Femoral lengthening over nails lon (lon) meaning
LON Method Limb Lengthening VS. Internal Limb Lengthening (Precice Nail)
What is LON Method?
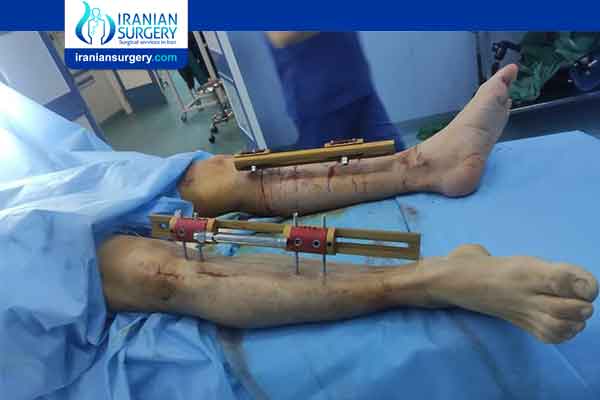
Lengthening over Nails (LON) is relatively new technique that combines external fixator distraction osteosynthesis with the convenience of intramedullary nail.
The Lon method, also known as external fixator combined with intramedullary nail, is a holding system attached by the skin. This method is used for broken bones and lengthening surgery.
The external device can be an Ilizarov fixator, a monolateral (rod-like) fixator, or any other device developed by some doctor anywhere, it is mainly up to the preference of the surgeon who practices limb lengthening.
An Intramedullary Nail or Rod, is generally a metallic nail type rod device which is surgically embedded within the bone cavity, during a Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Methodology.

Read more about : What is Internal Limb Lengthening?
Read more about : The Swedish patient saved $ 90,000 by choosing Iran over the United States to have leg lengthening surgery.(Lon Method)
Read more about : Siavash from Germany talks about his successful experience in leg lengthening surgery (LON Method)
Before Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Method
Why it’s done
This “LON” methodology is highly preferred by patients for these simple reasons:
. High reliability, in comparison to classical external methods. Intramedullary nails add more stabilization to the bone.
. Early removal of external devices, which allows earlier return to regular daily life activities. To compare, in the Holyfix method, patients have to walk, sleep, and live with external devices for 9-12 months or more.
. Most importantly, reasonable costs, in comparison to other latest systems such as PRECICE or STRYDE.
Cause of Limb Length Discrepancy
. Previous Injury to a Bone in the Leg
A broken leg bone can lead to a limb length discrepancy if it heals in a shortened position. This is more likely to happen if the bone was broken into many pieces. It is also more likely to happen if the skin and muscle tissue around the bone were severely injured and exposed, as occurs in an open fracture.
In a child, a broken bone sometimes grows faster for several years after healing, causing it to become longer than the bone on the opposite side. This type of overgrowth occurs most often in young children with femur (thighbone) fractures.
Alternatively, a break in a child’s bone through the growth plate near the end of the bone may cause slower growth, resulting in a shorter leg.
. Bone Infection
Bone infections that occur in growing children may cause a significant limb length discrepancy. This is especially true if the infection happens in infancy.
. Bone Diseases (Dysplasias)
Certain bone diseases may cause limb length discrepancy, including:
. Neurofibromatosis
. Multiple hereditary exostoses
. Ollier disease
Other Causes
Other causes of limb length discrepancy include:
. Neurologic conditions
. Conditions that cause inflammation of the joints during growth, such as juvenile arthritis.
In some cases, the cause of limb length discrepancy is “idiopathic,” or unknown. This is particularly true in cases involving underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg, or partial overgrowth of one side of the body.
These conditions are usually present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected early on. As the child grows, however, the discrepancy increases and becomes more noticeable. In underdevelopment, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle is abnormally short. The child may also have related foot or knee problems.
Hemihypertrophy (one side too big) and hemiatrophy (one side too small) are rare conditions that cause limb length discrepancy. In patients with these conditions, the arm and leg on one side of the body are either longer or shorter than the arm and leg on the opposite side. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. In some cases, the exact cause of these conditions cannot be determined.
Read more about : Walking after Leg Lengthening Surgery
Read more about : Running after Limb (Leg) Lengthening
Symptoms of limb length discrepancy
The effects of limb length discrepancy vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause and size of the difference.
Patients who have differences of 3-1/2 to 4 percent of total leg length (about 4 cm or 1-2/3 inches in an average adult) may limp or have other difficulties when walking. Because these differences require the patient to exert more effort to walk, he or she may tire easily.
Some studies show that patients with limb length discrepancies are more likely to experience low back pain and are more susceptible to injury. Other studies do not support this finding, however.

Diagnosis
How is limb length discrepancy diagnosed?
. Doctor Examination
Parents are usually the first to detect a leg length discrepancy when they notice a problem with the way their child walks. Discrepancies are also sometimes detected when a child undergoes a screening at school for curvature of the spine (scoliosis). It is important to note, however, that leg length discrepancy does not cause scoliosis.
Your doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination and use tests to confirm or diagnosis a discrepancy in length.
. Physical Examination
During the exam, your doctor will ask about your child’s general health, medical history, and symptoms. He or she will then perform a careful examination, observing how your child sits, stands, and moves.
. Gait analysis. During the examination, your doctor will closely observe your child’s gait (the way he or she walks). Young children may compensate for a limb length discrepancy by flexing their knee or walking on their toes.
. Measuring the discrepancy. In most cases, the doctor will measure the discrepancy when your child is standing barefoot. He or she will place a series of wooden blocks under the short leg until the hips are level, then measure the blocks to determine the discrepancy.
