What are the risks of a liver biopsy?
Does a liver biopsy hurt?
Can you drive after a liver biopsy?
Can you die from a liver biopsy?
How long does it take to get the results of a liver biopsy?
why do a liver biopsy?
A liver biopsy is a procedure in which a small needle is inserted into the liver to collect a tissue sample. The tissue is then analyzed in a laboratory to help doctors diagnose a variety of disorders and diseases in the liver. A liver biopsy is most often performed to help identify the cause of:
Persistent abnormal liver blood tests (liver enzymes)
Unexplained yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
A liver abnormality found on ultrasound, CT scan, or nuclear scan
Unexplained enlargement of the liver
A liver biopsy can also be used to estimate the degree of liver damage, to grade and stage hepatitis B and C, and to determine the best treatment for the damage or disease.
Read more about : What does it mean if your AST SGOT is high?
Read more about : What are the signs of a transplanted kidney being rejected?
Read more about : What is Kidney Transplant?
Why it's done
A liver biopsy may be done to:
- Diagnose a liver problem that can't be otherwise identified
- Obtain a sample of tissue from an abnormality found by an imaging study
- Determine the severity of liver disease a process called staging
- Help develop treatment plans based on the liver's condition
- Determine how well treatment for liver disease is working
- Monitor the liver after a liver transplant
Why would a doctor order a liver biopsy?
- Abnormal liver test results that can't be explained
- A mass (tumor) or other abnormalities on your liver as seen on imaging tests
- Ongoing, unexplained fevers
A liver biopsy also is commonly performed to help diagnose and stage certain liver diseases, including:
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Chronic hepatitis B or C
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson's disease
Read more about : Pancreatic cancer
Read more about : Prostate Cancer Treatments Pros and Cons
Are there different types of liver biopsy?
Yes. In each type of liver biopsy, doctors take the sample of liver tissue in a different way. Common types of liver biopsy are described below.
Percutaneous liver biopsy
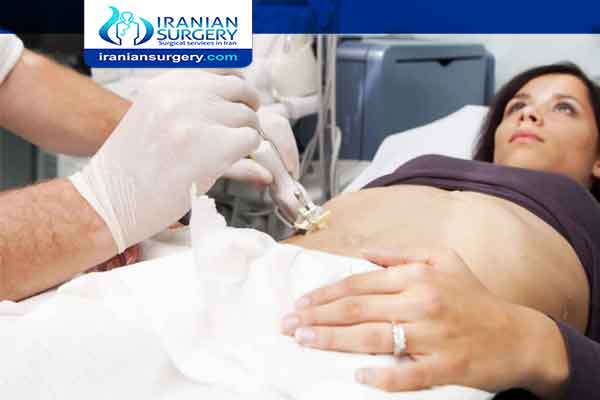
In percutaneous liver biopsy, the doctor inserts a needle through your skin in the upper part of the abdomen to take a small piece of your liver tissue.
Percutaneous liver biopsy is the most common type of liver biopsy and has been performed routinely for many years. Your doctor may perform an ultrasound NIH external link or computed tomography (CT) scan to be sure that the needle is positioned in the correct place.
Transjugular liver biopsy
In transjugular liver biopsy, a doctor inserts a needle into a vein in your neck called the jugular vein. The doctor passes the needle through your veins to your liver to take a small piece of tissue.
Doctors usually perform transjugular biopsy in people who have a higher risk of problems with percutaneous liver biopsy. For example, bleeding after a percutaneous biopsy is more likely in people who have problems with blood clotting NIH external link. In people who have ascites a buildup of fluid in the abdomen that is a complication of cirrhosis percutaneous biopsy is difficult because the liver is too far away from the skin and hard to target.
Transjugular biopsy also allows doctors to measure pressure in the veins of the liver at the same time that they perform the biopsy.
Surgical liver biopsy
If you need a liver biopsy and you are having surgery for other reasons, a doctor may perform a liver biopsy during the surgery.
before liver biopsy
- Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure to you. Ask him or her any questions you have about the procedure.
- You may be asked to sign a consent form that gives permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything is not clear.
- Your provider will ask questions about your past health. He or she may give you a physical exam. This is to make sure you are in good health before you have surgery. You may also need blood tests and other diagnostic tests.
- Tell your provider if you are sensitive to or allergic to any medicines, latex, tape, and anesthesia medicines (local and general).
- Tell your provider about all the medicines you take. This includes both over-the-counter and prescription medicines. It also includes vitamins, herbs, and other supplements.
