetics.
. Pain – Pain caused by bruising from the operation is normal in the first two months, and you'll probably still need to take painkillers at six weeks to help you sleep through the night. You may still have some pain for as long as six months. If you still have pain after this, speak to your physiotherapist or GP.
. Swelling – Swelling is a very common problem after a knee replacement, particularly affecting the ankle and foot, and may last for up to three months or so after the operation. The ankle swelling usually settles as your walking ability improves. Swelling of the knee itself is also common over the first few months after surgery. Applying ice can be very helpful for a swollen joint, but make sure you protect your skin from direct contact with the ice pack. Ice can be applied for up to 20 minutes at a time. Raising your foot above hip height (on a footstool or similar) is another good way of reducing swelling, but make sure you get up and walk around for at least five minutes every hour to help reduce the risk of a blood clot.
. Infection – You should speak to your GP or hospital if you notice any signs of infection, for example:
. Walking
It's important to use crutches or walking sticks at first because the thigh muscles (quadriceps) will be weak after the operation, and falling could damage your new joint. Don't twist your knee as you turn around. Take several small steps instead.
After two weeks, or sooner if you’re confident, you can go down to one crutch and then a walking stick. After about six weeks, if your muscles feel strong and supportive, you can try walking without aids. This process may take less time if you’ve had a partial knee replacement or longer if you’ve had a more complex operation.
You should be able to walk outside within three weeks of having surgery but make sure you wear good supportive outdoor shoes. After three weeks, try to take longer strides so you can fully straighten (extend) your leg.
. Going up and down stairs
When going up stairs put your unoperated leg onto the step first, then move your operated leg up. When going down stairs, put your operated leg down first, followed by your unoperated leg.
. Sitting and kneeling
Don’t sit with your legs crossed for the first six weeks. You can try kneeling on a soft surface after three months when the scar tissue has healed enough. Kneeling may never be completely comfortable but should become easier as the scar tissue hardens.
. Sleeping
You don't need to sleep in a special position after knee surgery. However, you shouldn't lie with a pillow under your knee. Although this may feel comfortable it can affect the muscles, making it difficult to straighten your knee.
. Household jobs
You should be able to manage light household tasks like dusting or washing dishes. But avoid heavier jobs like vacuuming or changing the beds, or get help with them, for the first three months. Avoid standing for long periods as this could lead to your ankles swelling. If you’re ironing, sit down if possible and take care not to twist. Avoid reaching up or bending down for the first six weeks.
. Driving
You’ll be able to drive after your joint replacement as long as you can safely control the vehicle and do an emergency stop. It’s important to check with your insurance company whether you’re covered during your recovery, and you need to be confident that you can control the vehicle in all circumstances.
You'll probably be able to drive again six weeks after a full knee replacement or about three weeks after a partial knee replacement. If you’ve had surgery on your left knee and you drive an automatic you should be able to drive earlier as long as you’re not taking strong painkillers.
. Breakdown of the wound with oozing/pus or sores
. Increased pain
. Redness and the affected area feeling warmer than usual or smelling unpleasant.
You should also look after your feet – see a doctor or podiatrist if you notice any problems such as ingrown toenails that could become infected.
. Getting back to normal
It will be some weeks before you recover from your operation and start to feel the benefits of your new knee joint. Make sure you have no major commitments – including long-haul air travel – for the first six weeks after the operation.
Keeping up your exercises will make a big difference to your recovery time. You’ll probably need painkillers as the exercise can be painful at first. Gradually you’ll be able to build up the exercises to strengthen your muscles so that you can move more easily.
. Exercise
Exercise and sport are recommended after knee replacement, apart from contact sports, which may weaken the cement and lead to loosening of the joint components. Recreational sports – including golf, tennis and skiing – will gradually become possible depending on how fit and sporty you were before the operation. Cycling is a very good way of building up strength and mobility after knee surgery.
Exercising the main muscle groups around your knee is very important both before and after having a knee replacement. You can download a selection of exercises that are designed to stretch, strengthen and stabilise the structures that support your knee. Try to perform these exercises regularly, for instance for 10 minutes six to eight times a day. However, it’s important to find a balance between rest and exercise so you don’t overwork your knee. It’s a good idea to get advice from your doctor or physiotherapist about specific exercises before you begin.
