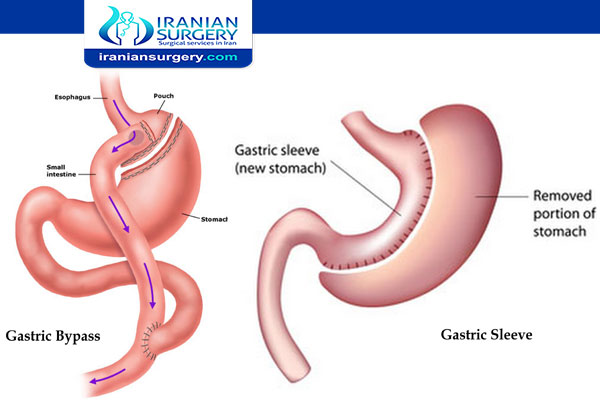
Gastric Bypass vs Duodenal Switch
Can you have a duodenal switch after gastric bypass?
Duodenal switch vs roux-en-y
Individuals who are considering bariatric surgery for weight loss have multiple options. From gastric bypass surgery to Duodenal Switch surgery to gastric sleeve, each type of surgery has its own benefits and risks.
When deciding which surgery is right for you, it is essential to compare your options. You should understand the similarities and differences between the two types of bariatric procedures. When reviewing Gastric Bypass vs Duodenal Switch, there are a number of factors to consider:
Comparison chart
Surgery Type | Duodenal Switch | Gastric Bypass |
Method of Weight Loss | Restrictive & Malabsorptive | Restrictive & Malabsorptive |
Stomach Alterations |
|
|
Changes to Intestine |
|
|
Operating Time |
|
|
Average Hospital Stay |
|
|
Full Recovery Time |
|
|
Read more about : Skin problem after bariatric surgery
Read more about : Bariatric surgery diet
Read more about : Duodenal Switch vs. Gastric Sleeve
Comparison between Duodenal Switch and Gastric Bypass Surgery
What is Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass is a restrictive and malabsorptive weight loss surgery procedure. It restricts the amount of food you can eat and reduces the number of calories (and nutrients) you absorb from food. The Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass – often called gastric bypass – is considered the ‘gold standard’ of weight loss surgery.
If you have high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes, gastric bypass surgery can make these conditions better, or even make them clear up completely. Up to six in 10 people with diabetes who have a gastric bypass find their sugar levels go back to normal after six years. Weight loss surgery may also make joint problems and breathing disorders, such as sleep apnea, better.
What is Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)?
The Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch – abbreviated as BPD/DS – is a procedure with two components. First, a smaller, tubular stomach pouch is created by removing a portion of the stomach, very similar to the sleeve gastrectomy. Next, a large portion of the small intestine is bypassed.
Comparing the procedure
How Gastric Bypass is performed
Gastric bypass, also called Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or RNY for short, is performed using the following steps:
. Cut and staple the top portion of the stomach to create a small pouch at the end of the esophagus.
. Leave the remainder of the stomach attached to the top of the small intestines.
. Go further down the small intestine, cut it, and attach it to the pouch.
. Take the end of the small intestine that is still connected with the non-pouch portion of the stomach and attach it to the bottom of the “Roux limb.” This allows the digestive juices produced by the stomach to “meet up” with the food in the intestines.
How Duodenal Switch is performed
The first step is sleeve gastrectomy in which about 80 percent of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller tube-shaped stomach, similar to a banana. However, the valve that releases food to the small intestine (the pyloric valve) remains, along with a limited portion of the small intestine that normally connects to the stomach (duodenum).
The second step bypasses the majority of the intestine by connecting the end portion of the intestine to the duodenum near the stomach. A BPD/DS both limits how much you can eat and reduces the absorption of nutrients, including proteins and fats.
Read more about : Lipomatic
Read more about : Liposuction in Iran
Comparing the Advantages and Disadvantages
Gastric Bypass Advantages:
. Produces significant long-term weight loss (60 to 80 percent excess weight loss)
. Restricts the amount of food that can be consumed
. May lead to conditions that increase energy expenditure
. Produces favorable changes in gut hormones that reduce appetite and enhance satiety.
Duodenal Switch Advantages:
. You will lose up to 70% of your excess weight within a year
. Allows patients to eventually eat near “normal” meals
. Causes favorable changes in gut hormones to reduce appetite and improve satiety.
. Duodenal switch surgery will cure or improve your diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, and at least 12 other conditions.
. You will feel full sooner while eating
. Your body will absorb fewer calories from the food you eat.
Gastric Bypass Disadvantages:
. Is technically a more complex operation than the AGB or LSG and potentially could result in greater complication rates.
. Can lead to long-term vitamin/mineral deficiencies particularly deficits in vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate.
. Not reversible
. Requires adherence to dietary recommendations, life-long vitamin/mineral supplementation, and follow-up compliance.
