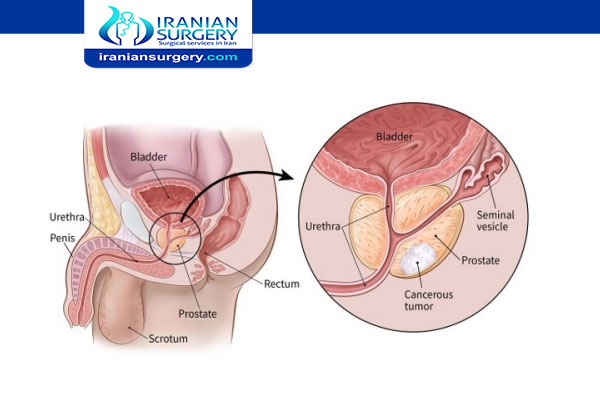
Prostate Cancer Treatments Pros and Cons
Types of Prostate Cancer Treatment
- Active Surveillance / Watchful Waiting
- Biologic Therapy / Immunotherapy
- Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation Therapy)
- Chemotherapy
- Cryosurgery (Cryotherapy)
- Cyberknife
- Da Vinci Robotic Prostatectomy/Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (RALRP).
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
- High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
- Hormone Therapy (Androgen deprivation/suppression)
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (LRP)
- Radical Perineal Prostatectomy (Open)
- Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy (Open)
Read more about : Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Signs a fissure is healing
Read more about : Arachnoid cyst size chart
Prostate Cancer Treatments Pros and Cons
Prostate Cancer Treatments Advantages and Disadvantages
- Active Surveillance / Watchful Waiting
Non-Treatment; Continued monitoring of Prostate Cancer through PSA blood tests, DREs, and ultrasound scans. Biopsies may be done as well to assess the aggressiveness of the prostate cancer.
Recommended For:
. PSA below 10
. Gleason Score below 7
. No symptoms
. Prostate Cancer that is expected to grow slowly (based on Gleason score)
. Small, contained cancer within the prostate
. Those with life expectancy less than 10 years, older in age, or have other serious health problems.
Pros of Active Surveillance / Watchful Waiting
. No surgery
. No hospitalization
. No direct side-effects
. Modern Technology and New Imaging allow for more accurate monitoring
Cons of Active Surveillance / Watchful Waiting
. Less proactive, wait-and-see approach
. Requires frequent follow-ups with doctors which may include PSA blood test and Digital Rectal Exams (DRE) every 3 to 6 months and Trans rectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsies once a year.
. Allows cancer to get worse and spread which may result in limiting treatment options and ultimately affect the chances of curing the cancer.
. May lead to further treatment if prostate cancer begins to grow or get worse
. Can create psychological stress
- Biologic Therapy / Immunotherapy
Biological substances made in a lab or by the body are used to boost the immune system to enhance the body’s ability to repair itself and prevent the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. Provenge is the first FDA approved Immunotherapy treatment and vaccine.
Read more about : Donating a testicle pros and cons
Read more about : Pros and cons of deviated septum surgery
Read more about : 5 essential secrets growing male breasts
Recommended For:
. Men with advanced, metastatic hormone resistant prostate cancer without any symptoms.
. Men who have not had success with other treatments
. Men who have had hormonal therapy
. Men with elevated PSA levels
Pros of Biologic Therapy / Immunotherapy
. Minimally invasive procedure
. Boosts immune system
. Helps to identify prostate cancer cells
. Can help change how prostate cancer cells behave
. Can help change how prostate cancer cells behave
. Can be performed in a hospital or at home
. Reduced toxicity
Cons of Biologic Therapy / Immunotherapy
. Fatigue
. Nausea
. Dizziness
. Appetite suppression
. Allergic reactions may develop
. Some cannot continue treatment
- Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation Therapy)
Also known as implantation or interstitial radiation therapy, where small radioactive pellets (or “seeds”) the size of a grain of rice are placed directly into the prostate. Permanent Brachytherapy (low dose rate) inserts radioactive (iodine-125 or palladium-103) pellets directly into the prostate with the use of a needle by going through the skin in the area between the anus and the scrotum. These low doses of radiation are release for weeks or months depending on the case.
Typically, 40 to 100 of these radioactive seeds are placed and left in the prostate until the radioactive material has been completely dissolved. Temporary Brachytherapy (high dose rate) delivers radioactive iridium-192 or cesium-137 through catheters and are kept in place for 5 to 15 minutes. The radioactive pellets are removed after each treatment and the catheters are removed after the final treatment.
