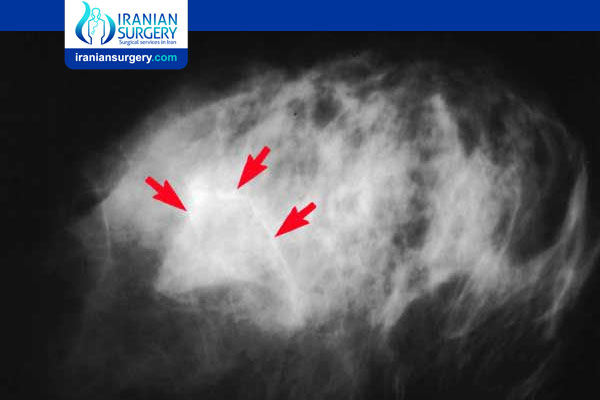
Breast Calcifications
What are Breast Calcifications?
Breast calcifications are small clusters of calcium deposits that develop in breast tissue, most commonly in women over 50. They are painless so women don’t know they have them unless they are detected by a mammogram. They are too small to feel, but can show up on a mammogram as small, bright, white spots.
While calcifications are usually harmless, they can be a sign that a woman is at risk for developing breast cancer and needs more testing. For instance, if the cluster of calcifications is tight or they are noted to present as lines of tiny calcifications, the radiologist may recommend additional mammogram images for further testing. The patient can talk to her doctor to learn more about her specific situation.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best Surgeons in Iran. The price of Breast Calcifications Treatment in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by an in-person assessment with the doctor.
For more information about the cost of Breast Calcifications Treatment in Iran and to schedule an appointment in advance, you can contact Iranian Surgery consultants via WhatsApp number 0098 901 929 0946. This service is completely free.
Before Breast Calcifications Treatment
What causes breast calcifications?
It is not known what causes calcifications to develop in breast tissue, but they are not caused by eating too much calcium or taking too many calcium supplements.
They are seen on mammograms of about half of all women over age 50. However, they also are seen in about 10 percent of mammograms on younger women. Women who have had breast surgery for any reason or who have injured their breasts, such as in a car accident, seem to be at higher risk for developing calcifications, as are women who have been treated for breast cancer in the past. Calcifications may also occur within vessels in the breast related to older age or from a past infection in the breast tissue.
What are the symptoms of breast calcifications?
Most women who have breast calcifications do not have any symptoms. They typically only learn they have them from a routine mammogram.
Are there different types of breast calcifications?
There are two types of breast calcification.
. Macrocalcifications: These appear as round and large bright white spots on a mammogram randomly scattered throughout the breast tissue. This is the most common type. They are typically not related to cancer and usually do not need follow up.
. Microcalcifications: These are smaller white spots on a mammogram. While these can be randomly scattered as well, they are sometimes grouped together and can be a sign of cancer. If your mammogram finds microcalcifications, your doctor will note any change in their appearance over time and probably order more tests.
How are breast calcifications diagnosed?
There are a number of tests that your healthcare provider can order to learn more about breast calcifications that have been found on a routine screening mammogram. These can include:
. Diagnostic mammogram: This is a more detailed mammogram than one that is done for routine screening. Pictures of the affected part of your breast may be taken from many angles to give the radiologist a closer look. This is typically the first test a doctor would order to learn more about breast calcifications. If the calcifications are benign (not cancerous), or probably benign, it is likely that the concerning calcifications are not cancer.
. Ultrasound: This is a procedure in which sound waves are used to create a picture of the breast tissue. This is noninvasive and painless. This test is usually reserved only for calcifications associated with a mass seen on a mammogram.
. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging is a more sophisticated test, using magnets and radio waves to get an even more detailed picture of the tissue. It is a painless procedure. This is not typically performed as a first-line test to evaluate calcifications. It is reserved for patients with new diagnosis of cancer to further evaluate the extent of disease.
. Ductography: This involves injecting a patient with dye to better visualize the tissue in the breast ducts. This test is only performed in patients presenting with new nipple discharge.
. Biopsy: This procedure involves using imaging to remove a small amount of breast tissue so that it can be examined by a pathologist. This can be done with a needle, or if the area that needs to be sampled is larger, a small surgical incision may be needed. Since breast calcifications are best noted on a mammogram, mammographic guidance is used for such a biopsy, which is called stereotactic biopsy of the breast.
Can I prevent breast calcifications?
Though breast calcifications cannot be prevented, early detection through a mammogram is important in treating any possible cancer that could develop.
Can a mammogram be incorrect in identifying breast calcifications?
Sometimes noncancerous lumps or cysts can be mistaken for calcifications on a mammogram, as can powders, creams or deodorants that are applied on skin near the breasts. That is why patients are asked to not wear deodorant to a mammogram, or to wipe it off before the test begins.
During Breast Calcifications Treatment
How are breast calcifications treated?
Most cases of breast calcification do not need to be treated. On any future mammograms, the radiologist can compare the images to previous ones to determine if they have changed.
If, however, one or more of the follow up tests indicate that the calcifications may be cancerous, your doctor will refer you to a doctor who specializes in cancer. The most common type of cancer to develop in conjunction with breast calcifications is ductal carcinoma in situ, often abbreviated DCIS.
As with all cancers, treatment options include closely watching the tissue to see if it changes over time, removing more of the breast tissue surgically, or undergoing chemotherapy or radiation. Each person’s decision about treatment needs to consider their own unique circumstances.
After Breast Calcifications Treatment
What do I need to do in the future if breast calcifications are found?
If breast calcifications are found during a mammogram, you may be referred to your doctor for further testing. It is important to continue routine mammograms as you age and keep discussing any concerns about breast calcifications with your doctor.
Source:
. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17802-breast-calcifications