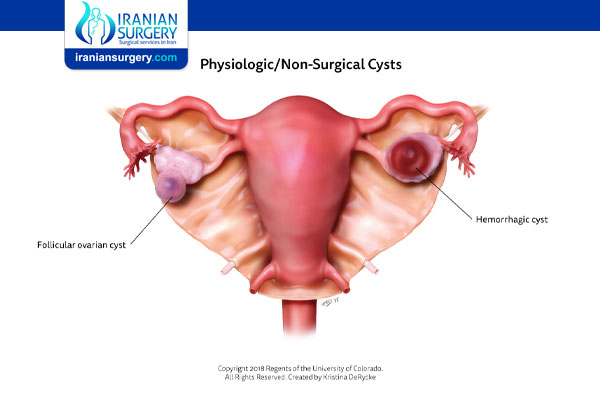
Ruptured Ovarian Cyst
What are the symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst?
A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause sudden pain in your pelvic area. The pain is usually sharp and most often on the lower right side.
But some cysts, such as endometriomas, could be on either side.
You might feel pain after sexual intercourse or when you’re exercising. The pain from an ovarian cyst is likely to begin at the midpoint of your menstrual cycle.
Different kinds of cysts that rupture may cause pain at other times during your menstrual cycle.
Read more about : Ovarian cyst size chart for surgery
In addition to pain, symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst can include:
. Bleeding from the vagina
. Nausea
. Vomiting
. Tenderness in the pelvic/abdominal area
. Weakness
. Feeling faint
. Fever
. Increased pain while sitting
. Full or heavy feeling in your pelvis
. Shoulder pain (if you have a lot of bleeding)
Read more about : How to burst a bartholin cyst at home?
Read more about : Ovarian Cyst Removal Surgery
What causes a ruptured ovarian cyst?
Most functional ovarian cysts are a normal part of a woman’s cycle, and they’re mostly benign, or noncancerous. Other types of ovarian cysts, such as endometriomas, are not normal.
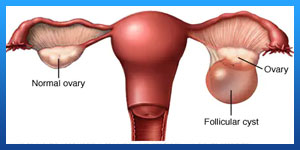
Exactly why a cyst ruptures isn’t known. But here are some possible risk factors:
. You’re more likely to have a ruptured ovarian cyst if you have a history of ovarian cysts or ruptured ovarian cysts.
. Cysts can rupture after strenuous exercise and after sexual intercourse.
. Larger cysts may burst more easily.
How are ruptured ovarian cysts treated?
If you have severe pelvic pain, see your doctor or go to the emergency room. Your doctor will take your medical history and do a physical exam.
You may undergo several tests to determine the cause of your pain, although not all are included in a routine evaluation of an ovarian cyst. These tests may include:
. Pregnancy test
. Complete blood workup
. Urine test to look for infection
. Ultrasound scan of your pelvis
. CT or MRI scan
. Laparoscopic surgery for diagnostic purposes
An ultrasound scan may indicate a ruptured ovarian cyst if it shows a mass and fluids in the pelvis.
The cyst itself may collapse after it opens. But a scan is not definitive, and the doctor will consider other factors in making a diagnosis.
Uncomplicated vs. complicated ruptured ovarian cysts
In most cases, a ruptured ovarian cyst without complications will be treated conservatively with observation and pain medication. Functional cysts are usually in this category.
If your ruptured cyst has complications, such as heavy or ongoing blood loss, your doctor may want to admit you to the hospital for observation.
Read more about : Best antibiotic for bartholin cyst
While you’re admitted to the hospital, they may:
. Monitor your vital signs and the ratio of your red blood cells to total blood volume (hematocrit)
. Conduct repeated scans to check for internal bleeding (hemoperitoneum) into the peritoneal space between the lining of the abdominal wall and your internal organs
If you need surgery
In some cases, laparoscopic surgery may be recommended to stop the bleeding.
Other factors that may indicate the need for surgery are:
. Cysts larger than 5 centimeters (cm), depending on the type of cyst
. Persistent pain
. Possibility that imaged masses may not be benign
Some cysts larger than 5 cm (even as big as 10 cm) don’t always need to be surgically removed. Some simple cysts can be managed if you’re premenopausal.
In the past, a ruptured ovarian cyst with bleeding and low blood pressure was routinely treated with surgery.
But depending on the type of cyst, many instances of a ruptured ovarian cyst can now be managed conservatively because of advances in imaging technology.
In cases with potential problems with some types of cysts, your doctor may advise you to take oral contraceptives to prevent ovulation and cyst formation.
What are the complications of an untreated ovarian cyst?
In most cases, a ruptured functional ovarian cyst will go away on its own and you may not know that it was there.
But when you have pain and other symptoms, it’s best to have your doctor check it out. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to complications:
. If your cyst is bleeding, you might have excessive blood loss.
. Rupture of an endometrioma can be associated with excessive bleeding.
. If you have an infection, there’s a danger that it will spread. A ruptured dermoid cyst, for example, may result in peritonitis, or inflammation of the perineum. This can become life threatening without prompt treatment.
. A ruptured cyst can mimic symptoms of ovarian torsion or cause torsion. Ovarian torsion happens when the ovaries twist and cut off their blood supply. This can be an emergency and cause you to lose an ovary.
Source:
. https://www.healthline.com/health/how-do-i-tell-if-i-have-a-ruptured-ovarian-cyst