Recommended For:
. Men with lower Gleason scores
. Men with prostate cancer in the earlier stages
. Men with relatively slow-growing prostate cancer
. Men healthy enough for surgery
Pros of Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation Therapy)
. One-time procedure
. Minimally invasive
. No surgical risks
. No hospital stays
. Most of the radiation is concentrated in the prostate
. Little to no damage to the tissue around the prostate (nerves, bladder, rectum).
Cons of Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation Therapy)
. May be forced to stay away from children and pregnant women due to the internal radiation.
. May be forced to strain urine in case of pellets moving
. Can cause bowel, urinary, and erectile issues
. No staging information after treatment
- Chemotherapy
Anti-cancer drugs are taken orally or injected into a vein and enter the bloodstream then spread throughout the body to stop the growth of prostate cancer cells by killing them or restricting their division to other parts of the body.
Recommended For:
. Men with prostate cancer that has spread outside of the prostate gland and through the body.
. Men for whom hormone therapy is not working
Pros of Chemotherapy
. Can slow down the growth of the prostate cancer
. Can reduce symptoms
Cons of Chemotherapy
. Hair loss
. Mouth sores
. Diarrhea
. No staging information after treatment
. Nausea and vomiting
. Loss of appetite
. Increased odds of infections
. Fatigue
. Easy bruising/bleeding
- Cryosurgery (Cryotherapy)
Also known as cryoablation, transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is used to guide multiple needles directly into the prostate through the skin between the anus and scrotum. Extremely cold gases are then sent through the needles, which then create ice balls that freeze and destroy the prostate. Warming catheter is inserted into the urethra to protect it from the freezing temperatures. Spinal, epidural, or general anesthesia is required.
Read more about Virgin tightening surgery before and after
Recommended For:
. Men older in age
. Men in early stages with early stages of cancer
. Men whose prostate cancer is confined
. Men who are not responding to standard treatments
. Men whose radiation therapy has failed
. Men who can’t tolerate surgery or radiation
Pros of Cryosurgery (Cryotherapy)
. Can slow down the growth of the prostate cancer
. Can reduce symptoms
Cons of Cryosurgery (Cryotherapy)
. Catheter needed for about 3 weeks
. Possible blood in the urine after surgery for a couple of days
. Freezing can lead to pain or burning sensations in the bladder and intestines
. Possible damage to nerves near the prostate due to freezing that can cause higher probability of erectile dysfunction.
- Cyberknife®
A form of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) that delivers high doses of radiation directly to the cancerous prostate by the use of a robotic arm that moves around the body. Using the guidance of real-time imaging to automatically adjust to the movement of the prostate, the Cyberknife system accurately and continuously targets the prostate during each treatment.
Recommended For:
. Men with low-risk to intermediate-risk prostate cancer
Pros of Cyberknife®
. Non-invasive and non-surgical procedure
. No incision
. No pain
. No anesthesia or hospitalization
. Little to no recovery time
Cons of Cyberknife®
. 4-5 treatments
. Possible mild fatigue and nausea
. Temporary urinary frequency
. Limited history and medical data of side effects and true effectiveness
- Da Vinci Robotic Prostatectomy/Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (RALRP)
Surgery is performed by a trained and skilled surgeon through the use of a computer-enhanced robotic surgical system positioned near the operating table. The Da Vinci Robotic surgical system is made up of three major components, which include a vision system with high magnification and resolution, robotic arms and instruments, and a console to provide the surgeon with a view of the operative field and control the instruments.
Recommended For:
. Men healthy enough for surgery
. If prostate cancer has been confined in the prostate (Stage T1 or T2 cancer)
Read more about side effects of having only one testicle
Read more about rectal bleeding
Read more about Laser Eye Surgery in Iran
Pros of Da Vinci Robotic Prostatectomy
. Proven to reduce prostate cancer death rates
. PSA levels help to reliably predict possible recurrences
. Little to no blood loss
. Less pain
. Shorter recovery times
. Shorter hospitalization (1-2 days)
. Catheter removed in just 5-7 days
. More maneuverability and precision for the robotic surgeon
. More visibility of prostate and surrounding tissue/organs
. Prostate cancer is removed with a higher cancer cure rate when performed by a skilled robotic surgeon.
Cons of Da Vinci Robotic Prostatectomy
. Possible erectile and urinary side effects post-surgery when the procedure is performed by a less-skilled and inexperienced surgeon.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
The prostate gland is targeted with beams of radiation (x-rays or proton) from a machine outside of the body. EBRT is a three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) which creates a precise map of the location of your prostate through the use of special computers. Then from several directions, shaped radiation beams are focused at the prostate. A fitted plastic mold will be created to ensure you are in the same position for each treatment session.
