How long does it take to recover from Cranioplasty?
Is a craniotomy a serious surgery?
Is Cranioplasty necessary?
What is considered a late postoperative complication following craniotomy?
Is a Cranioplasty brain surgery?
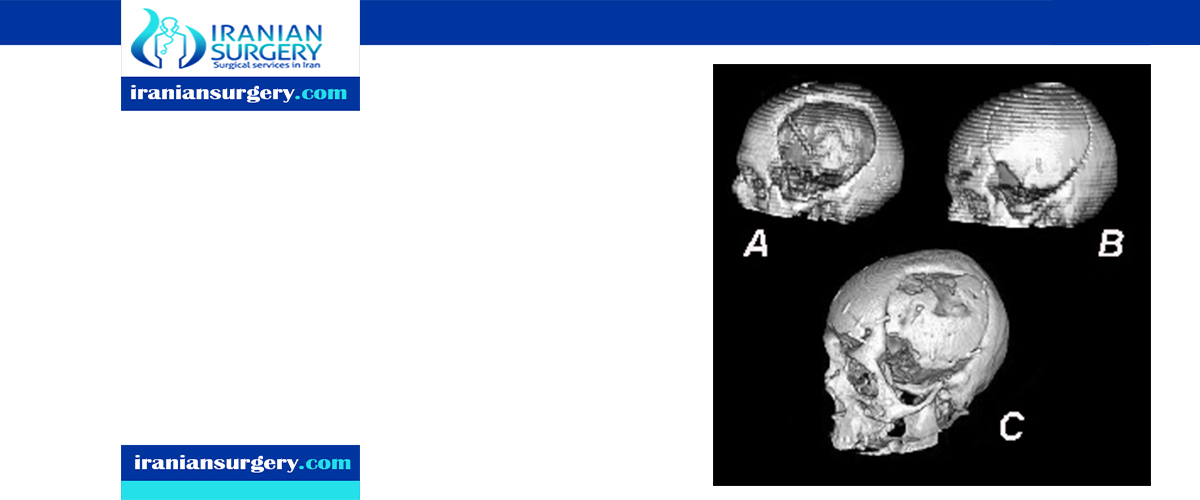
Decompressive craniectomy is a potentially life-saving procedure used in the treatment of medically refractory intracranial hypertension, most commonly in the setting of trauma or cerebral infarction. Once performed, surviving patients are obligated to undergo a second procedure for cranial reconstruction. The complications following cranial reconstruction are not well described in the literature and may very well be underreported. A review of the complications would suggest measures to improve the care of these patients.
As in the case of any surgery, you should discuss the risks with your surgeon, including (but not limited to) the following:
- Infection (which may need to be treated with antibiotics)
- Post-operative blood clot requiring drainage
- Stroke
- Seizure
- Clot in the legs (which rarely can travel to the lungs)
- Complication not related directly to the surgery:
- Pneumonia
- Heart attack
- Urinary infection
Read more about: During Cranioplasty surgery
Read more about: What size arachnoid cyst is considered large?
How long does it take to recover from Cranioplasty?
Immediately following cranioplasty, the patient will typically recover from the anesthetic in under an hour, but will need to stay in the hospital for 5-7 days. The area will be bandaged, and drains may be used to release the build-up of any fluids the body cannot naturally absorb. In some cases, external fixators are needed to help position the skull as it heals.
The sutures may usually be removed in about a week, though bandages are often removed before then. Specific instructions regarding recovery times and physical activity will be given for the particular situation. Typically, normal activities may be resumed in 2-3 weeks, providing the head is protected from accidental impacts.
Very rare complications of this procedure include infection, nerve damage, brain damage, seizures and blood clots. These will be discussed thoroughly with the patient prior to the procedure.
Read more about: craniotomy surgery
Is a craniotomy a serious surgery?
A craniotomy is a brain surgery that involves the temporary removal of bone from the skull to make repairs in the brain. It is highly intensive and comes with certain risks, which make it a serious surgery.
Read more about: Brain aneurysm treatment
Is Cranioplasty necessary?
Cranioplasty is required for protecting the brain exposed through the skull defect brain, and also for cosmetic purposes. Moreover, there is an increasing body of evidence in the recent literature, which demonstrates that cranioplasty may also accelerate and improve neurological recovery. Cranioplasty might be performed for any of the following reasons:
- Protection: In certain places, a cranial defect can leave the brain vulnerable to damage.
- Function: Cranioplasty may improve neurological function for some patients. In some instances, a customized cranial implant is designed ahead of time to help the surgeon obtain an ideal shape and outcome, as well as to house embedded neuro technologies.
- Aesthetics: A noticeable skull defect can affect a patient’s appearance and confidence.
- Headaches: Cranioplasty can reduce headaches due to previous surgery or injury.
Read more about: Endoscopic Brain Surgery
What is considered a late postoperative complication following craniotomy?
A late complication following craniectomy is the “sinking” of the skin flap over the surgical site, known as the “Sunken brain and Scalp Flap Syndrome” (SSFS) or “Motor Trephine Syndrome”.
Is a Cranioplasty brain surgery?
Cranioplasty is a surgical procedure performed to restore a defect on the cranial vault after a previous decompressive craniectomy made for traumatic brain injury, ischemic or hemorrhagic disease, or even after the removal of cranial tumors.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery after stroke