Organ Transplant in Iran
 What is organ transplant?
What is organ transplant?
Organ transplant is the process of surgically transferring a donated organ to someone diagnosed with organ failure. Many diseases can lead to organ failure, including heart disease, diabetes, hepatitis, cystic fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Injury and birth defects may also cause organ failure.
Organ transplant is the last suggested procedure in cases of organ failure, and is undertaken only in critical cases and emergency medical situations. In such situations, at the critical end of organ failure, a healthy organ/organs for transplant from a person living or deceased is transplanted into the organ transplant recipient, offering them a new chance of survival.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best organ transplant surgeons in Iran. The price of an organ transplant in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined based on an in-person assessment with the doctor.
For more information about the cost of organ transplant in Iran and to schedule an appointment in advance, you can contact Iranian Surgery consultants via WhatsApp number 0098 901 929 0946. This service is completely free.
Read more about : A patient who came from Iraq to Iran for Kidney transplant
Read more about : Miracle of Iranian surgeons with successful Leg lengthening surgery
Before Organ Transplant
Why is an organ transplant done?
An organ transplant is done when a critical organ in the body is functioning very poorly, and determined to ultimately fail and cause mortality. To prevent the death of a patient whose organ failure is already determined, doctors will suggest organ transplantation as an end state measure, after determining suitability of such a procedure on the patient.
Some of the chronic conditions that require an organ transplant due to terminal organ failure include chronic kidney disease, cystic fibrosis, acute diabetes, congenital heart disease (CHD). Liver failure due to cirrhosis, and accidents and injuries are also reasons that an organ transplant process may be suggested.
Organ transplant offers a recipient a new lease of life in cases where they are determined to not survive due to end stage critical organ failure, and currently, organ transplant surgery has become highly specialised to cater to a significant population that can be benefitted by organ transplantation.
What organs and tissues can be transplanted?
Organs and tissues that can be transplanted include:
. Heart
. Lung
. Liver
. Kidney
. Pancreas
. Intestine
. Cornea
. Skin
. Middle ear
. Connective tissue
. Vascularized composite allografts

Finding a Donor
For people who need an organ, finding a donor may take weeks, months, or longer. It is more feasible for a living donor to be found in case they are relatives, which enables patients to bypass the organ transplant waiting list and receive a transplant less likely to be rejected. However, organ transplant donation itself is often as easy as filling a card, and any organ donor can donate multiple organs, saving many lives in the process.
Finding a donor is usually done by a doctor in touch with a medical board. Once a thorough evaluation is conducted of a patient, deeming them suitable for organ transplantation, the patient is put on an organ transplant list. This list matches an organ transplant patient with a donor at the earliest available opportunity. The donor is usually deceased and has granted permission for organs to be donated after death.
There are two legal ways to obtain an organ:
. A person can wait for a donor to become available on the transplant list.
. A person can find their own donor. This is usually a family member or friend of the person who needs a transplant, but some people are willing to donate to people they don’t know. Some people even advertise for donors using social media, radio, or billboards.
There are two types of donor:
. Living donors can donate a kidney, a lung, or a portion of the pancreas, liver, or intestines. They must be in reasonably good health.
. Deceased donors can donate two kidneys, two lungs, the heart, pancreas, corneas, and intestines. They may also donate body tissue, such as heart valves, tendons, or skin.
What are the types of living-organ donation?
The living-organ donation can be of two types – directed donation and nondirected donation.
. Directed donation: Directed donation is a common type of organ donation, where the donor directs the organ to a specific recipient for transplant. The donor can be the following –
. A first-degree relative, such as a parent, brother, sister or adult child
. Biologically related relatives, such as uncles, aunts or cousins
. The donor can also be a biologically-unrelated person who has a connection with the transplant candidate, such as a spouse, friend, or a co-worker.
