Are Frozen Donor Eggs as Good as Fresh?
Are Frozen Donor Eggs as Good as Fresh?
For those who may have difficulties conceiving a child on their own, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) offers a safe and relatively reliable way to get pregnant. It may also be the only option for gay or lesbian couples looking to have a child that carries at least one of the partners’ genes.
IVF involves extracting the eggs from the mother or an egg donor and either immediately fertilizing it or freezing it to later be fertilized. The embryo is then implanted into the mother’s uterus where it hopefully attaches to the inner wall. Although very similar, using fresh or frozen donor eggs for IVF is not identical.
Who Should Consider IVF?
IVF is definitely not for everyone. If you are a straight couple with no known issues conceiving you should first try to conceive naturally before attempting IVF. However, if you are unable to birth or carry a child and need a surrogate, or if you are a same-sex couple, IVF might be your only choice.
Fresh or Frozen Donor Eggs?
While extremely similar, fresh eggs and frozen eggs are not identical. There is not a “one-size-fits-all” solution to this question. Depending on things such as your age, budget, time constraints, and reason for seeking IVF, the answer to this question will vary.
The Case for Fresh Eggs
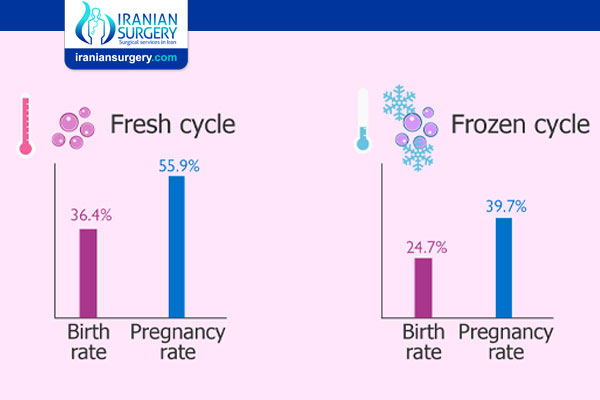
A study completed by Duke University and the University of Colorado Boulder in February 2020 concluded that “Using freshly donated eggs for women undergoing in-vitro fertilization (IVF) provides a small but statistically significant advantage in birth outcomes compared to frozen donated eggs”.
The study found that fresh eggs resulted in a 2% better success rate than frozen eggs (24% in fresh vs. 22% in frozen). The study, which examined nearly 37,000 IVF cycles and 3 years of data, found that implantation (of the embryo into the uterine wall), live birth rates, and successful pregnancies were all higher for fresh eggs.
Also, the use of fresh eggs means that you can use an intended parent rather than select from a limited number of frozen egg donors. If the first round of attempts fails, or if you later wish to have another child with the same parent, a fresh donor would easily be able to repeat the process.
You are also entitled to all eggs obtained during the egg retrieval process. Whereas frozen eggs come in “cohorts” of pre-specified numbers of eggs, fresh egg retrieval often results in more eggs than a frozen cohort. This means that you will have more attempts to conceive and if you have extra, they can be frozen for future use.
The Case for Frozen Eggs
While fresh egg donation has proven to be more flexible and slightly more likely to succeed, this does not mean that it is absolutely the right option for you. A major drawback of fresh eggs is that the donor’s cycle must be synced with the recipient’s. This can cost you a lot of time.
For women using frozen eggs, they can begin the IVF process whenever they like, without the need to coordinate with another individual. This can be ideal if you have a constrained schedule, or if you simply don’t want the stress of having to rely on another individual.
A single cohort of frozen eggs also costs less than one of fresh eggs. However, fresh egg retrieval typically results in a higher number of eggs so the chances of successful conception are higher with fresh eggs, not including the fact that fresh eggs are also more likely to implant.
This is also something that you should consider based on personal factors. A study by UPenn Medicine showed that IVF success rates fell off sharply with age. Women younger than 35 have a >20% success rate, compared to 17% for women 35-37, 11.1% for women 38-40, and 5.7% for women 41-42. For older women, fresh eggs are likely a better option as they will have more attempts as well as a slight increase in implantation chance (as reported by Duke University).
Fresh Eggs vs Frozen Eggs
Though everyone should consult a fertility specialist before making this decision, knowing the pros and cons of both methods can save you a lot of time in your search for a sperm/egg donor. Fresh egg cycles are proven to produce more eggs than a typical frozen egg cohort, and the use of fresh eggs has been found to have slightly, but still statistically significant, better odds at successful conception and birth.
Frozen eggs, on the other hand, allow you a lot more flexibility in your timing and can save you the cost of needing to pay to transport your egg donor to you. This could be particularly good for gay couples who would be more likely to need to fly out a potential egg donor.
For the majority of individuals, particularly those who are not overly time-constrained, the studies show that the benefits provided by fresh egg donations outweigh those provided by frozen ones.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best doctors and fertility specialists in Iran. The price of IVF Using Donor Eggs in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by an in-person assessment with the doctor.
For more information about the cost of IVF Using Donor Eggs in Iran and to schedule an appointment in advance, you can contact Iranian Surgery consultants via WhatsApp number 0098 901 929 0946. This service is completely free.
Source:
https://www.modamily.com/blog/fresh-donor-eggs-vs-frozen-eggs-which-is-better