Ovarian cancer Medscape
ovarian cancer Medscape
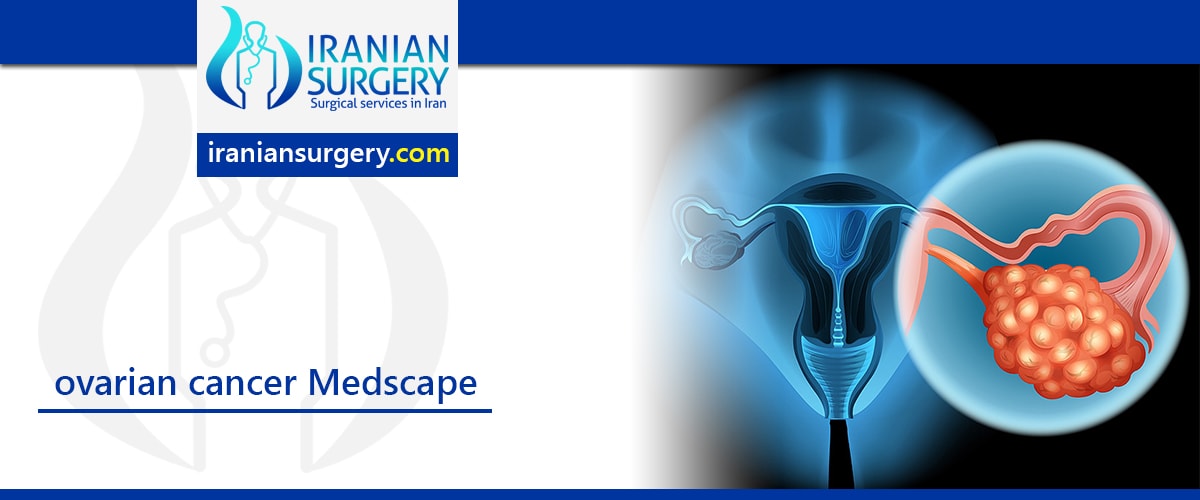
Ovarian cancer is the most common cause of cancer death from gynecologic tumors in the United States. Malignant ovarian lesions include primary lesions arising from normal structures within the ovary and secondary lesions from cancers arising elsewhere in the body. Primary lesions include epithelial ovarian carcinoma (70% of all ovarian malignancies). Current research suggests that the majority of these originate from the fallopian tubes.
Stromal tumors of the ovary include germ-cell tumors, sex-cord stromal tumors, and other more rare types. Metastases to the ovaries are relatively frequent; common sources are tumors in the endometrium, breast, colon, stomach, and cervix.
The presence of advanced ovarian cancer is often suspected on clinical grounds but can be confirmed only pathologically by removal of the ovaries or, when disease is advanced, by sampling tissue or ascitic fluid.
Current guidelines from the Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the American Society of Clinical Oncology recommend that the primary clinical evaluation for ovarian cancer include a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and intravenous contrast, and chest imaging (CT preferred) to evaluate the extent of disease and the feasibility of surgical resection. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend ultrasound and/or abdominal/pelvic CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as clinically indicated, and chest CT or x-ray, as clinically indicated.
10 common questions about Ovarian cancer Medscape
[kkstarratings]


