Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms
Causes of Brachial Plexus Injury
Brachial Plexus Injuries Diagnosis
Brachial Plexus Injury Risk factors
Brachial Plexus Injury Nonsurgical Treatment
Brachial Plexus Injury Surgical Treatment
Brachial Plexus Injury Recovery
Overview
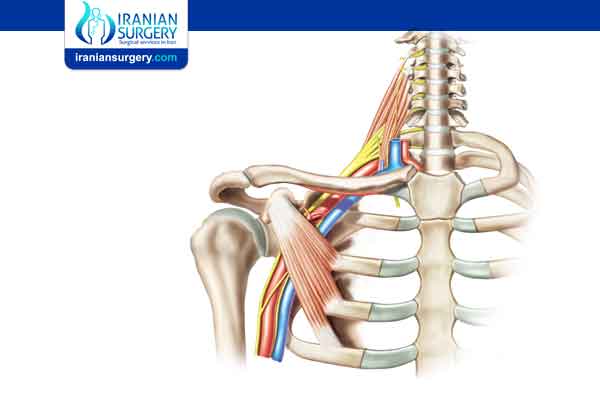
The brachial plexus is a network of intertwined nerves that control movement and sensation in the arm and hand. A traumatic brachial plexus injury involves sudden damage to these nerves, and may cause weakness, loss of feeling, or loss of movement in the shoulder, arm, or hand.
The brachial plexus begins at the neck and crosses the upper chest to the armpit. Injury to this network of nerves often occurs when the arm is forcibly pulled or stretched.
Mild brachial plexus injuries may heal without treatment. More severe injuries may require surgery to regain function of the arm or hand.
Read more about: Nonsurgical Treatments for Herniated Disc
Read more about: Manual therapy for spinal stenosis
Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Brachial plexus birth injuries are often categorized according to the type of nerve injury and the pattern of nerves involved. There are four types of nerve injuries.
Stretch (neurapraxia)
- nerve has been stretched, but not torn
- injury occurs outside the spinal cord
- most common form
- usually affected nerve(s) may recover on their own usually within first 3 months of the baby’s life
Rupture
- nerve is torn, but not where it attaches to the spine
- injury occurs outside the spinal cord
- common form
- may require surgical repair
Avulsion
- nerve roots are torn from the spinal cord
- injury occurs at the spinal cord
- less common form (roughly 10 to 20 percent of cases)
- cannot be surgically repaired directly — damaged tissue must be surgically replaced (nerve transfers)
- can injure the nerve to the diaphragm, causing difficulty with breathing
- droopy eyelid on the affected side may indicate a more severe injury, such as Horner’s syndrome
Neuroma
- nerve has tried to heal, but scar tissue has formed and presses against the injured nerve or interferes with nerve function
- may require surgical treatment with nerve reconstruction and/or secondary tendon transfers

Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms
Symptoms depend on where along the length of the brachial plexus the injuries occur and how severe they are. Injuries to nerves that root higher up on the spinal cord, in the neck, affect the shoulder. If nerves that originate lower in the brachial plexus are injured, the arm, wrist and hand are affected.
Common symptoms of brachial plexus injuries are:
- Numbness or loss of feeling in the hand or arm.
- Inability to control or move the shoulder, arm, wrist or hand.
- An arm that hangs limply.
- Burning, stinging or severe and sudden pain in the shoulder or arm.
Brachial plexus injury pain can be mild to severe, and temporary to chronic, depending on the type and extent of the injury. For instance, a simple stretched nerve may hurt for a week or so, but a ruptured nerve can cause serious, long-term pain that might require physical therapy and potentially surgery.
Read more about: spinal disc herniation
When to see a doctor
Brachial plexus injuries can cause permanent weakness or disability. Even if yours seems minor, you may need medical care. See your doctor if you have:
- Recurrent burners and stingers
- Weakness in your hand or arm
- Neck pain
- Symptoms in both arms
Read more about: Benign spinal tumor treatment
Causes of Brachial Plexus Injury
Damage to the upper nerves that make up the brachial plexus tends to occur when your shoulder is forced down while your neck stretches up and away from the injured shoulder. The lower nerves are more likely to be injured when your arm is forced above your head.
These injuries can occur in several ways, including:
- Contact sports. Many football players experience burners or stingers, which can occur when the nerves in the brachial plexus get stretched beyond their limit during collisions with other players.
- Difficult births. Newborns can sustain brachial plexus injuries. These may be associated with high birth weight, breech presentation or prolonged labor. If an infant's shoulders get wedged within the birth canal, there is an increased risk of a brachial plexus palsy. Most often, the upper nerves are injured, a condition called Erb's palsy.
- Trauma. Several types of trauma — including motor vehicle accidents, motorcycle accidents, falls or bullet wounds — can result in brachial plexus injuries.
- Tumors and cancer treatments. Tumors can grow in or along the brachial plexus, or put pressure on the brachial plexus or spread to the nerves. Radiation treatments to the chest may cause damage to the brachial plexus.
Read more about: Spinal Tumor surgery
Brachial Plexus Injuries Diagnosis
A health care provider will examine the hand and arm and test for sensation and function to help diagnose a brachial plexus injury.
These are other diagnostic tests often used:
- An X-ray of the neck and shoulder area to identify fractures or other injuries to the bone and dense tissues around the nerves of the brachial plexus.
- Imaging tests, such as MRI or a CT scan, during which contrast dye may be injected to show the injury to the nerves of the brachial plexus.
- Tests that use needle electrodes to determine nerve function and electrical activity, including a nerve conduction study and electromyogram.
These tests may be repeated every few weeks or months to allow your doctor to monitor your progress.
