prostate biopsy anesthesia
Prostate Biopsy Procedure Types
What is a Prostate Biopsy?
The prostate gland is found only in males. It sits below the bladder and wraps around the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body). The prostate helps make semen.
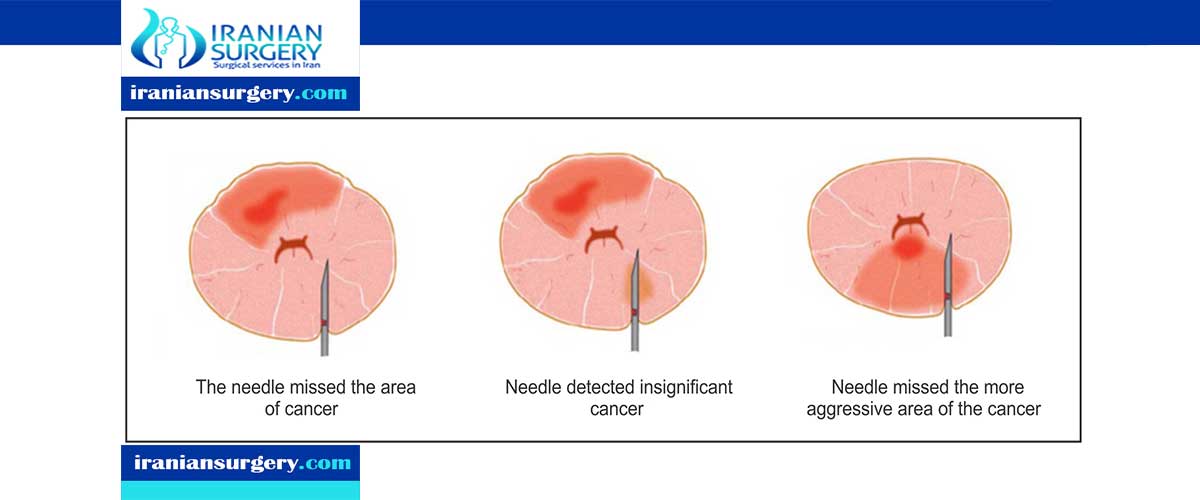
A biopsy is a procedure used to remove a small piece of tissue or cells from the body so it can be examined under a microscope.
In a prostate biopsy, prostate gland tissue is taken out with a biopsy needle or during surgery. The tissue is checked to see if there are cancer or other abnormal cells in the prostate gland.
Read more about : Pancreatic cancer
Read more about : Prostate Cancer Treatments Pros and Cons
A prostate biopsy may be done in several different ways:
. Transrectal method. This is done through the rectum and is the most common.
. Perineal method. This is done through the skin between the scrotum and the rectum.
. Transurethral method. This is done through the urethra using a cystoscope (a flexible tube and viewing device).
Ultrasound is usually used to look at the prostate gland and guide the biopsy needle.
What happens during a prostate biopsy?
A prostate biopsy is usually done on an outpatient basis. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your healthcare provider's practices.
Read more about : Cancer Treatment
Read more about : Pancreatic Cancer Stages
Generally, a prostate biopsy follows one of these processes:
. Transrectal method
- You will remove your clothing and put on a hospital gown.
- You will be positioned on your left side, with your knees bent.
- This type of biopsy may be done with a local anesthetic to numb the tissue the needle will pass through.
- Usually, a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) will be used to guide the placement of the biopsy needle.
- The healthcare provider will use a spring-loaded tool that quickly inserts a needle through the wall of the rectum into the prostate gland. You may feel discomfort or pressure when the needle enters the prostate gland.
- The needle is put in several times to take tissue samples from different parts of the gland.
- The prostate tissue samples will be sent to the lab for exam.
. Perineal method
- You will remove your clothing and put on a hospital gown.
- You will be positioned on your left side, with your knees bent, or lying on your back with your knees bent and thighs apart.
- The skin between your scrotum and rectum will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- You will feel a needle stick when the local anesthetic is injected. This may cause a brief stinging sensation.
- When the area is numb, the healthcare provider may make a tiny incision (cut) in the skin.
- The healthcare provider will place a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum to locate and stabilize the prostate gland.
- The biopsy needle will be inserted through the incision and into the prostate several times to get samples from different parts of the gland.
- The biopsy needle will be removed and firm pressure will be applied to the biopsy site until the bleeding has stopped. Sutures are usually not needed.
- The prostate tissue samples will be sent to the lab for exam.
. Transurethral method
- You will remove your clothing and put on a hospital gown.
- You will be positioned on your back with knees bent and thighs apart.
- The procedure may be done under a local or general anesthetic. (Local anesthetic means medicines are used to make you numb. General anesthetic means medicines are used to put you into a deep sleep during the procedure.)
- The healthcare provider will insert a cystoscope (a flexible tube and viewing device) into the opening at the end of your penis, through the urethra, and up to the prostate gland.
- The healthcare provider will insert tiny instruments through the cystoscope to take out samples of the prostate gland.
- The cystoscope will be removed.
- The prostate tissue samples will be sent to the lab for exam.
Read more about 2nd iui success rate
Read more about Virgin tightening surgery before and after
Read more about Ovarian cyst size chart


4 Comments
hi,please tell can prostate biopsy make the cancer spread?
according to Mayo researchers ,cancer biopsies do not promote cancer spread. however other studies shows that there is small possibility for that in prostate biopsy.
my doktor tell me my prostat biger get, i do biopsi an now i bled shud I go to doctor bakc or you tell me mi problem?
Thank you for leaving us a comment and asking about your condition, our first suggestion would be to check up with your physician because we are not familiar with any of your conditions or how serious your problem is.
However, normally, during a prostate biopsy, a needle is used to collect a number of tissue samples from the prostate gland. This procedure is performed by a doctor who specializes in the urinary system and male sexual organs (urology).
Bleeding at the biopsy site like anal bleeding is common after a prostate biopsy. Blood in the semen is usually seen after a prostate biopsy too. Bleeding in semen may continue for several weeks after the biopsy and if you see Blood in the urine, it is usually minor.