Mastoidectomy
What is a Mastoidectomy?
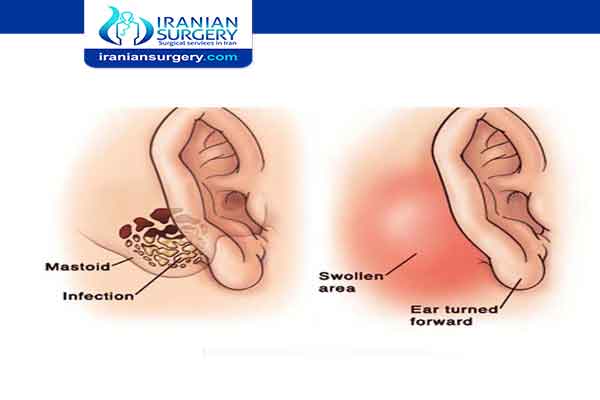
A mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes diseased mastoid air cells. The mastoid is the part of your skull located behind your ear. It’s filled with air cells made of bone and looks like a honey comb. The diseased cells are often the result of an ear infection that has spread into your skull. The procedure can also be used to remove an abnormal growth of the ear known as a cholesteatoma.
Read more about : Septum deviated surgery
Before Mastoidectomy
Why do I need a mastoidectomy?
A mastoidectomy can treat complications of chronic otitis media (COM). COM is an ongoing ear infection in your middle ear. A cholesteatoma, which is a skin cyst, can be a complication from these ongoing infections. The cyst grows gradually over time and may lead to serious complications such as:
. Abscess in the brain
. Deafness
. Dizziness or vertigo
. Damage to your facial nerve that causes facial paralysis
. Meningitis, or inflammation of the membranes of your brain
. Labyrinthitis, or inflammation of your inner ear
. Ongoing ear drainage
Your doctor may also perform a mastoidectomy to put in a cochlear implant. This small, complex electronic device can help provide you with a sense of sound if you’re profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing.
This surgery can also remove abnormal growths at the base of your skull.
Read more about : Mastoidectomy side effects
What complications are associated with a mastoidectomy?
Complications of a mastoidectomy can include:
. Facial nerve paralysis or weakness, which is a rare complication caused by facial nerve injury.
. Sensorineural hearing loss, which is a type of inner ear hearing loss
. Dizziness or vertigo, which may persist for several days
. A change in taste that causes food to seem metallic, sour, or otherwise off, and often resolves after a few months.
. Tinnitus, which causes abnormal noises in your ear such as ringing, buzzing, and hissing.
Call your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms. You should also call your doctor if you have heavy ear bleeding or discharge, a fever over 100.5°F (38°C), or if your wound is not healing properly.
Read more about : Rhinoplasty vs Septoplasty
During Mastoidectomy
Types of Mastoidectomy
There are variations of mastoidectomy procedures, including:
. Simple mastoidectomy, in which your surgeon opens your mastoid bone, removes the infected air cells, and drains your middle ear
. Radical mastoidectomy, in which your surgeon may remove your mastoid air cells, your eardrum, most of your middle ear structures, and your ear canal. This procedure is reserved for complicated mastoid disease.
. Modified radical mastoidectomy, which is a less severe form of radical mastoidectomy that involves removing mastoid air cells along with some, but not all, middle ear structures
You can expect some hearing loss from a radical and modified radical mastoidectomy.
How is a mastoidectomy performed?
Your doctor usually performs a mastoidectomy using general anesthesia. This ensures that you’re asleep and unable to feel pain. For a simple mastoidectomy, your surgeon will usually:
. Access your mastoid bone through a cut made behind your ear.
. Use a microscope and a small drill to open your mastoid bone.
. Use suction irrigation to keep the surgical area free of bone dust.
. Drill out the infected air cells.
. Stitch up the operative site.
. Cover the site with gauze to keep the wound clean and dry.
Your surgeon may also use a facial nerve monitor during surgery. This helps to limit injury to the facial nerve.
After Mastoidectomy
What is the recovery process after a mastoidectomy?
You can expect to have bandages over your ear when you wake up. There will also be stitches close to your ear. You may have a headache, discomfort, and some numbness.
After surgery, your doctor may:
. Prescribe pain medication
. Give you antibiotics to treat any infection
. Ask you to schedule a return for wound check and removal of any bandages and stitches.
Follow your doctor’s specific instructions on caring for your wound, as well when you can swim or bathe. You should avoid all strenuous activity for at least two to four weeks afterward, depending on your surgery. Also refrain from putting pressure on your ear.
What is the long-term outlook?
The outlook varies depending on the reason for the mastoidectomy and the type of mastoidectomy procedure. Some hearing loss is common with both modified radical and radical mastoidectomy.
You need to have regular follow-up appointments with your doctor if you had a cholesteatoma. At your post-operative follow-up, your doctor will check to make sure that your ear is healing correctly and that any complications are resolving.
Source:
. https://www.healthline.com/health/mastoidectomy