. A person who has heard about the transplant candidate’s need and offered to help
. Nondirected donation: Here, the donor does not name the recipient. The nondirected donation is also called as good Samaritan or altruistic donation. The organ will be donated to a recipient based on the medical requirement and blood type compatibility. In some cases, the donor may choose not to know the organ recipient, but in other cases, the donor and the recipient can meet if both agree and the transplant centre allows it.
What can you expect from organ transplantation?
Organ transplant is performed in people who have a serious illness and will die without a new organ. There are other cases as well, where the transplant is done to improve a person’s quality of life, such as restoring the sight with a cornea transplant.
The first step of the transplantation process is to get one’s name on the organ transplant list. To do this, the doctor has to examine the person, diagnose a serious medical condition and conclude that they match all the criteria to receive an organ transplant.
The process of organ transplantation is a complicated one. The donor must be a close match to the recipient and have compatible blood types for the transplantation to work. There are other relevant factors as well depending on the organ involved. For instance, in kidney transplantation, it is necessary for the donors and their recipients to have compatible antibodies and similar body sizes.
Once a person reaches the top of the waiting list, they can receive an organ transplant depending on the availability of the next matched donor. When an organ is available, immediate surgery is arranged and the recipient gets the transplant. After the transplant, the recipient has to stay in the hospital for a few days so that their condition can be monitored. The length of the stay will depend on their overall health and how well the surgery went.
Can I become an organ transplant donor?
Yes, you can become an organ transplant donor by signing up for donation. If you are below 18 years of age, you will require parental consent to pledge your organs. Signing up to be a donor for organ transplant can help save many lives once you are deceased, and does not hamper your current life in any way.
If you are legally an adult, you can directly register as an organ transplant donor to consent to the use of your organs for organ transplant process after your death.
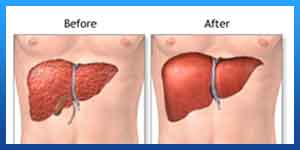
Benefits
What are the benefits of organ transplantation?
The benefits of an organ transplant depend on the organ a person receives. Some benefits may include:
. Avoiding medical procedures such as dialysis
. Living a longer life
. Living a healthier or less painful life
. Gaining an improved quality of life, such as when a cornea transplant restores a person’s sight.
. Correcting congenital disabilities that endanger a person’s life
. Spending less time in the hospital, needing fewer surgeries, or taking fewer medications.
Risks and Complications
For almost all organ transplant recipients, the benefits far outweigh the risks.
Most people who need an organ will die or live a much shorter life without a transplant. However, organ transplants are risky surgeries, especially since those who need them often are very ill.
Some risks associated with organ transplant surgery include:
. Complications related to the use of anesthesia, including death
. Bleeding or other complications during the procedure
. Postsurgical complications, such as infection
. A higher risk of infections and other illnesses due to anti-rejection or other transplant-related drugs.
. Organ rejection
. Organ failure
Preparing for an organ transplant
Organ transplantation requires financial, psychological, mental as well as physical preparation. Once a patient is on the organ transplant list, it is essential that they cultivate patience and a positive attitude to enable themselves to look forwards towards a time without disease. It is necessary to be upfront with the medical team in charge of the organ transplant regarding psychological conditions, and undergo treatment, if deemed necessary.
Once a patient is deemed fit to undergo the organ transplant surgery, attention should be paid to financial conditions that accompany such a situation. The waiting time for a patient awaiting an organ transplant from a deceased donor is often the best time to prepare for the organ transplant surgery. Physical fitness, as much as can be achieved, should be aimed for, and any suggested medication regimen should be rigorously followed.
During Organ Transplant
Types of organ transplant
While organ transplant was initially restricted to transplantation of vital organs, today, medical and surgical processes have developed to allow transplantation of several organs that allow not only a longer lifespan, but an improved quality of life to recipient patients. Organ transplant types today include:
- Heart transplant
Since a heart is a vital organ, an organ transplant is provided to the donor from a deceased patient who has suffered brain death, often in the case of an accident. This replaces the organ transplant recipient's damaged heart and offers them a completely new one to afford them a chance at an extended life. Strict organ transplant guidelines surround such a procedure, and the organ transplant surgery is carried out by highly specialised doctors working round the clock to monitor the patient's vital sign throughout the organ transplant process. Due to a scarcity of donors, heart transplants are one of the most critical and least performed organ transplant surgeries, and operations are very few annually.
