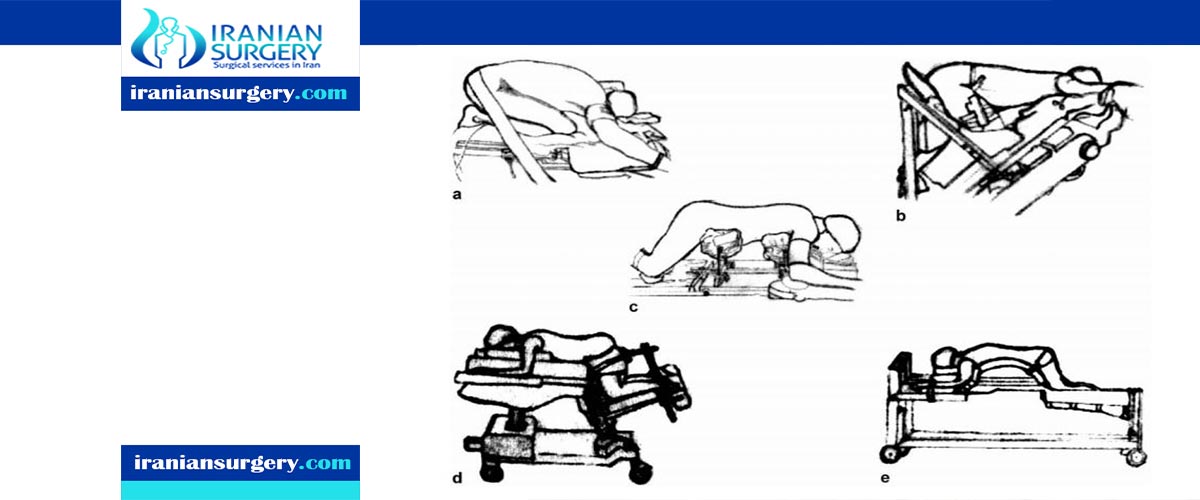
Laminectomy Surgery Positioning on Surgical Table
Positioning on the surgical table is one of the most important steps in any spinal surgical procedure. The “prone position” has traditionally been and remains the most common position used to access the dorsolumbar-sacral spine. Over the years, several authors have focused their attention on the anatomy and pathophysiology of both the vascular system and ventilation in order to reduce the amount of venous bleeding, as well as to prevent other complications and facilitate safe posterior approaches.
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Total knee replacement surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Kidney transplant in Iran success story in Iran
Read more about : Cancer treatment success story in Iran
Read more about : Sex reassignment surgery success story
The ideal position for spinal surgery should facilitate exposure, minimize both bleeding and the likelihood of damage to vital structures, and allow proper ventilation of the anesthetized patient. Additionally, it is imperative to avoid any postoperative morbidity secondary to the position during surgery.
These goals are more important, or potentially more difficult to achieve, in spinal surgery because of the deep exposures, and occasionally related difficulties, the accuracy required to identify the correct level, and the inherent risks of the various positions.
Read more about : Leg lengthening surgery success story in Iran
Read more about : Total knee replacement surgery success story in Iran
Neither supine nor lateral positioning directly affects intraoperative bleeding, because neither alters the physiology of the cardio-pulmonary system. On the contrary, a common complication of the prone position is increased bleeding, mostly due to damage to engorged vertebral veins or to excessive stretching of muscles.
This decubitus is frequently required for patients undergoing posterior spinal operations for lumbar disc herniation, fusion surgery, and surgical correction of scoliosis. The prone position is comfortable for surgeons, providing an adequate vision of both bone and neural structures. Surgical frames, kneeling attachments and special operating tables have been designed over the years to promote good prone positioning, lower intra-abdominal pressure, and reduce epidural bleeding.
Read more about: What is Ankle Arthroscopy Surgery?
Read more about: How to sleep after knee arthroscopy?
Read more about: Knee replacement surgery
Read more about: Hip Replacement Surgery
Read more about : Total knee replacement
Read more about : Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Read more about : Herniated disk treatment