- Tell your provider if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any blood-thinning (anticoagulant) medicines, aspirin, ibuprofen, or other medicines that affect blood clotting. You may need to stop taking these medicines before the biopsy.
- Tell your provider if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant.
- You may be asked to not eat or drink anything before the biopsy. This often means no food or drink after midnight. Your provider will give you specific instructions.
- You may be given medicine to help you relax (a sedative) before the surgery. Because the sedative may make you drowsy, someone must drive you home.
Read more about: Breast cancer biopsy
How a liver biopsy is performed
Just before the procedure, you’ll change into a hospital gown. Your doctor will give you a sedative through an intravenous (IV) line to help you relax.
There are three basic types of liver biopsies.
- Percutaneous: Also called a needle biopsy, this biopsy involves putting a thin needle through the abdomen and into the liver.
- Transjugular: This procedure involves making a small incision at the neck. A thin flexible tube is inserted through the neck’s jugular vein and into the liver. This method is used for people who have bleeding disorders.
- Laparoscopic: This technique uses tube-like instruments that collect the sample through a small incision in the abdomen.
The kind of anesthesia your doctor gives you will depend on which type of liver biopsy they perform. The percutaneous and transjugular biopsies use local anesthesia, meaning that only the affected area is numbed. Laparoscopic biopsies require general anesthesia, so you’ll be in a deep, painless sleep during the procedure.
When your biopsy is complete, any incision wounds will be closed with stitches and properly bandaged. You will typically have to lie in bed for a few hours after the procedure while doctors monitor your vital signs.
Once you receive approval from your doctor, you are free to go home. You should take it easy and rest for the next 24 hours. However, you should be able to get back to your normal life after a few days.
After a Liver Biopsy
After the tissue sample is taken, it will be sent to a laboratory for testing. This could take up to a few weeks.
When the results are back, your doctor will call you or ask you in for a follow-up appointment to share the results. Once a diagnosis is reached, your doctor will discuss any recommend treatment plans or next steps with you.
What are the risks of a liver biopsy?
Some possible complications may include:
- Pain and bruising at the biopsy site
- Bleeding for a long time from the biopsy site, either inside or outside the body
- Infection near the biopsy site
- Accidental injury to another organ
If your liver biopsy is done using X-rays, the amount of radiation used is small. The risk for radiation exposure is low.
In some cases, a liver biopsy may not be advised. This includes cases where you have:
- A condition that affects the blood's ability to clot
- A lot of fluid collecting in your belly or abdomen (severe ascites)
- An infection of your biliary tract or the part of your belly around your liver
You may have other risks that are unique to you. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before the procedure.
What side do you lay on after a liver biopsy?
The doctor will place a bandage over the cut on your abdomen. You may be asked to lie on your right side after the biopsy, and you will need to remain lying down for a few hours.
Read more about: Testicular Biopsy
Does a liver biopsy hurt?
Pain at the biopsy site is the most common complication after a liver biopsy. Pain after a liver biopsy is usually a mild discomfort. If pain makes you uncomfortable, you may be given a narcotic pain medication, such as acetaminophen with codeine (Tylenol with Codeine). The referred pain usually lasts less than 12 hours. You may have a small amount of bleeding from the procedure site. You will need to take it easy at home for 1 to 3 days after the procedure. You will probably be able to return to work and most of your usual activities after that.
Can you drive after a liver biopsy?
You will stay in a recovery room for up to 4 hours for observation. You may feel minor pain or soreness at the biopsy site and discomfort or a dull pain in your shoulders or back. If necessary, a pain medication will be prescribed for you. Do not drive or operate machinery for at least eight hours after the procedure.
Read more about: What is MRI biopsy?
Can you die from a liver biopsy?
A liver biopsy is a safe procedure when performed by an experienced doctor. Possible risks include: Pain. Pain at the biopsy site is the most common complication after a liver biopsy. Severe bleeding is uncommon, occurring in 1 to 2500 to 10,000 patients (6) undergoing biopsy to obtain random liver histology. Further, the most feared complication, death after liver biopsy, is usually related to aggressive hemorrhage. Death occurs in approximately 1 in 10,000 patients.
How long does it take to get the results of a liver biopsy?
After a liver biopsy, a pathologist will examine the biopsy tissue with a microscope to look for signs of damage or disease. A result can often be given within 2 to 3 days after the biopsy. A result that requires a more complicated analysis can take 7 to 10 days.
Read more about: Cervical biopsy procedure in Iran