What are the causes of pilonidal sinus?
What are the pilonidal sinus symptoms?
How to Prevent from pilonidal cysts
Are pilonidal cysts cancerous?
What happens if pilonidal cyst goes untreated?
Why do pilonidal cysts smell so bad?
Does everyone have a pilonidal sinus?
How long can a pilonidal cyst go untreated?
What are the causes of pilonidal sinus?
It's not clear what causes a pilonidal sinus.
A skin problem, pressure or friction may cause hair between the buttocks to be pushed inwards.
This may either be hair growing around the buttock area, or loose hair shed from the buttocks or elsewhere that gathers around the buttock cleft and enters the pilonidal sinus.
Pilonidal sinuses are more common in men because they tend to be hairier.
Sitting for long periods can also increase your chances of getting a pilonidal sinus.

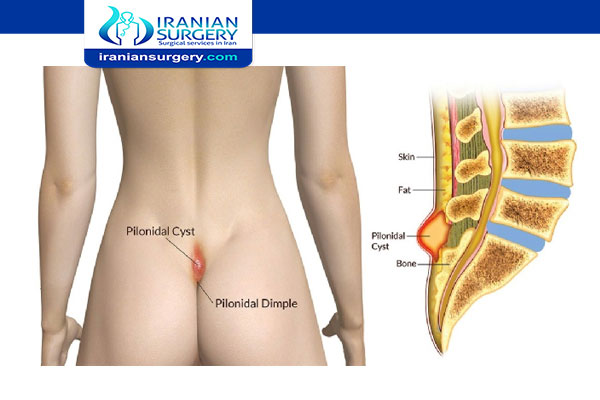
What are the pilonidal sinus symptoms?
- pain when you are sitting (sometimes it can be very painful)
- redness and swelling in the area of your tailbone and just above the crease between your buttocks
- pus oozing from the swollen area
- tenderness when the swollen area is touched
- sometimes fever, weakness, or nausea
The size of the pilonidal cyst may range from a small tender dimple to a large painful area.
Read more about: Pilonidal cyst surgery recovery wound
How to Prevent from pilonidal cysts
To help prevent pilonidal cysts, try to:
- Keep the area clean
- Lose weight if needed
- Avoid prolonged sitting
If you've had pilonidal cysts in the past, you might want to regularly shave the area or use hair removal products to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Read more about: Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Are pilonidal cysts cancerous?
While the cyst is not serious, it can become an infection and should therefore be treated. When a pilonidal cyst gets infected, it forms an abscess, eventually draining pus through a sinus. The abscess causes pain, a foul smell, and drainage. This condition is not serious. If a chronically infected pilonidal cyst isn't treated properly, you may be at slightly increased risk of developing a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Read more about: Exercise after pilonidal cyst surgery
What happens if pilonidal cyst goes untreated?
Pilonidal cysts can cause pain and need to be treated. Pilonidal cysts can be a one-time (acute) problem or you may have chronic (returning) cysts. If they're not treated, chronic pilonidal cysts can also lead to abscesses (swollen pockets of infection) and sinus cavities (empty spaces underneath the skin).
Why do pilonidal cysts smell so bad?
When a pilonidal cyst gets infected, it forms an abscess, eventually draining pus through a sinus. The abscess causes pain, a foul smell, and drainage. The cells that form the walls of the cysts secrete a protein, keratin, into the cyst. When the cyst drains, the secretions can be foul-smelling.
Read more about: Pilonidal sinus surgery recovery time
Does everyone have a pilonidal sinus?
Pilonidal sinuses are most common in young adults and are rarely seen in children or people over 40 years old . They happen slightly more often in men than women and seem to occur more often in people with a lot of body hair Certain factors increase the risk of developing a pilonidal sinus including:
- spending lots of time sitting down
-obesity.
-a previous injury to the skin
-frequent irritation of the skin
- a family history of the condition.
Read more about: Pilonidal sinus treatment
How long can a pilonidal cyst go untreated?
If a chronically infected pilonidal cyst is left untreated, you may be at a slightly increased risk of developing skin cancer. Such type of skin cancer caused by pilonidal sinus is called squamous cell carcinoma(SCC). This occurs in rare and severe cases of pilonidal sinus, but if SCC occurs the right treatment of both cancer and the pilonidal sinus is required. If a person leaves pilonidal sinus untreated or faces the troubles of recurrent pilonidal sinus, he or she is at increased risk of skin cancer. Such type of skin cancer that pilonidal sinus causes are called squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma occurs in rare and severe cases of pilonidal sinus. But, if it occurs, proper treatment of both cancer and the pilonidal sinus is mandatory.
Read more about: Pilonidal Sinus

