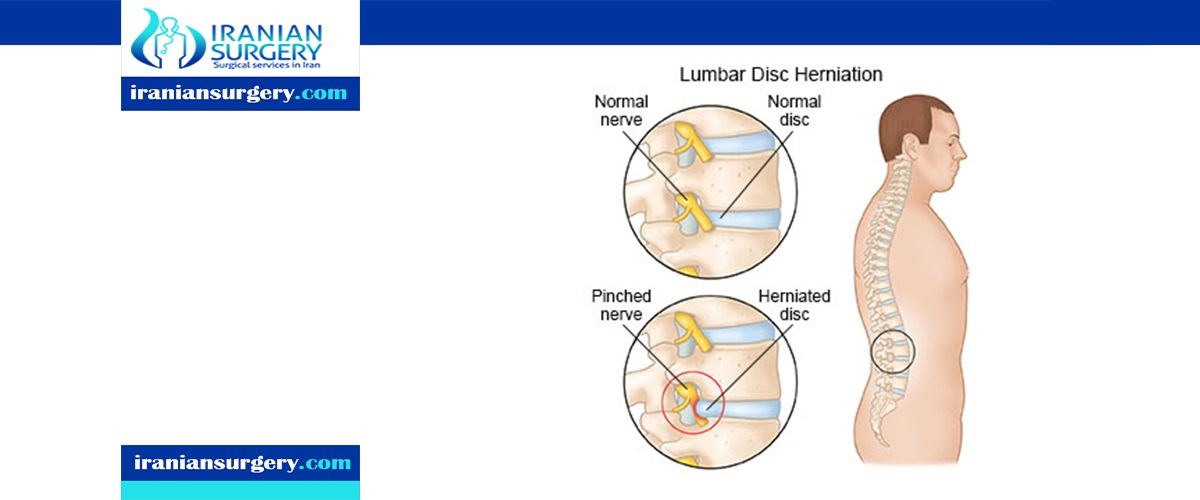
What are the symptoms and signs of spinal disc herniation?
Can a herniated disc heal on its own?
How do you fix a herniated disc?
How do I know if I have sciatica or a herniated disc?
What happens if a herniated disc goes untreated?
What are the symptoms and signs of spinal disc herniation?
Most herniated disks occur in the lower back, although they can also occur in the neck. Signs and symptoms depend on where the disk is situated and whether the disk is pressing on a nerve. They usually affect one side of the body. Typically, symptoms are experienced on one side of the body only.
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the types of soft tissue involved. They can range from little or no pain, if the disc is the only tissue injured, to severe and unrelenting neck pain or low back pain that radiates into regions served by nerve roots which have been irritated or impinged by the herniated material. Often, herniated discs are not diagnosed immediately, as patients present with undefined pains in the thighs, knees, or feet.
Symptoms may include sensory changes such as numbness, tingling, paresthesia, and motor changes such as muscular weakness, paralysis, and affection of reflexes. If the herniated disc is in the lumbar region, the patient may also experience sciatica due to irritation of one of the nerve roots of the sciatic nerve. Unlike a pulsating pain or pain that comes and goes, which can be caused by muscle spasm, pain from a herniated disc is usually continuous or at least continuous in a specific position of the body.
Read more about : Cycling after knee arthroscopy
Read more about : Heart attack
Read more about : Open heart surgery
Read more about : Arachnoid Cyst Treatment
It is possible to have a herniated disc without pain or noticeable symptoms if the extruded nucleus pulposus material doesn't press on soft tissues or nerves. A small-sample study examining the cervical spine in symptom-free volunteers found focal disc protrusions in 50% of participants, suggesting that a considerable part of the population might have focal herniated discs in their cervical region that do not cause noticeable symptoms.
A herniated disc in the lumbar spine may cause radiating nerve pain in the lower extremities or groin area and may sometimes be associated with bowel or bladder incontinence.
Typically, symptoms are experienced only on one side of the body, but if a herniation is very large and presses on the nerves on both sides within the spinal column or the cauda equina, both sides of the body may be affected, often with serious consequences. Compression of the cauda equina can cause permanent nerve damage or paralysis which can result in loss of bowel and bladder control and sexual dysfunction. This disorder is called cauda equina syndrome. Other complications include chronic pain.
Can a herniated disc heal on its own?
Usually a herniated disc will heal on its own over time. Be patient, and keep following your treatment plan. If your symptoms don't get better in a few months, you may want to talk to your doctor about surgery. In most cases, the pain from a herniated disc will get better within a couple days and completely resolve in 4 to 6 weeks. Restricting your activity, ice/heat therapy, and taking over the counter medications will help your recovery.
Read more about: Herniated disc treatment
Read more about: Herniated Disc Surgery
How do you fix a herniated disc?
Treatment
For the majority of patients, a herniated lumbar disk will slowly improve over a period of several days to weeks. Typically, most patients are free of symptoms by 3 to 4 months. However, some patients do experience episodes of pain during their recovery.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Initial treatment for a herniated disk is usually nonsurgical in nature. Treatment focuses on providing pain relief.
Nonsurgical treatment may include:
Rest. One to 2 days of bed rest will usually help relieve back and leg pain. Do not stay off your feet for longer, however. When you resume activity, try to do the following:
- Take rest breaks throughout the day, but avoid sitting for long periods.
- Make all your physical activity slow and controlled, especially bending forward and lifting.
- Change your daily activities to avoid movements that can cause further pain.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain.
Physical therapy. Specific exercises will help strengthen your lower back and abdominal muscles.
Epidural steroid injection. An injection of a cortisone-like drug into the space around the nerve may provide short-term pain relief by reducing inflammation.
There is good evidence that epidural injections can successfully relieve pain in many patients who have not been helped by 6 weeks or more of other nonsurgical care.
Surgical Treatment
Only a small percentage of patients with lumbar disk herniation require surgery. Spine surgery is typically recommended only after a period of nonsurgical treatment has not relieved painful symptoms, or for patients who are experiencing the following symptoms:
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
Microdiskectomy. The most common procedure used to treat a single herniated disk is microdiskectomy. The procedure is done through a small incision at the level of the disk herniation and often involves the use of a microscope.
The herniated part of the disk is removed along with any additional fragments that are putting pressure on the spinal nerve.
A larger procedure may be required if there are disk herniations at more than one level.
Rehabilitation. Your doctor or a physical therapist may recommend a simple walking program (such as 30 minutes each day), along with specific exercises to help restore strength and flexibility to your back and legs.
To reduce the risk of repeat herniation, you may be prohibited from bending, lifting, and twisting for the first few weeks after surgery.
Read more about: Disc Herniation Surgery Risks
Read more about: Disc Herniation Surgery Recovery
How do I know if I have sciatica or a herniated disc?
If your pain is ongoing (chronic) or severe, your doctor might also get some imaging tests done. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can look for herniated disks or bone spurs that clearly would be causes of sciatica. An electromyography (EMG) test can also tell him what nerves in your back are being compressed. One of the most important differences between the two conditions is the fact that sciatica can be treated in a relatively short period of time. Herniated discs, on the other hand, require greater care. These represent a permanent condition.
What happens if a herniated disc goes untreated?
Left untreated, a herniated disc can lead to more severe complications which can turn into a chronic condition. If the pain starts to interfere with your daily activities, it is highly advised to seek a diagnosis and treatment recommendations from a spine specialist as soon as possible.
Read more about: spinal disc herniation
Read more about: Disc herniation
Read more about: Disc Herniation Surgery Success Rate
Read more about: Slipped disc (herniated disc)