Tympanoplasty surgery procedure
How long does tympanoplasty surgery take?
How painful is a tympanoplasty?
Why is Tympanoplasty done?
What happens if tympanoplasty fails?
Tympanoplasty surgery types and procedure
Patch Tympanoplasty is the most minor of the procedures. It is performed in the office in adults and under anesthesia in children. The edges of the hole are irritated with an instrument, and a biologic tissue paper patch is placed over the hole and held on with a drop of blood from the irritation
Fat Tympanoplasty is another minor procedure that can be performed in the office. The ear lobe is frozen, a small amount of fat is removed, the eardrum is irritated and the fat is placed through the hole. The earlobe is sutured.
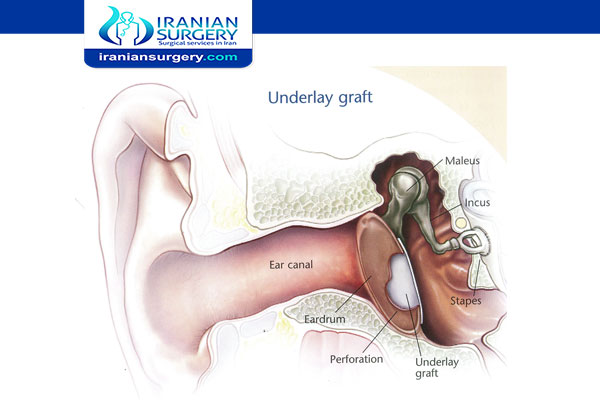
Medial Tympanoplasty is performed in the operating room under local or general anesthesia. It can sometimes be performed working through the ear canal, but is usually performed via an incision behind the ear. Incisions are made in the ear canal and the remnant of the eardrum is lifted up. The ear canal may be widened. A tissue graft from the ear muscle (fascia) or cartilage is obtained and is slid under the eardrum. Packing is placed in the middle ear and ear canal to hold the graft and drum against each other to heal.
Lateral Tympanoplasty is performed under general anesthesia in ears with large holes, holes in the front part of the eardrum or when previous surgeries have failed to close a perforation. It is performed through an incision behind the ear and the ear canal is widened. Some or most of the original eardrum is removed. A fascia graft is harvested, and used to create a new eardrum. A small skin graft is often taken from behind the outer ear and used to line the surface of the widened ear canal to get the ear canal to heal quickly.
Read more about: Adenoidectomy Surgery
Read more about: Cochlear Implants Surgery
Read more about: tympanoplasty surgery recovery
How long does tympanoplasty surgery take?
Tympanoplasty usually takes from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
Read more about: Tympanoplasty surgery complications
How painful is a tympanoplasty?
There is usually only mild pain following ear surgery. Some discomfort may be felt for the first 24 hours if a pressure dressing is applied to the ear. Once this is removed, however, most discomfort subsides. There may be occasional fleeting, stabbing pain in the ear up to one week after surgery.
Read more about : Sign of infection after rhinoplasty
Read more about : how to fix a deviated septum without surgery?
Why is Tympanoplasty done?
Doctors do a tympanoplasty when the eardrum (or tympanic membrane) has a hole that doesn't close on its own. It is done to improve hearing and prevent water from getting into the middle ear.
Kids can get a hole in an eardrum from:
- infections that cause the eardrum to burst
- ventilation (ear) tubes that fall out or are removed
- injury, such as puncturing the eardrum with a cotton swab
- cholesteatoma, a growth within or behind the eardrum
Most of the time, the eardrum can repair itself. So at first, doctors closely watch a hole in a child's eardrum rather than fix it right away. They might wait years to repair one in a very young child. This lets the ear develop enough to help prevent complications after the surgery. Surgery might also wait if a child has ongoing problems with ear infections.
Read more about: tympanoplasty surgery recovery
What happens if tympanoplasty fails?
In most cases, eardrum repairs are very successful. More than 90 percent of patients recover from tympanoplasty with no complications. The outcome of the surgery may not be as good if the bones of your middle ear need to be repaired in addition to your eardrum. Failure of tympanoplasty can occur either from an immediate infection during the healing period, from water getting into the ear, or from displacement of the graft after surgery. Most patients can expect a full “take” of the grafted eardrum and improvement in hearing.
Read more about: Steps of tympanoplasty

