How long does cranioplasty surgery take?
Is a Cranioplasty brain surgery?
Is Cranioplasty necessary?
How long after craniotomy can you drive?
What should I avoid after brain surgery?
How long does cranioplasty surgery take?
With respect to the time of surgical procedure, most patients were operated between 61–120 minutes (69.49%, n = 164) followed by between 121–180 minutes 23.73% (n = 56), with a mean operative time of 119.51 minutes.
Read more about: Cranioplasty side effects
Is a Cranioplasty brain surgery?
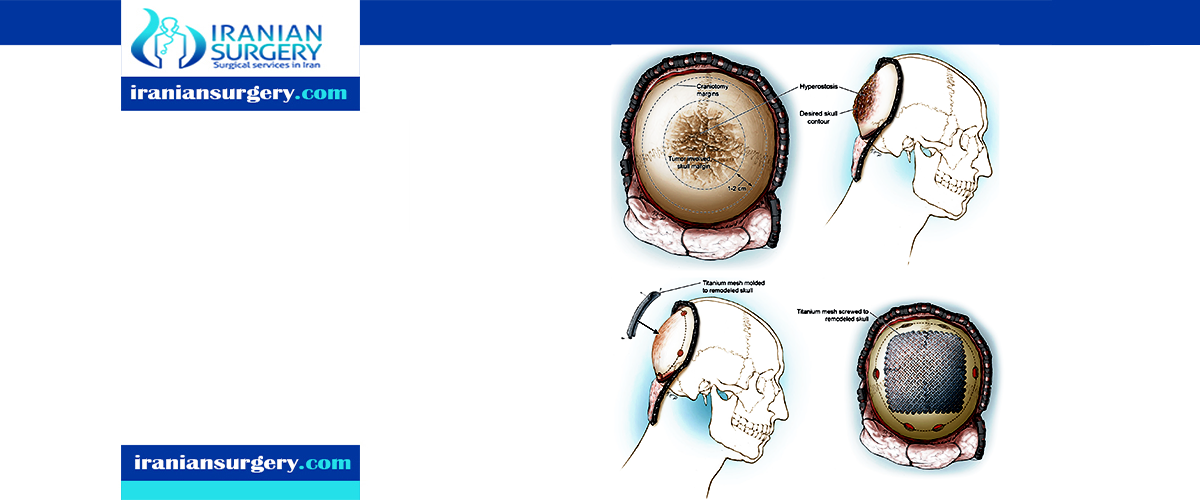
Cranioplasty is the surgical repair of a bone defect in the skull resulting from a previous operation or injury. There are different kinds of cranioplasties, but most involve lifting the scalp and restoring the contour of the skull with the original skull piece or a custom contoured graft made from material such as:
- Titanium (plate or mesh).
- Synthetic bone substitute (in liquid form).
- Solid biomaterial (prefabricated customized implant to match the exact contour and shape of the skull).
Conventional cranioplasty methods, which have been used by neurosurgeons for more than 100 years, involve peeling back all five layers of the scalp to place the bone remnant or custom implant into the proper cranial location. For the pericranial-onlay cranioplasty the surgeon gently pulls back only the three uppermost layers of the scalp and inserts the bone or implant in between the bottom layers of the scalp protecting the brain. This type of cranioplasty procedure is safer and less invasive.
Read more about: What is the average size of an arachnoid cyst?
Is Cranioplasty necessary?
Cranioplasty is a surgical procedure performed to restore a defect on the cranial vault after a previous decompressive craniectomy made for traumatic brain injury, ischemic or hemorrhagic disease, or even after the removal of cranial tumors. Cranioplasty might be performed for any of the following reasons:
- Protection: In certain places, a cranial defect can leave the brain vulnerable to damage.
- Function: Cranioplasty may improve neurological function for some patients. In some instances, a customized cranial implant is designed ahead of time to help the surgeon obtain an ideal shape and outcome, as well as to house embedded neuro technologies.
- Aesthetics: A noticeable skull defect can affect a patient’s appearance and confidence.
- Headaches: Cranioplasty can reduce headaches due to previous surgery or injury.
How long after craniotomy can you drive?
You can usually drive again after you have recovered from treatment for a pituitary tumour. If you had a type of surgery called craniotomy, you need to tell the DVLA and you need to stop driving for 6 months.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery recovery
Craniotomy recovery
A craniotomy is surgery to open your skull to fix a problem in your brain. It can be done for many reasons. For example, you may need this surgery if your brain or blood vessels are damaged or if you have a tumour or an infection in your brain.
You will probably feel very tired for several weeks after surgery. You may also have headaches or problems concentrating. It can take 4 to 8 weeks to recover from surgery.
Your cuts (incisions) may be sore for about 5 days after surgery. You may also have numbness and shooting pains near your wound. And you may have swelling and bruising around your eyes. As your wound starts to heal, it may begin to itch. Medicines and ice packs can help with headaches, pain, swelling, and itching.
The stitches that hold your incisions together may go away on their own or will be removed in 7 to 10 days. This depends on the type of stitches the doctor uses.
It is common for your scalp to swell with fluid. After the swelling goes down, you may have a dent in your head.
Some kinds of plates stay attached to hold the skull flap to your head. If your head was shaved, you may want to wear hats or scarves on your head until your hair grows back. Or it may not bother you.
You may need to go to a short-term rehabilitation centre after you leave the hospital. This can help you learn to do the tasks you need to do after you go home.
This care sheet gives you a general idea about how long it will take for you to recover. But each person recovers at a different pace. Follow the steps below to get better as quickly as possible.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery risks
What should I avoid after brain surgery?
The following top tips can help you stay healthy after brain injury:
- Keep your salt levels down
Salt is known to raise blood pressure and increase the risk of stroke. Many people with taste and smell problems add more salt than they should, so use alternatives such as lemon juice to boost flavour.
- Avoid sugary food and drink
Sugar can lead to weight gain and other health problems and can cause a ‘sugar crash’, where energy levels drop – a particular problem for people experiencing fatigue.
- Avoid caffeinated drinks
In addition to energy spikes, caffeine can have a negative effect for people who experience urinary symptoms after brain injury.
- Limit your intake of processed and fatty foods
These foods often contain high amounts of salt and sugar, tend to have lower nutritional content, and may lead to weight gain.
- Be cautious with supplements
While supplements may be necessary for some people, always speak to your doctor or dietitian before taking them as they could interfere with any medication you are taking.
Read more about: Endoscopic Brain Surgery
10 common questions about Cranioplasty surgery duration
Related Posts:
- Hip Revision Surgery
- Nose Tip Surgery
- Dimple Surgery Fail
- Why You Must Avoid Alcohol Before Surgery
- Best Surgery to Get Rid of Love Handles
- What Happens After Male to Female Surgery?
- Why Do Persians Get Plastic Surgery?
- What Is a Full Body Surgery?
- How Do I Tone My Body After Bariatric Surgery?
- Popular Plastic Surgery in The World