What is cranioplasty surgery?
Recovery of Cranioplasty
Risks of Cranioplasty
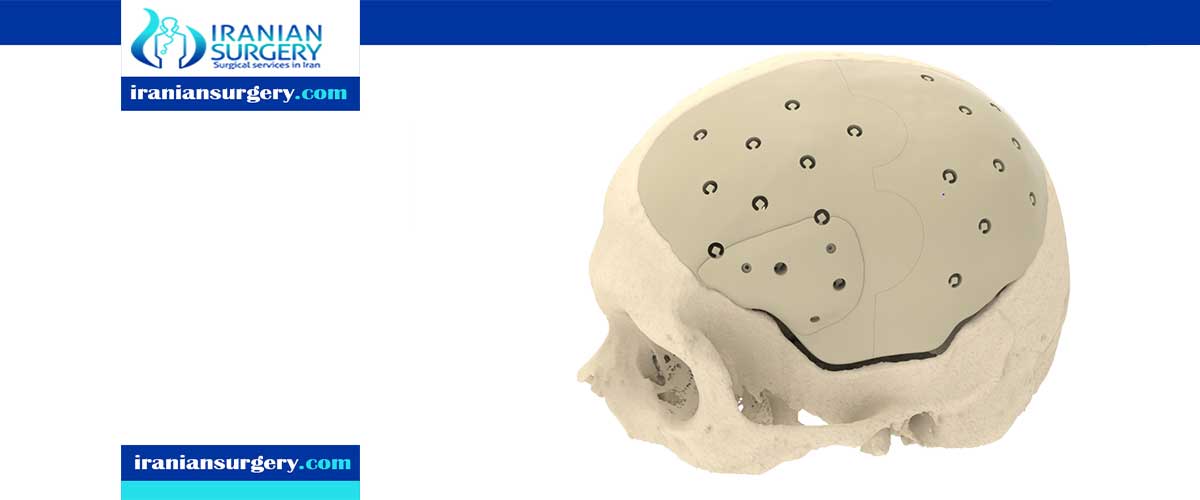
Cranioplasty is a neurosurgical procedure designed to repair or reshape irregularities or imperfections in the skull. A bone graft from elsewhere in the body or a synthetic material may be used to repair defects or gaps in the cranial (skull) bones. here are different kinds of cranioplasties, but most involve lifting the scalp and restoring the contour of the skull with the original skull piece or a custom contoured graft made from material such as
- Titanium (plate or mesh)
- Synthetic bone substitute
- Acrylic (prefabricated or molded at the time of surgery)
Read more about: Brain cancer
Read more about: Cranioplasty side effects
Read more about: Side Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
The Cranioplasty Procedure
A cranioplasty is performed in a hospital setting with the patient under general anesthetic. A portion of the scalp will be shaved and a topical cleanser is applied to prevent infection. Doctor then makes an incision in the skin to access the skull bones. If the existing bone is intact and undamaged, your doctor can reshape and reposition it and use special discs as well as titanium plates and screws to secure it in place. It is generally considered optimal to use the patient’s original bone if it remains functional. However, in cases where the bone has been badly damaged or removed, there are several options available. Prior to the surgery, it will be determined exactly what substance will be used to replace the bone. Depending on a number of factors, the surgeon may choose to graft a piece of bone that has been removed from the patient’s rib, skull or pelvis; use a bone substitute made from a synthetic material; or employ an acrylic insert that can be fitted into the defective area. All of these are attached to the nearby bones with titanium plates and screws.
What to Expect
If you don’t already have a referral, schedule an appointment with one of our cranioplasty specialists. The surgeon will examine your skull and ask questions to determine if you’re a candidate for a cranioplasty procedure. If surgery is recommended, you’ll discuss risks and potential complications of surgery and what will happen during surgery. You will receive directions on what to do prior to your surgery.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery after stroke
During Cranioplasty
During your surgery, you will receive anesthesia to avoid feeling pain. While you are unconscious, the surgical team will prepare your skull with a local anesthetic to further prevent pain.
Surgical techniques may be used to address your condition. These may include:
- Bone cement, or hydroxyapatite, may be used to smooth irregularities and fill creases of the skull.
- Autologous cranioplasty uses your own bone to restore the normal shape of the head. This bone may be taken from the skull itself, the ribs or the hip.
- An implant may be used when a large amount of skull bone needs to be replaced. These implants are created before surgery using a CT scan of your head.
- Microvascular surgery lets the surgeon bring healthy tissue from a different part of the body, place on a wounded part of the head, and connect the arteries and veins from the transplanted tissue to the existing head tissue.
- Tissue expansion places a device similar to an empty water balloon beneath the skin. This device is expanded using water and enlarges the skin, creating normal healthy skin that can be used to cover exposed bone or damaged tissue.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery recovery
Recovery of Cranioplasty
After undergoing a cranioplasty procedure, patients are typically required to stay in the hospital for a period of five to seven days. Drains may be needed initially to help the body remove any excess fluid that has accumulated in the area. Most patients will experience some headaches in the days following the surgery, but these respond well to pain relievers that will be prescribed by your doctor. Fatigue is also a common side effect that should subside within the first few weeks.
Risks of Cranioplasty
All surgical procedures carry some form of risk. The most common risks associated with a cranioplasty include infection, blood clot formation, seizures and stroke. Choosing an experienced surgeon who has performed this procedure many times can lessen the chance of developing a complication after undergoing a cranioplasty.
Read more about: Cranioplasty surgery risks
How long does cranioplasty surgery take?
With respect to the time of surgical procedure, most patients were operated between 61–120 minutes (69.49%, n = 164) followed by between 121–180 minutes 23.73% (n = 56), with a mean operative time of 119.51 minutes. The mean operative time of autologous and artificial cranioplasty was 118.34 ± 34.58 minutes and 125.25 ± 27.07 minutes, respectively (P = 0.235).
Is Cranioplasty necessary?
Cranioplasty is required for protecting the brain exposed through the skull defect brain, and also for cosmetic purposes. Moreover, there is an increasing body of evidence in the recent literature, which demonstrates that cranioplasty may also accelerate and improve neurological recovery. Cranioplasty might be performed for any of the following reasons:
- Protection: In certain places, a cranial defect can leave the brain vulnerable to damage.
- Function: Cranioplasty may improve neurological function for some patients. In some instances, a customized cranial implant is designed ahead of time to help the surgeon obtain an ideal shape and outcome, as well as to house embedded neuro technologies.
- Aesthetics: A noticeable skull defect can affect a patient’s appearance and confidence.
- Headaches: Cranioplasty can reduce headaches due to previous surgery or injury.
Read more about: During Cranioplasty surgery
Is a Cranioplasty brain surgery?
Cranioplasty, the repair of a skull vault defect by insertion of an object (bone or nonbiological materials such as metal or plastic plates), is a well-known procedure in modern neurosurgery. Brain protection and cosmetic aspects are the major indications of cranioplasty, so a craniotomy is a brain surgery that involves the temporary removal of bone from the skull to make repairs in the brain.
Read more about: Endoscopic Brain Surgery