Adenoidectomy surgery in adults
Do adults have their adenoids removed?
Do adults have their adenoids removed?
What are the symptoms of enlarged adenoids in adults?
Can adenoids grow back in adults?
How long does it take to recover from an adenoidectomy?
Adenoidectomy surgery in adults
Do adults have their adenoids removed?
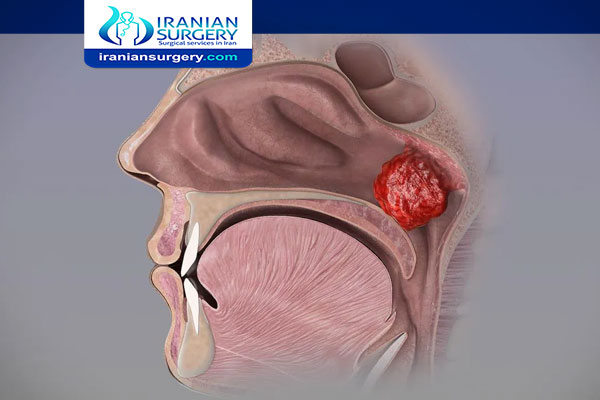
Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the mass of lymphatic tissue situated at the back of the nose. Unlike the tonsils, they are out of sight. They are removed by approaching them from the back of the throat using specialist instruments and a mirror. For most people, the adenoids become very small or disappear once they reach their teenage years. As a result, adenoid removal mostly occurs in young children. However, adults may occasionally require adenoid removal if there is a possibility of cancer or a tumor on the adenoids
Read more about : Cancer treatment success story in Iran
Read more about : Sex reassignment surgery success story
Read more about : Parkinson's disease treatment success story
Enlarged tonsils and adenoids are a common cause of snoring and sleep disruption in children. The tonsils are clusters of lymphoid tissue in the back of the throat or tongue, while the adenoids are a similar mound of tissue in the back of the nose. Although less enlarged in adults, some adults can receive excellent resolution of snoring through removal of tonsils and/or adenoids. Unlike the tonsils, your surgeon cannot completely remove all adenoid tissue in the back of the nose (although today's instruments allow us to do a pretty good job). It is therefore possible for the adenoid to “grow back” and cause symptoms again.
Read more about : Arachnoid Cyst Treatment
Read more about : Arachnoid cyst size 3 cm
Read more about : Herniated disk treatment
Do adults have their adenoids removed?
Adults may occasionally require adenoid removal if there is a possibility of cancer or a tumor on the adenoids.
What are the symptoms of enlarged adenoids in adults?
People cannot see the adenoids by looking into the mouth, so it is not possible to tell if they are enlarged by sight.
A doctor can look at the adenoids using a special mirror or lighted camera on the end of a flexible tube.
The signs and symptoms of enlarged adenoids include:
- snoring
- pauses in breathing during sleep
- strained or noisy breathing
- restless sleep
- breathing more through the mouth than the nose
- bad breath or dry, cracked lips resulting from mouth breathing
- difficulty swallowinga nasal-sounding speaking voice
- a persistent runny nose
- frequent ear infections
- frequent colds
- swollen glands in the neck
- sleeping in an unusual position, with the head back and the knees to the chest while the person is lying on their front
Read more about : Knee Replacement Surgery
Read more about : Spinal Fusion Surgery
Can adenoids grow back in adults?
It is possible for the adenoid to “grow back” and cause symptoms again following a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy if your surgeon does not completely remove all of the lymphoid tissue during surgery. Even a very tiny amount of tissue can cause them to grow back. However, this isn't a common occurrence.
How long does it take to recover from an adenoidectomy?
Most patients require a recovery time at home of approximately one week but may continue to experience a sore throat for two weeks. You'll receive medication to reduce pain and swelling. Complete recovery from an adenoidectomy usually takes one to two weeks, Bleeding after adenoidectomy is very rare but can occur and you will be observed on the unit for 2-3 hours after the operation to reduce the risk of problems occurring after discharge. We observe for excessive swallowing, coughing or vomiting of fresh blood and this needs to be continued by you after discharge. If there is bleeding from the nose, pinch the soft part of the nose for 3-5 minutes.
Read more about : General surgery
Read more about : 2nd iui success rate
Read more about : Carpal tunnel operation
Read more about : Total knee replacement

