Implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery (ICD)
Defibrillator surgery
Before implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery
Who is the candidate for ICD implantation of the heart?
How long does defibrillator surgery take?
Is getting a defibrillator a major surgery?
Are you awake during ICD surgery?
During the implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery in Iran
After the implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery (ICD) in Iran
Treating pain after your procedure in Iran
Battery life
Living with an ICD
What is the difference between a pacemaker and a defibrillator?
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery (ICD) in Iran
ICD is a battery-powered device that is placed under the skin to track a person's heart rate. ICD thin wires attach to the heart and, if an abnormal heart rate is detected, the device produces an electric shock to restore normal heart rate. The new generation of ICDs also have dual function including the ability to act as a pacemaker. This characteristic can stimulate the heart to beat in cases where the previous beat is drastically reduced.
ICDs are very effective in preventing sudden death in patients with stable and well-known tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Studies have also shown that ICDs are helpful in preventing myocardial infarction in patients at risk for ventricular arrhythmias.
Read more about : Heart pacemaker surgery
Read more about : Closed heart surgery
Read more about : Heart Bypass Surgery
Read more about : Open heart surgery
Read more about : Angiography in Iran
Defibrillator surgery
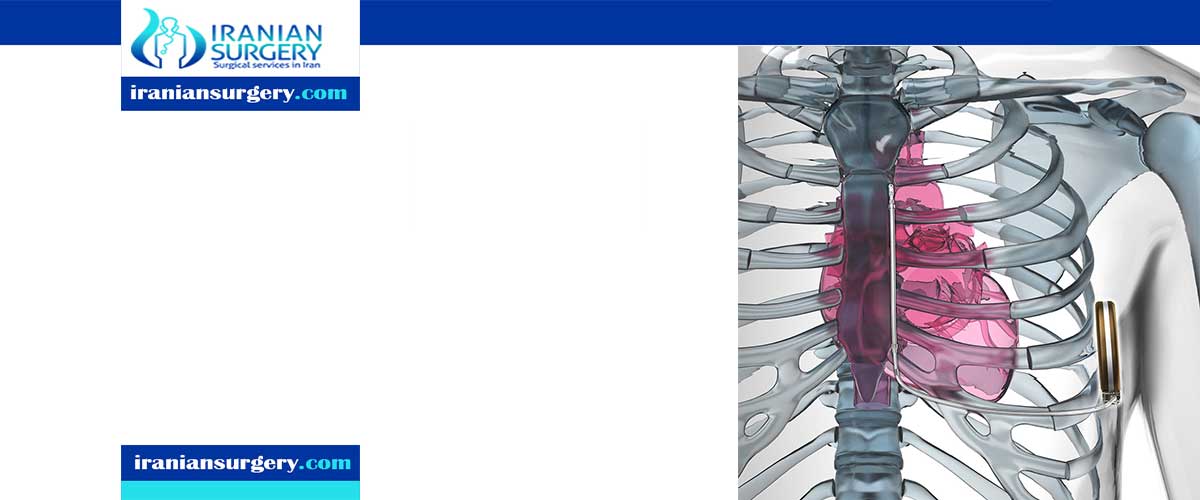
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is a small battery-powered device placed in your chest to monitor your heart rhythm and detect irregular heartbeats, Defibrillators usually are implanted through small incisions in the skin, near the collarbone.
Before implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery
How you prepare for implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery?
To determine whether you need an ICD, your doctor might perform a variety of diagnostic tests, which may include:
- Electrocardiography (ECG). In this noninvasive test, sensor pads with wires attached (electrodes) are placed on your chest and sometimes limbs to measure your heart's electrical impulses. Your heart's beating pattern can offer clues to the type of irregular heartbeat you have.
- Echocardiography. This noninvasive test uses harmless sound waves that allow your doctor to see your heart without making an incision. During the procedure, a small, plastic instrument called a transducer is placed on your chest.
It collects reflected sound waves (echoes) from your heart and transmits them to a machine that uses the sound wave patterns to compose images of your beating heart on a monitor. These images show how well your heart is functioning, and recorded images allow your doctor to measure the size and thickness of your heart muscle.
