dilation and curettage procedure steps in Iran

dilation and curettage procedure steps in Iran
A dilation and curettage, also called a D & C or D and C, is a minor surgery that involves dilating or opening the cervix. The cervix is the opening to your uterus or womb. After dilating your cervix, your doctor uses a spoon-shaped object called a curette to remove tissue from the inner lining of your uterus.
The procedure occurs in a doctor’s office, a women’s health clinic, a day surgery center, or a hospital.
Why is a D and C used?
There are many reasons that a doctor might order this procedure. The most common are:
to determine the reason for heavy bleeding during or between your menstrual periods
to remove noncancerous tumors, or fibroids
to remove and examine potentially cancerous tumors
to remove infected tissue, which is often caused by a sexually transmitted disease called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
to remove tissue left behind in the womb after miscarriage or childbirth
to perform an elective abortion
to remove an intrauterine device (IUD), which is a form of birth control
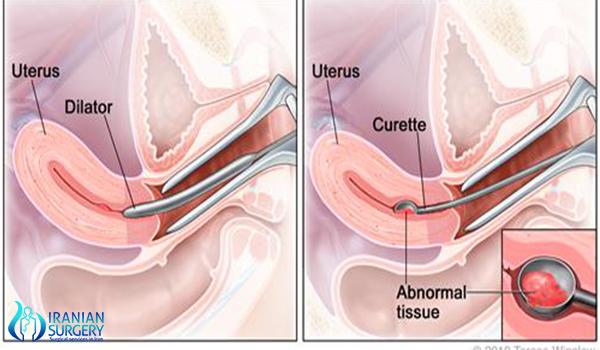
Risks
Dilation and curettage is usually very safe, and complications are rare. However, there are risks. These include:
Perforation of the uterus. Perforation of the uterus occurs when a surgical instrument pokes a hole in the uterus. This happens more often in women who were recently pregnant and in women who have gone through menopause. Most perforations heal on their own. However, if a blood vessel or other organ is damaged, a second procedure may be necessary to repair it.
Damage to the cervix. If the cervix is torn during the D&C, your doctor can apply pressure or medicine to stop the bleeding, or can close the wound with stitches (sutures).
Scar tissue on the uterine wall. Rarely, a D&C results in development of scar tissue in the uterus, a condition known as Asherman's syndrome. Asherman's syndrome happens most often when the D&C is done after a miscarriage or delivery. This can lead to abnormal, absent or painful menstrual cycles, future miscarriages and infertility.
Infection. Infection after a D&C is possible, but rare.
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following after a D&C:
Bleeding that's heavy enough that you need to change pads every hour
Light bleeding that lasts longer than two weeks
Fever
Cramps lasting more than 48 hours
Pain that gets worse instead of better
Foul-smelling discharge from the vagina
Before the dilation and curettage procedure in iran
Dilation and curettage may be performed in a hospital, clinic or your doctor's office, and it's usually done as an outpatient procedure.
Follow your doctor's instructions on limiting food and drink.
Arrange for someone to help you get home because you may be drowsy after the anesthesia wears off.
Clear your schedule to allow enough time for the procedure and recovery afterward. You'll likely spend a few hours in recovery after the procedure.
You should be able to resume your normal activities within a day or two.
In some cases, your doctor may start the process of dilating your cervix a few hours or even a day before the procedure. This helps your cervix open gradually and is usually done when your cervix needs to be dilated more than in a standard D&C, such as during pregnancy terminations or with certain types of hysteroscopy.
To promote dilation, your doctor uses a medication called misoprostol (Cytotec) — given orally or vaginally — to soften the cervix or inserts a slender rod made of laminaria into your cervix. The laminaria gradually expands by absorbing the fluid in your cervix, causing your cervix to open.