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) uses a machine that moves around the patient while it targets and delivers radiation. The doctor can adjust the intensity of radiation with this machine. New computer-driven radiation machines have imaging scanners and this form of treatment is called image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT).
Recommended For:
. Men with prostate cancer in its earlier stage
. Men with cancer outside of the prostate gland
. Men who are not healthy enough for surgery
. Men over the age of 70
. Men who need help relieving bone pain
Pros of External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
. No incisions
. No hospitalization
. No anesthesia
. Painless procedure
. Activities unrestricted
. Very little side effects immediately after treatment
Cons of External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
. Increased tiredness or fatigue due to radiation
. Requires frequent treatments (up to 5 days a week for about 7 to 9 weeks)
. Can cause rectal soreness
. Higher probability of developing erectile dysfunction, bladder, or urinary problems (radiation cystitis, incontinence) that can worsen over time.
. Can cause bowel problems due to radiation (radiation proctitis)
. No staging information after treatment
- High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
Precision-focused ultrasound waves are used to heat and destroy the targeted prostate cancer tissue. It is performed on an outpatient basis and can be repeated as necessary with each treatment taking anywhere from 1 to 3 hours.
Recommended For:
. Men with localized prostate cancer
. Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
. Men with Gleason scores 6 and below
Pros of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
. Non-invasive procedure
. Surrounding healthy tissue is not damaged
Cons of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
. Possible incontinence
. Urinary issues due to scarring of the prostate
. Chances of erectile dysfunction
. Blood in the urine
. Limited information as it is a newer form of treatment
- Hormone Therapy (Androgen deprivation/suppression)
Also called ADT, the levels of male hormones (or androgen) are reduced in the body to stop the growth of prostate cancer cells.
Recommended For:
. Men with advanced or high-grade prostate cancer
. Men whose prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate and are no longer candidates for surgery or radiation.
. Men with recurring prostate cancer
Pros of Hormone Therapy (Androgen deprivation/suppression)
. Can help stop the growth and/or spread of cancer in the prostate
. Can shrink an enlarged prostate
Cons of Hormone Therapy (Androgen deprivation/suppression)
. Can lead to erectile dysfunction
. Can cause osteoporosis
. Loss of libido
. Decrease in muscle mass
. Hot flashes
. Breast enlargement
. Decreased mental acuity
. Blood in the urine
. Depression
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (LRP)
Several small incisions are made and the prostate is removed through the use of special long medical instruments. These tools vary in use, as one will have a tiny camera on the end to allow the surgeon to see inside of the abdomen.
Recommended For:
. Men healthy enough for surgery
. If prostate cancer is confined to the prostate (Stage T1 or T2 cancer)
Pros of Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (LRP)
. Minimal blood loss
. Less pain
. Shorter hospital stays
. Faster recovery time
. Removed tissue allows for accurate staging of cancer
Cons of Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (LRP)
. Increased risk of incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and bowel issues if performed by an inexperienced surgeon.
- Radical Perineal Prostatectomy (Open)
An incision is made in the skin between the anus and scrotum (perineum) and the prostate is removed.
Recommended For:
. Men healthy enough for surgery
. Men whose medical conditions restrict them from Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy.
. If prostate cancer is confined to the prostate (Stage T1 or T2 cancer)
Pros of Radical Perineal Prostatectomy (Open)
. Removes the cancerous prostate and can cure you of prostate cancer if surgery is performed correctly.
. Shorter operation
Cons of Radical Perineal Prostatectomy (Open)
. Hospitalization required
. Catheter required for up to 2 weeks during recovery
. Limited activity for up to 5 weeks
. More likely to lead to erectile dysfunction
. Can lead to other medical conditions
- Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy (Open)
An incision is made in the lower abdomen from the belly button to the pubic bone and the entire prostate is removed along with nearby tissues and seminal vesicles. Lymph nodes may also be removed based on the PSA level, DRE, and biopsy results. If cancer cells are found in lymph nodes during surgery, the operation may be cancelled, as surgery alone will not cure the patient. General, spinal, or epidural anesthesia is required.
Recommended For:
. Men healthy enough for surgery
. If prostate cancer is confined to the prostate (Stage T1 or T2 cancer)
Pros of Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy (Open)
. Removes the cancerous prostate and can cure you of prostate cancer if surgery is performed correctly.
Cons of Radical Perineal Prostatectomy (Open)
. Hospitalization required
. Catheter required for up to 2 weeks during recovery
. Limited activity for up to 5 weeks