- Lung transplant
Another vital organ, healthy lungs are taken from a deceased patient and transplanted into the organ transplant recipient. Due to the lack of donors and the criticality of time of transport, lung transplants also remain rare across the globe. The organ transplant process is highly dependent on finding a highly suitable donor to prevent organ transplant rejection and avoid the immune system attacking the new transplant.
- Liver transplant
In cases of irreversible liver disease, a patient's unhealthy liver is removed and replaced with either a portion of a liver from a living donor, such as a relative, or with a complete healthy liver from a deceased donor. End-stage liver disease, especially cirrhosis of the liver due to alcohol abuse, is the most common reason for organ transplant surgery for the liver. Other causes may include chronic hepatitis B or chronic hepatitis C, autoimmune hepatitis, metabolic disorders and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The organ transplant success rate for liver transplants is relatively high, and 75% of patients are alive after five years of a liver transplant.
- Pancreas transplant
Kidney and pancreas double transplant is the most common type of organ transplant surgery requiring a pancreas transplant; it is seldom carried out alone. Type 1 diabetes causing kidney failure is the reason for this type of organ transplant surgery, and in most cases, both organs come from a single deceased donor. It is possible, however, that in the kidney-pancreas double transplant, the kidney comes from a living donor, usually a relative, and only the pancreas from a deceased donor. In rare cases of Type 2 diabetes, and organ transplantation involving a kidney as well as the pancreas may be advised.
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not make enough insulin, and the kidney failure is progressive. In order to help a patient survive through this, an organ transplant may be advised, and the transplanted pancreas can produce adequate insulin.
- Cornea transplant
In cases where corneal tissue is scarred or otherwise irreparably damaged due to disease or injury, a corneal transplant is suggested. The organ transplant statistics for this type of organ transplant surgery shows a high rate of success and this is one of the more commonly performed organ transplantations. Since corneal eye disease is one of the most common reasons for blindness, corneal transplants are becoming more commonly suggested, and the advances in this organ transplant type has been immense from a surgical perspective.
Some reasons making a corneal transplant necessary include scarring from eye infections such as keratitis or herpes, and other eye diseases such as keratoconus where the shape of the cornea is distorted, making an organ transplant the only way to restore complete vision. Hereditary conditions can also cause corneal disease. Organ transplantation involving the cornea may also be suggested in cases where cataract and LASIK surgeries have been unsuccessful and caused further complications.
- Kidney transplant
Renal disease affects a large part of the population today. Kidneys are an essential part of the human mechanism, helping to filter out toxins from the blood, and ensuring an electrolyte balance that allows the body to function normally. Kidney failure can be contained by either dialysis or kidney transplants. In cases where dialysis is ruled out for the patient due to the severity of the kidney failure or overall health conditions, an organ transplant surgery is suggested. Either one, or both kidneys may be replaced for such patients. A single kidney transplant usually involves a living organ transplant donor and both of them are put on specialised diets and medication to reduce chances of organ transplantation complications such as rejection of the donor organ or blood infections. Patients with cancer, hepatitis or cardiovascular disease are not chosen as candidates for most organ transplant processes, including kidney transplant.
Receiving a kidney from a living relative reduces the chance of rejection of the organ and is suggested as a better choice of organ transplant. This also enables the patient awaiting transfer to bypass the wait of many years to receive the organ transplant.
- Trachea transplant
One of the least conducted organ transplant surgeries, tracheal transplant is performed when the trachea or the airway hardens or is scarred due to disease or injury. Tracheal transplant helps patients who are unable to have a normal life due to trauma from tracheal dysfunction to have a more normal life. The organ transplant process involves procuring the trachea from a deceased donor and replacing the patient's trachea.