Read more about: Spinal Fusion Surgery
Brachial Plexus Injury Risk factors
Participating in contact sports, particularly football and wrestling, or being involved in high-speed motor-vehicle accidents increases your risk of brachial plexus injury.
Complications
Given enough time, many brachial plexus injuries in both children and adults heal with little if any lasting damage. But some injuries can cause temporary or permanent problems, such as:
- Stiff joints.If you experience paralysis of your hand or arm, your joints can stiffen. This can make movement difficult, even if you eventually regain use of your limb. For that reason, your doctor is likely to recommend ongoing physical therapy during your recovery.
- This results from nerve damage and may become chronic.
- If you lose feeling in your arm or hand, you run the risk of burning or injuring yourself without knowing it.
- Muscle atrophy.Nerves regrow slowly and can take several years to heal after injury. During that time, lack of use may cause the affected muscles to break down.
- Permanent disability.How well you recover from a serious brachial plexus injury depends on a number of factors, including your age and the type, location and severity of the injury. Even with surgery, some people experience permanent muscle weakness or paralysis.
Read more about: Cervical spinal stenosisTop of Form
Brachial Plexus Injury Nonsurgical Treatment
Many injuries to the brachial plexus will recover spontaneously without surgery over a period of weeks to months, especially if they are mild. Nerve injuries that heal on their own tend to have better functional outcomes. If your doctor believes that the injury has a good potential for recovery without surgery, he or she may delay procedures and simply monitor your injury.
The process of the nerve healing itself takes time and your doctor may recommend physical therapy to prevent joint and muscle stiffness.
Read more about: Can spinal tumors be cured?
Brachial Plexus Injury Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment is typically recommended when the nerves fail to recover on their own or fail to recover enough to restore necessary function to the arm and hand. It is important to note that depending upon the severity of the injury, even surgery may not be able to return the arm or hand to preinjury abilities.
Considerations
- Recovery. During your discussion with your doctor, it will be important to set realistic goals and expectations for surgical treatment. Nerves heal slowly. The recovery period after surgery is often long, and requires a strong commitment to a comprehensive rehabilitation program to restore physical abilities. This is something that should be considered in making the decision to proceed with surgery.
- Candidates for surgery.Although brachial plexus surgery can help to restore function in many patients, there are some factors that prevent a patient from being a candidate for surgery, most importantly, unrealistic expectations. Other factors include having joint stiffness and contractures, advanced age, additional injuries or medical conditions, traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injury. Your doctor will discuss with you whether you are a candidate for surgery.
- It is possible that surgical treatment will not restore desired movement or that the surgical wound may become infected. Both of these outcomes could require further surgery. In addition, patients with pre-existing medical problems have additional potential risks related to any large reconstructive surgery, including chronic pain, blood clots, heart attack, stroke, and even death.
Read more about: Spinal stenosis treatment
Surgical Procedures
Several surgical techniques are used to treat nerve injury, depending upon the type of injury and the length of time that has passed since the injury.
In most procedures, an incision is made near the neck above the collarbone. If the injury extends down the brachial plexus, another incision at the front of the shoulder may be required. To repair or reconnect nerves, surgeons often use high-powered microscopes and small, specialized instruments.
- Nerve repair.In this procedure, the surgeon reattaches the two torn edges of a severed nerve. Nerve repair is typically performed immediately for sharp lacerations to the nerves, such as in a knife wound.
- Nerve graft. Nerve grafting is a procedure in which a healthy nerve taken from another part of the body is sewn in between the two ends of a lacerated nerve. The transplanted nerve acts as a scaffold to support the injured ends as they regenerate and grow back together. Nerve grafting can only be performed if there is a functioning nerve stump at the spinal cord to conduct a nerve signal. The goal is for the transplanted nerve to guide nerve regrowth and to ultimately restore nerve signals to power the paralyzed muscles.
- Nerve transfer.A nerve transfer procedure is used when there are no functioning nerve stumps in the neck to which nerve grafts can be connected. In this procedure, a healthy donor nerve is cut and reconnected to the injured nerve to provide a signal to a paralyzed muscle. In many cases, the healthy nerve is connected closer to the affected muscle. In other cases, the healthy nerve is connected to the damaged nerve within the brachial plexus.
- Tendon and muscle transfers.Patients who delay that first visit to the doctor for more than 12 months after injury tend to have poor outcomes with surgery to reconstruct nerves. These patients are managed better with surgery that focuses on reconstructing the tendon (tendon transfer) or muscle (free-functioning muscle transfer).
A tendon transfer is a type of surgery in which the tendon of a functioning muscle is cut and sewn into a nonfunctioning muscle tendon to restore a specific motion or motor function.
In a free-functioning muscle transfer, a muscle from one part of the body is moved to the injured area, along with its tendon, artery, vein, and nerve. Each of these structures is connected to the corresponding structures of the injured area in order to restore motion or motor function.
Brachial Plexus Injury Recovery
The patient must do several things to keep up muscle activity and prevent the joints from getting stiff. Your doctor may recommend therapy to keep these joints flexible. If the joints become stiff, they will not move even after muscles begin to work again, like a hinge that has rusted.
When a sensory nerve has been injured, the patient must be extra careful not to burn or cut fingers while there is no feeling in the affected area. During nerve recovery, the brain may not interpret the new nerve signals properly, and a procedure called sensory re-education may be needed to optimize muscle control and feeling in the hand or fingers. Your doctor will recommend the appropriate therapy based on the nature of your injury.
Factors that may affect results after a brachial plexus injury include patient age and the type, severity and location of the injury. Though these injuries will result in lasting problems for the patient, care by a hand surgeon and proper therapy can maximize function.
Read more about: Spinal cord injury