Can hydrocephalus be treated with drugs?
What medication is commonly used to treat hydrocephalus?
Can hydrocephalus be cured naturally?
Does hydrocephalus go away?
What is the survival rate of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus treatment drugs
What medication is commonly used to treat hydrocephalus?
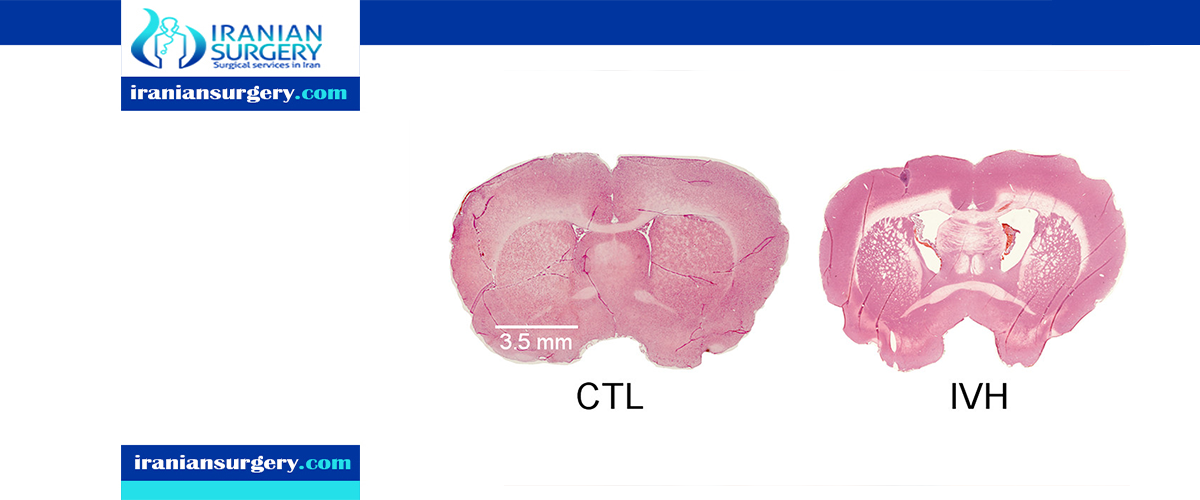
Acetazolamide is the most suitable drug alone or in combination with furosemide for treatment of hydrocephaly, Acetazolamide (ACZ) and furosemide (FUR) treat posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates. Both are diuretics that also appear to decrease secretion of CSF at the level of the choroid plexus. ACZ can be used alone or in conjunction with FUR. The combination enhances efficacy of ACZ in decreasing CSF secretion by the choroid plexus. If ACZ is used alone, it appears to lower risk of nephrocalcinosis significantly.
Drugs
|
| |
Acetazolamide
| (ACZ)
| Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension (raised brain pressure of unclear cause), and heart failure. |
Furosemide
| (FUR) |
Furosemide is a loop diuretic (water pill) that prevents your body from absorbing too much salt. This allows the salt to instead be passed in your urine. Furosemide is used to treat fluid retention (edema) in people with congestive heart failure, liver disease, or a kidney disorder such as nephrotic syndrome. Furosemide is also used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). |
Read more about: Herniated disc surgery
Read more about: Heart attack
Read more about: Arachnoid cyst size chart
Read more about: Hydrocephalus treatment drugs
Read more about Do arachnoid cysts require surgery?
Can hydrocephalus be treated with drugs?
Medication as treatment for hydrocephalus is controversial. It should be used only as a temporary measure for posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates, or when shunting is not possible.
Can hydrocephalus be cured naturally?
Does hydrocephalus go away?
Hydrocephalus is a chronic condition. It can be controlled, but usually not cured. With appropriate early treatment, however, many people with hydrocephalus lead normal lives with few limitations. Hydrocephalus can occur at any age, but is most common in infants and adults age 60 and older. There is currently no known way to prevent or cure hydrocephalus and the only treatment option today requires brain surgery. With early detection and appropriate intervention of hydrocephalus, the future for many is promising. Without treatment, hydrocephalus results in compromised mental functioning, visual disturbances, walking difficulty, incontinence, and reduced conscious state.
What is the survival rate of hydrocephalus?
The mortality rate for hydrocephalus and associated therapy ranges from 0 to 3%. This rate is highly dependent on the duration of follow-up care. The shunt event-free survival is approximately 70% at 12 months and is nearly half that at 10 years, post-operatively.
Read more about: Hydrocephalus treatment in adults
Read more about: Hydrocephalus treatment options
Read more about: Hydrocephalus treatment shunt
10 common questions about Hydrocephalus treatment drugs
[kkstarratings]