- Holter monitoring. Also known as an ambulatory electrocardiogram monitor, a Holter monitor records your heart rhythm for 24 hours. Wires from electrodes on your chest go to a battery-operated recording device carried in your pocket or worn on a belt or shoulder strap.
While wearing the monitor, you'll keep a diary of your activities and symptoms. Your doctor will compare the diary with the electrical recordings and try to figure out the cause of your symptoms.
- Event recorder. Your doctor might ask you to wear a pager-sized device that records your heart activity for more than 24 hours. Unlike a Holter monitor, it doesn't operate continuously you turn it on when you feel your heart is beating abnormally.
- Electrophysiology study (EPS). Electrodes are guided through blood vessels to your heart and used to test the function of your heart's electrical system. This can identify whether you have or might develop heart rhythm problems.
It's likely you'll be asked not to eat or drink for at least eight hours before your surgery. Talk to your doctor about the medications you take and whether you should continue to take them before your procedure to implant an ICD.

Read more about : What are the types of heart arrhythmia?
Read more about : Heart attack causes
Read more about : Angiogram procedure
Read more about : Echocardiogram
Who is the candidate for ICD implantation of the heart?
The American Heart Association recommends that before arriving as a candidate for cardiac ICD, the arrhythmia must be threatening and dangerous and the physician has rejected the correctable causes of arrhythmia, including:
- Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle)
- Electrolyte abnormalities and drug poisoning
Because many patients are unaware of background conditions such as heart failure or genetic susceptibility to the risk of sudden heart attack, and also because ICDs are primarily used to prevent sudden myocardial infarction, assessing the benefits and comparisons thereof. It is incomprehensible with the limitations of ICD implantation.
It may be important for you to know that ICD will not alter the terrestrial conditions that led to ICD implantation. Whether under conditions of heart failure or genetic risks of sudden heart attack, ICD can be used to prevent sudden heart attack. While using ICD does not lead to reversal of heart disease or altered genes, it can reduce the risk of heart attack. However, you should follow your doctor's instructions for treating ground conditions.
How long does defibrillator surgery take?
The device implant procedure may last from 2 to 4 hours. If the doctor only has to change the generator battery, the procedure may only take 1 to 2 hours.
Is getting a defibrillator a major surgery?
The procedure to implant a defibrillator does not require open heart surgery, and most people go home within 24 hours. Before the surgery, medication may be given to make you sleepy and comfortable. Generally, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Read more about: Types Of Heart Surgery
Are you awake during ICD surgery?
You'll likely be awake during ICD surgery, which typically takes a few hours. You'll have an intravenous line placed, through which you might receive medication to help you relax. Most pacemaker implantations are done using local anesthesia to numb the area of incisions.
Read more about: Heart transplantation
During the implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
Usually, the procedure to implant an ICD can be performed with numbing medication and a sedative that relaxes you but allows you to remain aware of your surroundings. In some cases, general anesthesia, which puts you to sleep, may be used.
The procedure usually takes a few hours. During surgery, one or more flexible, insulated wires (leads) are inserted into veins near your collarbone and guided, with the help of X-ray images, to your heart. The ends of the leads are secured to your heart, while the other ends are attached to the generator, which is usually implanted under the skin beneath your collarbone.
Once the ICD is in place, your doctor will test it and program it for your heart rhythm problem. Testing the ICD might require speeding up your heart and then shocking it back into normal rhythm.
Read more about : Heart valve replacement recovery?
Read more about : How long is heart valve replacement surgery?
After the implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery (ICD) in Iran
You'll stay in the hospital one or two days, and the ICD might be tested once more before you're discharged. Additional testing of your ICD usually doesn't require surgery.
Treating pain after your procedure in Iran
After surgery, you may have some pain in the incision area, which can remain swollen and tender for a few days or weeks. Your doctor might prescribe pain medication. As your pain lessens, you can take no aspirin pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others).
Unless your doctor instructs you to do so, don't take pain medication containing aspirin because it can increase bleeding risk.