Results
For most people, knee replacement provides pain relief, improved mobility and a better quality of life. And most knee replacements can be expected to last more than 15 years.


19 Comments
I need a hip replaced and i want get it done in iran, please tell me how much it cost in iran and how long does it take?
my gmail is [email protected]
thx
hello iran surgery
Can you explain about the risks of knee replacement?
Blood clots
Dislocation of the kneecap
Infection
Instability/falls
Limited range of motion.
Loosening of the joint.
Nerve injury.
hello iranian surgery
Coul you explain about Safe Knee Replacement Sleeping Positions
thx
1. Back: This is the optimal position. Prop your surgical leg up with 2-3 pillows. Do not put pillows behind the knee. …
2. Non-Operative Side: You can sleep on the opposite side of your replacement. This means your operating side will face the ceiling
Can I cycle after a knee replacement AND IS IT RIGHT?
During outpatient physical therapy, your therapist may have you ride a stationarybicycle to help improve the mobility around your knee. Biking can be a great exercise after a total knee replacement. Just be sure to ask your doctor or physical therapist if it is right for your specific condition.
I hve tribble ache because of my knee and I am 38,What is the best age to have a knee replacement?
Numerous studies have evaluated patients considered to be young to have a knee replacement. The average age of having a knee replacement in the United States isright around 65 years old. Generally, surgeons consider anyone under the age of 50 to be ‘young’ for the purposes of having a knee replacement.
I need to know that what activities can I do not after knee replacement? Thank you
Doctors highly recommend that knee replacement patients avoid doing sport such as football, soccer, aerobics, jogging, baseball and basketball because of the fact that heavy physical activities might contribute to the early failure of artificial joints, ultimately leading to the need for a second surgery.
Hi dear doctor, I have asked this question several time and I would be grateful if you answerd me..Is There an age limit on knee replacement surgery?
At the present time, there is no age limit on knee replacement, however, individuals are concerned that medical device corporations may be taking advantage of senior citizens and elderlies in pain from osteoarthritis. Over 90% of knee replacements are done on the elderly yet orthopedic surgeons persist that the main consideration is the degree of pain a person is in, not their age. The elderly people may be less able to cope with the stress of procedure as well as the post-operative physical condition that total knee replacement requires. The older a knee replacement patient is, the greater the odds that they will not have sufficient bone structure to handle a total knee replacement surgery.
Do I need general anesthesia for hip or knee replacement surgery?
Although general anesthesia is a reliable method, both types of hip or knee replacement surgeries can also be performed under regional anesthesia, which includes epidural or spinal anesthesia or a variety of nerve blocks. Today, many surgeons and specialists Anesthesia is preferred to regional anesthesia because it reduces complications and relieves anesthesia, as the patient will have less pain and nausea and less sleep.
Recently, the adapter channel blocking method has been invented as a neural block method without weakening muscle strength to reduce postoperative knee pain.
How long do I need to be hospitalized after a knee replacement surgeon?
As mentioned in previous issues, before knee replacement surgery, the patient should learn about the benefits and difficulties of surgery and how to properly use the knee joint.
More than 5% of patients have significant pain relief after knee replacement and can perform their daily activities better.
After surgery they can perform activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, driving, and climbing stairs.
But activities such as mountaineering, skiing, and tennis are not very suitable for artificial joints.
Such activities shorten the life of the Artificial joint and lead to early wear. In optimal conditions, the longevity of the knee prosthesis is about 5 years, however, if the infection develops, periarticular fractures, loose or tearing of the prosthesis, inaccurate surgery, or the use of low quality prostheses, the joint replacement life is reduced. In this situation the patient must then undergo more complex prosthetic surgery.
What causes knee pain?
There are many causes for knee pain, but the most common is arthritis. At the junction of all joints such as the knee joint, there is a layer of soft cartilage. This cartilage provides a soft surface to move the joint easily. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage disappears gradually and the bones come in contact. bones Friction together can lead to joint pain, swelling and stiffness.