- Skin transplant
Burn or other skin injuries that are too severe to be repaired by the body's own system can be helped through skin transplants. This type of organ transplantation involves grafting of donor skin onto a patient's body and the use of immunosuppressive drugs to prevent graft rejection. Once the organ transplant surgery is carried out, the patient is kept under medical observation for a length of time. This organ transplant process is usually only carried out in cases of severe injury where a patient's own skin cannot be grafted. Once the donor skin is successfully transplanted, doctors may also transplant the patient's own skin onto other parts of their body.
More often, however, organ transplantation involving the skin does not require a donor, and healthy skin is grafted from the patient's own body onto the burnt area. The injured skin can be more easily replaced as chances of rejection of the organ transplant is lowered.
The organ transplant procedure
The organ transplant procedure depends completely upon the organ transplant type, and in simple terms, involves the removal of a healthy organ from a donor, either living or deceased, and transplanting this into a patient with end-stage irreversible organ damage. The organ transplant surgery is preceded and succeeded by the use of drugs to prevent transplant rejection, as well as continuous medical evaluation to determine the feasibility of the transplant.
After Organ Transplant
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery after any surgery is something that needs to be paid attention to, and despite feeling better overall, the body can undergo many changes resulting from an organ transplant surgery. Therefore, the road to recovery is something that is planned for since before the surgery itself, and must be adhered to by the patient.
Most patients who have undergone organ transplant surgery can return to normal life after a span of 2-3 months, and sometimes earlier in case of a skin or corneal transplant. The patient is kept under medical observation for a certain length of time after undergoing the organ transplant process where their condition, response to drugs and vital signs are continuously monitored by the medical team. Once a patient is discharged into the care of family, they are required to follow lifestyle guidance and medication regimens, and come in for regular follow-up medical evaluations.
If all steps are strictly followed, it is possible for patients to live a fulfilling life after an organ transplant.
 Medications required after organ transplant
Medications required after organ transplant
Most patients immediately enjoy a better quality of life after an organ transplant, but constant vigilance in terms of lifestyle and medication are strictly necessary and remain a lifelong process for patients who have undergone organ transplantation. Risky behaviors such as smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol, and often any consumption of alcohol, use of recreational drugs, and skipping prescribed medication increase chances of organ transplant failure and morbidity.
Medication required after organ transplant is prescribed by the doctor and their team of medical experts and should be followed as a strict regimen. It is also important to schedule regular check-ups with the medical team who have the organ transplant history of the patient.
Immunosuppressant drugs that are prescribed before and after the organ transplant surgery may be subject to change dependent on the patient's reaction, and some drugs do not perform as well over time. This necessitates regular follow ups with the medical team for the patient to aid in near-complete recovery.
Precautions to take
While the quality of life is improved for a patient who undergoes a successful organ transplant surgery, they have to continually take several precautions, often requiring a change in lifestyle.
In addition to a medication regimen, patients will have to monitor their activity, and depending on their doctor's advice, they may be prescribed higher or lower levels of physical activity.
Patients who have undergone organ transplantation will also have to ensure a nutritious diet that allows their body access to all micro and macronutrients on a regular basis. Organ transplant surgery will also see patients having to maintain strict hygienic conditions around their homes and offices, and in many cases, receive professional help from therapists to help with their mental and psychological conditions.
Organ transplant success rate
Depending on the type of organ transplantation, overall health and the body's immune system response, the chances of successful organ transplant surgery and subsequent recovery range from the single digits to over 73% percent for a five year period. It is advisable to follow all instructions of the doctor in charge of the organ transplant surgery if you deemed suitable to become an organ recipient to aid chances of recovery.
What are the signs of organ rejection?
Some of the general signs of organ rejection include:
. Pain at the transplant site
. Flu-like symptoms
. Children may feel cranky
. Feeling unwell
. Fever
. Swelling
. Changes in weight
. Urinating less often
. Changes in heart rate

