What is cochlear implant meaning?
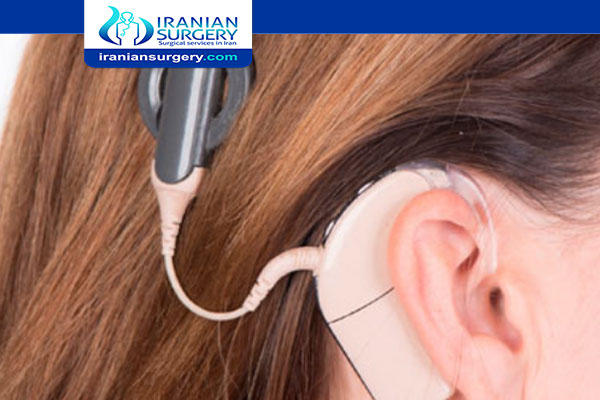
Cochlear Implant Meaning
What is a Cochlear Implant?
A cochlear implant is a small electronic medical device that improves moderate to severe hearing loss. It’s used to help hearing loss in adults, children, and babies.
This type of device is very different from a hearing aid, which serves only to amplify sound. A cochlear implant transforms sounds into electrical signals and transmits these signals directly to the auditory nerve of the inner ear, bypassing any damaged structures in the ear that are impeding normal hearing.
Parts of a Cochlear Implant
All cochlear implants, regardless of manufacturer, consist of two general components:
. Internal device: The internal portion of the implant consists of two parts: the receiver/stimulator and the intracochlear electrode array.
. External hardware: The external portion consists of three parts: a microphone, a speech processor, and a transmitting coil.
How a Cochlear Implant Works
. Sound is picked up by the microphone, where it is sent down a cord to the speech processor.
. The speech processor filters the incoming acoustic signal into separate frequency bands, and then converts this information into digital form.
. The digitized signal is sent back up the cord to the transmitting coil, which is held in place by a magnet.
. The coil transmits the digitized information across the skin to the internal receiver/stimulator.
. The internal receiver/stimulator decodes the incoming signal and sends information in each frequency band to a different electrode within the cochlea. (The internal receiver/stimulator also contains a magnet to which the external coil sticks.)
. High-frequency information is sent to electrodes in the basal end of the cochlea, and low-frequency information is sent to electrodes in the apical end of the cochlea.
. Electrical stimulation from the intracochlear electrodes takes the place of damaged cochlear structures or hair cell - nerve synapses.
. The auditory nerve picks up the electrical signals from the electrodes and relays that information to the brain where it is interpreted as sound.
Read more about : Cochlear Implant Batteries
Why it's done
Cochlear implants can restore hearing in people with severe hearing loss who are no longer helped by using hearing aids. Cochlear implants can improve their communication and quality of life.
Cochlear implants may be placed in one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). Cochlear implants in both ears have started to be used more often to treat bilateral severe hearing loss — particularly for infants and children who are learning to speak and process language.
Adults and children who are as young as six to 12 months old can benefit from cochlear implants. People who have cochlear implants report improved:
. Ability to hear speech without needing visual cues such as reading lips
. Recognition of normal, everyday environmental sounds
. Ability to listen in a noisy environment
. Ability to find where sounds are coming from
. Ability to hear television programs, music and telephone conversations


2 Comments
I am Faisal from Pakistan. I want my daughter who is deaf to get cochlear plant. Do I know the cost of this surgery?
hello dear faisal, please contact me on whatsApp to provide you with the cost of Cochlear implant surgery in Iran. this is my whatsApp number +989019290946. thank you