. Dumping Syndrome is Common
Duodenal Switch Disadvantages:
. Requires a longer hospital stay than the AGB or LSG
. Has a greater potential to cause protein deficiencies and long-term deficiencies in a number of vitamin and minerals, i.e. iron, calcium, zinc, fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D.
. Compliance with follow-up visits and care and strict adherence to dietary and vitamin supplementation guidelines are critical to avoid serious complications from protein and certain vitamin deficiencies.
. More frequent bowel movements.
Read more about : Virgin tightening surgery
Read more about : How to massage lumps after liposuction?
Comparing the Risks and Complications
Gastric Bypass Risks and Complications:
. Breakage
. Dumping syndrome
. Gallstones (risk increases with rapid or substantial weight loss)
. Hernia
. Internal bleeding or profuse bleeding of the surgical wound
. Leakage
. Perforation of stomach or intestines
. Pouch/anastomotic obstruction or bowel obstruction
. Protein or calorie malnutrition
. Pulmonary and/or cardiac problems
. Skin separation
. Spleen or other organ injury
. Stomach or intestine ulceration
. Stricture
. Vitamin or iron deficiency
Duodenal Switch Risks and Complications:
Risks associated with BPD/DS include:
. Excessive bleeding
. Infection
. Adverse reactions to anesthesia
. Blood clots
. Lung or breathing problems
. Leaks in your gastrointestinal system
Longer term risks and complications of a BPD/DS may include:
. Bowel obstruction
. Dumping syndrome, causing diarrhea, nausea or vomiting
. Gallstones
. Hernias
. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
. Vitamin deficiency/ Malnutrition
. Stomach perforation
. Ulcers
. Digestion issues
. Sagging skin
. Weight Regain
Read more about : Bariatric surgery risks
Who is a good candidate?
Is a gastric bypass right for me?
You may be eligible for gastric bypass surgery if:
. Your BMI (body mass index) score is 40 or more.
. Your BMI is 35 or more and you have other medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes or high blood pressure that may be improved by losing weight.
. You are fit enough to have a general anaesthetic and surgery.
. You are committed to losing weight and maintaining your weight loss through lifestyle and gastric bypass diet changes.
. You have tried to lose weight in other ways such as eating healthily, exercising and taking relevant medicines.
Read more about : Bariatric surgery requirements
Is a Duodenal Switch right for me?
You may be eligible for Duodenal Switch surgery if:
. You have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or more, OR
. Your BMI is between 35 and 39.9 and you have a serious obesity-related health problem
Read more about : High bmi for liposuction
Read more about : How to avoid loose skin after bariatric surgery?
How long does each procedure take?
Gastric bypass
The operation can take between two and three hours, but this may vary between surgeons.
Duodenal Switch
The operation can take between three and four hours, but this may vary between surgeons.
What can I expect during recovery?
Gastric bypass
Your gastric bypass recovery will include:
. Timeline: 4 to 6 weeks to full recovery
. Hospital Stay: 2 to 3 days
. Time Off Work: 1 to 3 weeks
. Pain: Same as after any laparoscopic surgery, managed with medication
. Diet: Slow transition from clear liquids to solid foods
. Activity: Slow transition back to regular activity and exercise
. Challenges: Dumping syndrome, digestive issues & weight regain if you “cheat” on your diet, potential dental issues, gallstones, kidney stones, & short-term hair loss, and sagging skin from rapid weight loss.
Duodenal Switch
. Hospital Stay: You will be in the hospital for 2 to 3 days
. Time off Work: You will need to take 1 to 3 weeks off of work
. Full Recovery: You will be “fully recovered” in 4 to 6 weeks
. Pain: The pain is manageable – it’s the same as any laparoscopic surgery and managed with medication.
. Diet & Activity: There will be a slow transition from clear liquids to solid foods and back to regular activity and exercise.
Read more about : Gastric balloon pros and cons
Diet
Gastric bypass
. Patients must eat three small meals a day.
. Patients must avoid sugar and fats to prevent Dumping Syndrome.
. Patients must take vitamin and protein supplements to avoid deficiency (Multivitamin, Calcium, Vitamin B12, and Iron for menstruating women)
Duodenal Switch
. Patients must eat three meals/day.
. Patients must strictly adhere to protein and vitamin supplements to avoid deficiencies. (Multivitamins, ADEK vitamins, Calcium, and Iron for Menstruating women).
Due to the extent of malabsorption after duodenal switch surgery, you will need to take 10 to 15 pills per day for the rest of your life. If you stop taking any prescribed vitamins, you will be twice as likely to develop vitamin deficiency.
Comparing cost
Gastric bypass
The cost of Gastric Bypass in Iran is between $ 3000-3500.
Factors such as the surgeon’s location, credentials, and the type of facility where the procedure is being performed all impact the final cost.
Duodenal Switch
The cost of Duodenal Switch in Iran is between $ 3200 - 3700.
Factors such as the surgeon’s location, credentials, and the type of facility where the procedure is being performed all impact the final cost.