When you're released from the hospital, you'll need to arrange for a ride home because you won't be able to drive for at least a week.
implantable cardioverter defibrillator Risks in Iran
Possible risks of ICD insertion include:
- Bleeding from the incision or catheter insertion site
- Damage to the blood vessel at the catheter insertion site
- Infection of the incision or catheter site
- Tearing of the heart muscle
- Collapsed lung
- Dislodging of the leads requiring another procedure to reposition the leads
If you are pregnant or think that you could be, or are currently breastfeeding, tell your healthcare provider.
If you are allergic to or sensitive to any medicines or latex, tell your healthcare provider.
Lying still on the procedure table for the length of the procedure may cause some discomfort or pain.
There may be other risks depending on your specific medical condition. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before the procedure.
Battery life
The lithium battery in your ICD can last up to seven years. The battery will be checked during regular checkups, which should occur every three to six months. When the battery is nearly out of power, your old shock generator is replaced with a new one during a minor outpatient procedure
Living with an ICD
Take the following precautions when you have an ICD implanted.
- Always carry an ID card that states you have an ICD. In addition, you may want to wear a medical ID bracelet showing that you have an ICD.
- If you travel by air, inform security screeners that you have an ICD before going through the metal detector. (It may help to say you have a pacemaker – which is true as pacemaker functions are built into ICDs – because security may not know what an ICD is.) In general, airport security detectors are safe for pacemakers and ICDs, but the small amount of metal in the device and leads may trigger the alarm. If you are selected for additional screening, politely remind the screener that the security wand contains a magnet, which may interfere with the programming or function of the ICD (pacemaker) if it is held over the device for more than a few seconds.
- Anti-theft systems or electronic article surveillance (EAS) used in department stores may interact with an ICD. Do not lean on or stand in this equipment. But it is OK to pass quickly through the detection system.
- Avoid large magnetic fields such as power generation sites and industrial sites, such as automobile junkyards that use large magnets.
- If an MRI has been recommended for you, contact your doctor. Some newer ICDs are compatible with MRI scanners with some restrictions.
- Do not use diathermy (the use of heat in physical therapy to treat muscles). Do not use a heating pad directly over your ICD.
- Avoid transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy. Talk to your doctor if you are considering this treatment.
- Turn off large motors, such as cars or boats, when working on them as they may create a magnetic field.
- Avoid high-voltage and radar machinery, such as radio or television transmitters, electric arc welders, high-tension wires, radar installations, or smelting furnaces.
- If you are scheduled for surgery, let the surgeon know well ahead of the operation that you have an ICD. Also, consult with your cardiologist before the procedure to find out if you need any special preparation.
- When involved in a physical, recreational, or sporting activity, protect yourself from trauma to the ICD. A blow to the chest near the ICD can affect its functioning. If you are hit in that area, you may want to see your doctor.
- Cell phones are generally safe to use, but keep them at least 6 inches away from your ICD. Avoid carrying a cell phone in your breast pocket over your ICD.
- Always see your doctor when you feel ill after an activity, or when you have questions about beginning a new activity.
- Always talk to your doctor if you have any questions concerning the use of equipment near your ICD.
Read more about : An Echocardiogram
Read more about : Heart Pacemaker Surgery
Read more about : Coronary Angiography
Read more about : Closed heart surgery definition
What is the difference between a pacemaker and a defibrillator?
The pacemaker is the steady hand guiding your heart through each day, while the defibrillator is the guardian angel standing ready to keep you safe if your heartbeat becomes dangerously irregular.
A pacemaker helps control abnormal heart rhythms. It uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate. It can speed up a slow heart rhythm, control a fast heart rhythm, and coordinate the chambers of the heart.
An ICD monitors heart rhythms. If it senses dangerous rhythms, it delivers shocks. This treatment is called defibrillation. An ICD can help control life-threatening arrhythmias, especially those that can cause sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). Most new ICDs can act as both a pacemaker and a defibrillator. Many ICDs also record the heart's electrical patterns when there is an abnormal heartbeat. This can help the doctor plan future treatment.
Read more about: Heart arrhythmia cure
10 common questions about implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery
[kkstarratings]