. Imaging Studies
. X-rays. An x-ray provides images of dense structures, such as bone. If your doctor needs a more precise measurement of the discrepancy, he or she may order x-rays of your child’s legs.
. Scanograms. This is a special type of x-ray that uses a series of three images and a ruler to measure the length of the bones in the legs. Your doctor may order a scanogram instead of, or in addition to, a traditional x-ray.
. Computerized tomography (CT) scans. These studies can provide a more detailed image of the bone and soft tissue in the legs. In some cases, your doctor will use a CT scan to measure the limb length discrepancy.
If your child is still growing, your doctor may repeat the physical examination and imaging studies every six months to a year to see if the discrepancy has increased or remained the same.
Because an x-ray measurement cannot be compared with a CT scan measurement, your doctor will follow your child with the same type of imaging study over time.
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery cost 2021
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery before and after photos
Read more about : Leg lenthenening surgery success story
What are the advantages of the Lon method?
Pros:
. Reach the extension in a short time
. Faster healing
. Mobile immediately after the operation
. Achieve more extension thanks to the external fixator
. External fixator is removed immediately after the extension
. Very safe / stable method because fixator and intramedullary nail (intramedullary screws) are combined.
. Can be loaded with full weight without walking aids, therefore sports can be done without any problems during treatment.
. In the event of a complication, the external fixator can be adjusted from the outside.
. Less risk of infection as minimal screws are attached to the bone
. A very inexpensive alternative to other methods
What are the disadvantages of the Lon method?
Cons:
. The duration of the surgical operation is longer in comparison to classical surgeries.
. Wound infection
. Limited choice of clothes
. Restricted sleeping position
. Care of the wounds and pins during the extension
. Removal of the intramedullary nail after 100% healing
The Lon Method risks
. Anesthesia incidents
. Bleeding during or after surgery
. Wound infections
During Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Method
How does a LON method surgery work?
During the Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Methodology, the external fixator is attached to the bone through the skin. The intramedullary nail (intramedullary screws) is inserted on the femur either through a small skin incision above the hip or below the kneecap. To extend the lower leg, the intramedullary nail is also inserted below the kneecap.
The extension is done with the external fixator, the patient extends with a special screw every day by 1 mm to – 1.5 mm every 6 hours (4×6 hours), with the screw on the outside of the external fixator by 0.25 mm – to 0 .5 mm, so that at the end of the day 1 to 1.5 mm can be reached.
With the external fixator, the thigh and lower leg bones are gently lengthened.
The surgery lasts on average between 3 to 5 hours under general anesthesia.
Once the LON apparatus is surgically attached to the patient’s legs; soon after 3-5 days of post-surgery hospitalization, the lengthening period begins at the hospital, whereby the external fixator is elongated or distracted by 1 mm per day, allowing the patient’s bone to separate, with the intramedullary nail inside their bones.
The biggest advantage of having an intramedullary nail in this method is that it helps in correcting any angular bone deformity, during this lengthening phase, as well. Within 60 to 80 days of lengthening, elongation of the bone is stopped, and we let the bone start to heal between the gaps created; and once there is ample weight-bearing bone consolidation, usually 30 to 45 days after the lengthening has been stopped; the doctors could remove the external fixator devices. This allows for quicker recovery time, in comparison to purely external fixator methods; as after this stage the patient’s bones would generally take around 5-6 months to fully heal. Thus, allowing the whole process to complete in 8 to 9 months; which in reality is as fast as any internal method; this is why LON is one of the most preferred methods of Limb Lengthening surgery by our patients worldwide.
After Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Method
After the procedure
. Lengthening begins after 4-5 days since the operation. The doctor gives necessary instructions on how to use a special key to turn to screws in order to lengthen bones 1 mm / day. Additionally, bandage change and pin site care instructions are also given. These are important for avoiding infection. After doing the first session of lengthening at the hospital, patients are released.
. Lengthening takes around 2-3 months (usually 1 mm / day. For example, 6 cm takes 2 months, and 7 cm takes 70 days) depending on the lengthened amount
. Another 2-4 weeks pass before slight consolidation is visible on x- rays. Then external fixators are removed.
. 1-1.5 yrs (or less, if bone consolidation is fast) after external fixators are removed, intramedullary nails can also be removed because at this time the bone is fully consolidated
. It is possible to walk during the entire period of fixation, although with some difficulties and limitations. After externals are removed, walking becomes a lot easier and patients are able to walk normally and live their daily life with the exception of doing sports (this will be possible after full consolidation)
. After the patient undergoes the surgery, there is around 3-5 days of hospitalization. Walking begins from the next day after surgery by taking a few steps with a walker.
Read more about : Leg lengthening recovery time
Read more about : Exercises after leg length discrepancy
Read more about : Limb Lengthening Surgery Pros and Cons
Read more about : Diagnosis code for leg length discrepancy
Read more about : What is the most common complication of bone lengthening using external fixation?
What is the maximum recommended amount of lengthening?
Lengthening varies, depending on the choice of bone the patients lengthens, the femurs or the tibias, in their Limb Lengthening Surgery by LON Methodology.
Under the Medical Safety and Surgical guidelines and recommendations, with a single limb lengthening surgery, the patients can lengthen up to 3 inches; or to be exact:
- Femurs (Thighs): 6 – 8 cms OR
- Tibias (Calf’s): 5 – 7 cms
However, you may even opt to have two limb-lengthening surgeries, with a gap of 6 months between the two surgeries and gain up to 6 inches or 12 – 15 cms. But it must be remembered that the flexibility of the patient’s legs is fundamental in the lengthening process and achieving the max height achievable within the safe limits. The more flexible your legs are, the more comfortable and pain-free, the patients would be during this lengthening period.