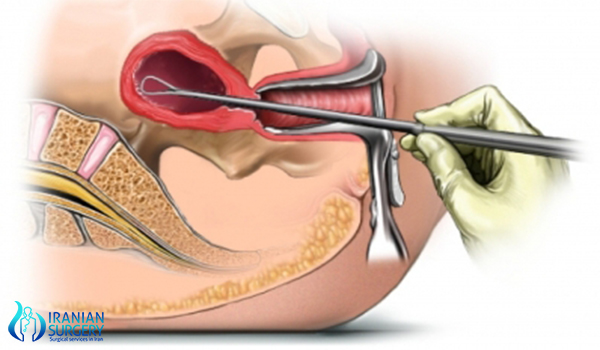
After dilation and curettage procedure
Antibiotics are given to prevent infection.
Rest quietly that day. You can do normal activities the following day, based on how you feel.
Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) or ibuprofen (such as Advil) can help relieve cramping pain. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
Medicines may be given to help the uterus contract and return to its prepregnancy size.
Do not have sexual intercourse for at least 1 week, or longer, as advised by your doctor.
When you start having intercourse again, use birth control. And use condoms to prevent infection. To learn more, see the topic Birth Control.
Ask your doctor if you can take acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) or ibuprofen (such as Advil). They may help relieve cramping pain. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
Signs of complications
Call your doctor immediately if you have any of these symptoms after an abortion:
Severe bleeding. Both medical and surgical abortions usually cause bleeding that is different from a normal menstrual period. Severe bleeding can mean:
Passing clots that are bigger than a golf ball, lasting 2 or more hours.
Soaking more than 2 large pads in an hour, for 2 hours in a row.
Bleeding heavily for 12 hours in a row.
Signs of infection in your whole body, such as headache, muscle aches, dizziness, or a general feeling of illness. Severe infection is possible without fever.
Severe pain in the belly that is not relieved by pain medicine, rest, or heat
Hot flushes or a fever of100.4°F (38°C) or higher that lasts longer than 4 hours
Vomiting lasting more than 4 to 6 hours
Sudden abdominal (belly) swelling or rapid heart rate
Vaginal discharge that has increased in amount or smells bad
Pain, swelling, or redness in the genital area
Call your doctor for an appointment if you have had any of these symptoms after a recent abortion:
Bleeding (not spotting) for longer than 2 weeks
New, unexplained symptoms that may be caused by medicines used in your treatment
No menstrual period within 6 weeks after the procedure
Signs and symptoms of depression. Hormonal changes after a pregnancy can cause depression that requires treatment.

Recovery Process: How Long Does It Take To Heal?
It’s common to feel tired and experience light cramps for a day or two after the procedure. You’ll remain in the facility a short time for observation. You won’t be able to drive immediately after the procedure. Arrange for a friend or family member to take you home.
Light bleeding is common after a D and C, so you’ll probably want to wear a menstrual pad. Don’t use a tampon because it could cause an infection. You may notice cramping for a few days. If your doctor doesn’t prescribe pain medication, ask them which over-the-counter brand will best help with your discomfort.
Even if it’s uncomfortable, get up and move around as soon as possible. This will keep your muscles strong and help prevent blood clots from forming in your legs.
You should be able to resume most of your routine within a day or two after the procedure. However, your doctor will ask you to refrain from taking a bath, douching, or having intercourse for at least three days and possibly longer.
If your doctor removes potentially cancerous tumors or materials, you’ll get a report from your doctor’s office on the laboratory findings. If the results are benign (noncancerous), you may not need a follow-up. If the results show cancerous or precancerous cells, your doctor will probably refer you to a specialist to talk about your next steps.
What is cost of D&C in Iran?
if you want to perform D&C procedure , "You pay a facility fee for where you have the procedure, you pay your doctor to do the procedure, you pay the anesthesiologist to give you anesthesia, you pay pathology to look at the tissue—the costs add up very fast.dilation and curettage cost in different countries starts from $3000,but you in Iran dilation and curettage costs starts from $430.


