1Can stage 4 testicular cancer be cured?
Around 80 out of 100 men (around 80%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis. Stage 4 is now classed as a stage 3C cancer. It means the cancer has spread to other organs in the body, such as the lungs. This is called metastatic cancer
2Can you die of testicular cancer?
Testicular cancer is not common: about 1 of every 250 males will develop testicular cancer at some point during their lifetime. ... Because testicular cancer usually can be treated successfully, a man's lifetime risk of dying from this cancer is very low: about 1 in 5,000
3What percentage of testicular lumps are cancerous?
Between 30 percent and 40 percent of testicular cancers are seminomas. Non-seminoma evolves from more mature germ cells. These tend to be more aggressive tumors. There are also testicular cancers that are a blend of both seminoma and non-seminoma
4How do you know if testicular cancer has spread?
When testicular cancer spreads, it most commonly spreads to the lung and the lymph nodes of the chest, pelvis, and the base of the neck. More advanced stages may have spread to the liver and bones. ... M0: The disease has not metastasized to distant lymph nodes or other organs.
5What are 5 warning signs of testicular cancer?
A painless lump or swelling on either testicle. If found early, a testicular tumor may be about the size of a pea or a marble, but it can grow much larger. Pain, discomfort, or numbness in a testicle or the scrotum, with or without swelling. Change in the way a testicle feels or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
6How many years can you live with testicular cancer?
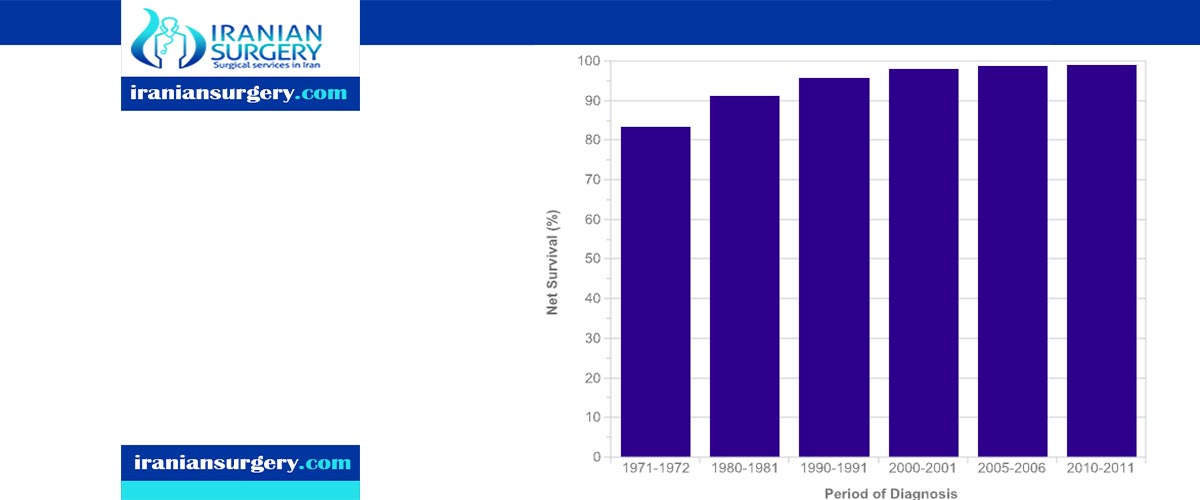
The general 5-year survival rate for men with testicular cancer is 95%. This means that 95 men out of every 100 men diagnosed with testicular cancer will live at least 5 years after diagnosis.
7Does testicular cancer spread quickly?
Seminomas are testicular cancers that grow slowly. They're usually confined to your testes, but your lymph nodes may also be involved. Nonseminomas are the more common form of testicular cancer. This type is faster growing and may spread to other parts of your body
8How long is a round of chemo for testicular cancer?
Chemo cycles generally last about 3 to 4 weeks. The main drugs used to treat testicular cancer are: Cisplatin.
9What happens if you leave testicular cancer untreated?
Testicular cancer. ... If diagnosed early, testicular cancer has a very high cure rate (around 90-95%) because the cancer is localised within the testicle. However, if left untreated, the cancer may spread to other parts of the body where it may be more difficult to treat.
10How big can testicular cysts get?
The epididymis is a tightly coiled tube about 20 feet long where the sperm matures as it passes through. It's located in the scrotum and surrounds the back and top of the testicle. Spermatoceles vary in size. They typically don't hurt, but they could cause pain if they grow too large