what is considered a large arachnoid cyst?
What is considered a large arachnoid cyst?
Do arachnoid cysts require surgery?
What is considered a large arachnoid cyst?
An arachnoid (pronounced ah-RACK-noid) cyst is a sac filled with fluid inside the head or spine. Arachnoid cysts develop between the brain or spinal cord and a membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord, called the arachnoid membrane. The fluid in the cyst often is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a clear liquid that protects and nourishes the brain and spinal cord.
Read more about: Arachnoid cyst treatment in Iran
Arachnoid cysts are more common inside the head than around the spinal cord. In a child’s head, an arachnoid cyst can be between the brain and the skull or inside the brain. Arachnoid cysts in the brain form in open spaces called ventricles that normally contain CSF.
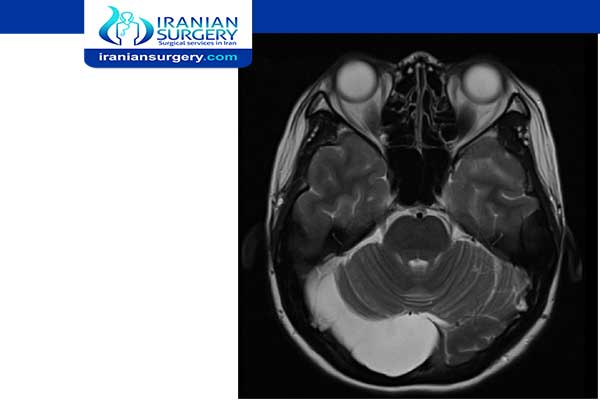
What is a large arachnoid cyst?
Arachnoid cysts are found in many parts of the brain. Most are in the middle or back of the brain. Large arachnoid cysts are often symptomatic because they compress surrounding structures; therefore, they must be treated surgically.
Read more about: arachnoid cyst treatment without surgery
Do arachnoid cysts require surgery?
Most arachnoid cysts are stable and do not require treatment. The rupture of the cyst wall appears to be essential for the arachnoid cyst to disappear. After rupture, subdural effusion must develop around the cyst. As this effusion is absorbed, the fluid in the cyst drains away, after which the cyst becomes smaller and gradually disappears.
Read more about: Arachnoid cyst size chart
10 common questions about what is considered a large arachnoid cyst
[kkstarratings]


