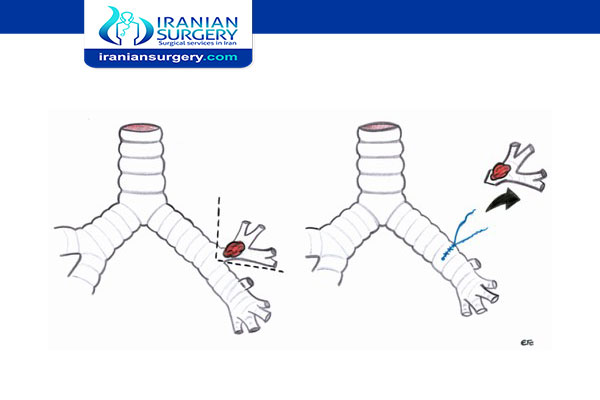
Bronchoplasty
What does bronchial thermoplasty do?
Who needs a bronchoplasty?
Why would a physician perform a bronchoscopy?
What is thoracotomy surgery?
How is bronchial thermoplasty performed?
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that lets doctors look at your lungs and air passages. It's usually performed by a doctor who specializes in lung disorders (a pulmonologist). During bronchoscopy, a thin tube (bronchoscope) is passed through your nose or mouth, down your throat and into your lungs.
Bronchoscopy is most commonly performed using a flexible bronchoscope. However, in certain situations, such as if there's a lot of bleeding in your lungs or a large object is stuck in your airway, a rigid bronchoscope may be needed.
Read more about: Segmentectomy (removal of an anatomic division of a particular lobe of the lung)
What does bronchial thermoplasty do?
Bronchial thermoplasty is an innovative, new, non-drug procedure developed for the treatment of severe persistent asthma. Bronchial thermoplasty delivered by the Alair® System uses thermal energy to reduce the muscle associated with airway constriction in asthma patients. Bronchial thermoplasty is performed in a bronchoscopy/ endoscopy suite and takes about an hour to complete. The minimally invasive procedure, like many other flexible endoscopy procedures, is done under moderate sedation.
Read more about: Lobectomy surgery in Iran(lung)
Who needs a bronchoplasty?
To be considered for bronchial thermoplasty treatment, you should:
- Be an adult between 18-65 years old
- Be a non-smoker for at least the past year
- Have severe or persistent asthma not well controlled by inhaled corticosteroids or long-acting bronchodilator medications
Read more about: Laparoscopy
Why would a physician perform a bronchoscopy?
Common reasons for needing bronchoscopy are a persistent cough, infection or something unusual seen on a chest X-ray or other test.
Bronchoscopy can also be used to obtain samples of mucus or tissue, to remove foreign bodies or other blockages from the airways or lungs, or to provide treatment for lung problems. Bronchoscopy is usually done to find the cause of a lung problem. For example, your doctor might refer you for bronchoscopy because you have a persistent cough or an abnormal chest X-ray.
Reasons for doing bronchoscopy include:
- Diagnosis of a lung problem
- Identification of a lung infection
- Biopsy of tissue from the lung
- Removal of mucus, a foreign body, or other obstruction in the airways or lungs, such as a tumor
- Placement of a small tube to hold open an airway (stent)
- Treatment of a lung problem (interventional bronchoscopy), such as bleeding, an abnormal narrowing of the airway (stricture) or a collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
During some procedures, special devices may be passed through the bronchoscope, such as a tool to obtain a biopsy, an electrocautery probe to control bleeding or a laser to reduce the size of an airway tumor. Special techniques are used to guide the collection of biopsies to ensure the desired area of the lung is sampled.
In people with lung cancer, a bronchoscope with a built-in ultrasound probe may be used to check the lymph nodes in the chest. This is called endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) and helps doctors determine the appropriate treatment. EBUS may be used for other types of cancer to determine if the cancer has spread.
Read more about: heart–lung transplant
What is thoracotomy surgery?
A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure in which a cut is made between the ribs to see and reach the lungs or other organs in the chest or thorax. Typically, a thoracotomy is performed on the right or left side of the chest. An incision on the front of the chest through the breast bone can also be used, but is rare. A thoracotomy is performed for diagnosis or treatment of a disease and allows doctors to visualize, biopsy or remove tissue as needed.
How is bronchial thermoplasty performed?
A full course of bronchial thermoplasty treatment includes three separate bronchoscopic procedures: one for the each lower lobe of the lung and another for both upper lobes. Each outpatient procedure is performed approximately at least three weeks apart.
Under sedation, a catheter inside a bronchoscope a thin, flexible tube-like instrument introduced through the patient’s nose or mouth, and into their lungs delivers thermal energy into the airways. The patient is monitored after the procedure, and usually, returns home that day or early the next day. After the procedure, you can expect some pain when taking a deep breath and will be prescribed pain medication. Your care team will have you use an incentive spirometer for breathing exercises to help prevent pneumonia while you recover. They may also instruct you on how to splint your chest for deep breathing and coughing.
Read more about: Sublobar resection (removal of part of lobe of the lung)


2 Comments
hello I’m John and my sister is 38 year old lady with no drinking or smoking habit but has a breathing problem and doctor has asked her to do bronchoplasty
would you kindly let me k ow what’s thermal bronchoplasty?
Hello John, hope your sister problems gets fixed soon
Thermal bronchoplasty or bronchial thermoplasty (BT) Severe asthmatics have increased airway smooth muscle (ASM) responsible for bronchoconstriction and increased resistance of airway. BT is a novel treatment modality that uses radiofrequency energy to reduce ASM mass and resistance of airway