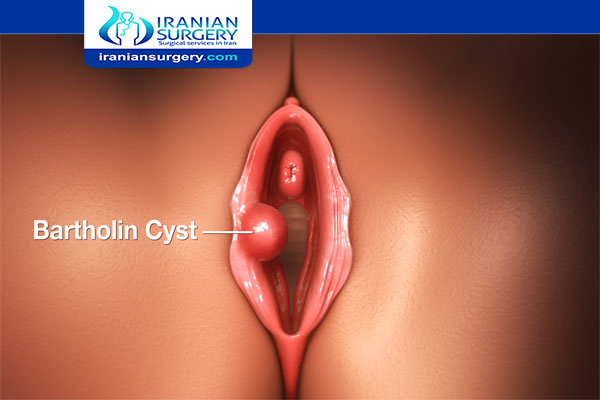
Will A Bartholin Cyst Go Away with Antibiotics?
What antibiotics treat Bartholin cyst?
Medication and antibiotics are used to treat Bartholin's cysts or abscesses as the infection is mostly caused by pathogens. Antibiotic therapy may not be necessary for healthy women with uncomplicated abscesses. Antibiotic therapies include Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline and Azithromycin.
Read more about : Disadvantages Of Removing Bartholin’s Gland
Read more about : How to pop a bartholin cyst yourself?
Read more about : pros and cons of bartholin gland removal
Read more about : Bartholin cyst drainage aftercare
Read more about : Smelly discharge after marsupialization
Bartholin's Cyst Treatment
Often a Bartholin's cyst requires no treatment — especially if the cyst causes no signs or symptoms. When needed, treatment depends on the size of the cyst, your discomfort level and whether it's infected, which can result in an abscess.
Treatment options your doctor may recommend include:
. Sitz baths. Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) several times a day for three or four days may help a small, infected cyst to rupture and drain on its own.
. Surgical drainage. You may need surgery to drain a cyst that's infected or very large. Drainage of a cyst can be done using local anesthesia or sedation.
For the procedure, your doctor makes a small incision in the cyst, allows it to drain, and then places a small rubber tube (catheter) in the incision. The catheter stays in place for up to six weeks to keep the incision open and allow complete drainage.
. Antibiotics. Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic if your cyst is infected or if testing reveals that you have a sexually transmitted infection. But if the abscess is drained properly, you may not need antibiotics.
. Marsupialization. If cysts recur or bother you, a marsupialization (mahr-soo-pee-ul-ih-ZAY-shun) procedure may help. Your doctor places stitches on each side of a drainage incision to create a permanent opening less than 1/4-inch (about 6-millimeter) long. An inserted catheter may be placed to promote drainage for a few days after the procedure and to help prevent recurrence.
Rarely, for persistent cysts that aren't effectively treated by the above procedures, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the Bartholin's gland. Surgical removal is usually done in a hospital under general anesthesia. Surgical removal of the gland carries a greater risk of bleeding or complications after the procedure.
Azithromycin Dosage for Bartholin Cyst
If the swelling and pain is mild without fluctuance (bartholinitis) or if the abscess is small, the patient can be placed on antibiotics, such as metronidazole (Flagyl), 500 mg bid × 7 days, or clindamycin (Cleocin), 300 mg qid × 7 days, and instructed to take warm sitz baths. Early follow-up should be provided. If there is any risk for a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that cannot be ruled out with rapid testing, give azithromycin (Zithromax), 1 g orally in a single dose, or oral doxycycline, 100 mg twice a day for 7 days. Also give ciprofloxacin (Cipro), 500 mg orally in a single dose.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies
Daily soaking in warm water, several times a day, may be adequate to resolve an infected Bartholin's cyst or abscess.
After a surgical procedure to treat an infected cyst or abscess, soaking in warm water is particularly important. Sitz baths help to keep the area clean, ease discomfort and promote effective drainage of the cyst. Pain relievers also may be helpful.
Source:


8 Comments
I have done surgery for bartholin abscess ..14 years back …but now again it started d pain n redness.i am doing hot bath twice a day…feel little better but still redness n slightly itching also.what antibiotics should I take .pls let me know ..
hello dear pema, Medication and antibiotics are used to treat Bartholin’s abscesses as the infection is mostly caused by pathogens. Antibiotic therapy may not be necessary for healthy women with uncomplicated abscesses. Antibiotic therapies include Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline and Azithromycin.
I get these often but I’ve been checked for sti and I don’t have any since 3 yrs I haven’t been sexually active so how and why do I get these? They seem to come back every other month and there small like as big as a nail and I mean a nail you use for building stuff with!
Unfortunately, Bartholin cyst can happen recurrently.
The reason could be infection caused by STI, poor hygiene or using public restroom, or even old injury in your genital area. sometimes it just happens without any of the reasons above.
Treatment depends on the size of the cyst, how painful the cyst is and whether the cyst is infected.
If it’s not painful or causes you discomfort, home treatment could be all you need.
If you are over 40, make sure to check it with your doctor.
Hello is for the second time thing appear on my vigina,can i bump it?
It depends on the size of the cyst, how painful the cyst is, whether the cyst is infected, your age and your previous treatment.
If you are over 40 or the cyst is painful and causes you discomfort check it with a medical doctor.
Is Augmentin good antibiotic to treat cyst?
All type antibiotic should be used only by medical doctor registration. If the bartholin cyst is infected type, your doctor decides whether the antibiotics or surgery is necessary.