Laparoscopic infertility treatment in iran
Laparoscopic infertility treatment in iran
Laparoscopic surgery is used to look more closely at infertility problems or to diagnose and treat complications such as adhesion, fibroids, infection, or endometriosis that may have caused infertility. Laparoscopy is less expensive than other surgical procedures, and it is faster to recover. Here's how you can do laparoscopy to diagnose and treat infertility problems and aftercare.
prescribe laparoscopic in the diagnosis of infertility
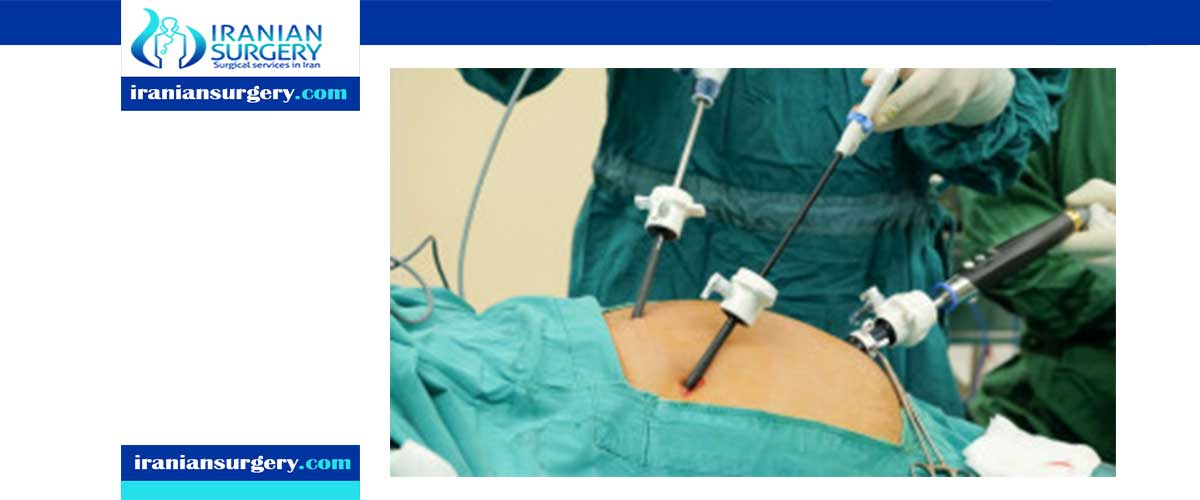
Laparoscopy is a simple, less invasive surgery in which one or more small incisions are made on the abdomen and inserted into a device called a laparoscope that has lights and a camera, the organs inside the abdominal or pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy can be used to find and treat complications such as cysts, adhesions, fibroids, endometriosis, and infections that may cause infertility. Your doctor may also treat the problem or remove the tissues if needed during laparoscopic surgery. In cases where the physician has not been able to detect infertility through tests or hysteroscopy, he may recommend laparoscopy for further examination. Laparoscopy is usually prescribed for infertility treatment if any:
- To examine and remove abnormal masses such as tumors in the abdomen or pelvis
- Evaluation and treatment of endometriosis
- Investigation and treatment of ectopic pregnancy
- Evaluation and treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Investigation and treatment of complications such as ovarian cysts, adhesions and fibroids
- For uterine or ovarian tissue biopsy
- Study and treatment of uterine tubes problem
 Pre-laparoscopic preparation
Pre-laparoscopic preparation
Your doctor or nurse will usually give you pre-operative advice before surgery. You need to pay attention and act on them. They advise you not to eat for 4 hours before performing a laparoscopy. You may need to go to the hospital two hours earlier on the day of surgery. Remember to wear jewelry, glasses or lenses when preparing for surgery. You may be prescribed medications for bowel emptying, which you may need to take a few hours or a day before laparoscopy, as instructed.
Your spouse, acquaintance, or friend will need to be with you on the day of the operation to accompany you and then bring you home. Before examining any problems that may affect this procedure, you will be prescribed ultrasound, CT or MRI, as well as blood and urine tests before the procedure begins. The results of these tests will look at problems such as infection or cancer that may affect this practice. You should tell your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Abdominal hernia
- Cancer of one of the abdominal organs
- Abdominal surgery history
- Taking any drug or drug allergy
- Taking blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin
- If you are pregnant or may become pregnant
How laparoscopic perform?
Laparoscopy is performed by a surgeon or gynecologist and is performed in a hospital. Complete anesthesia is usually used to do this, but doctors may also diagnose other types of anesthesia, such as spinal or spinal anesthesia. Your urine should be empty about an hour before surgery. Liquids and medicines will enter your body through IV injection, or iv. You may also be given a sedative.
After anesthesia, the respiratory tract and catheter are usually inserted. Then one to three incisions are made in the abdomen and at the belly button, and to create enough space for the work, a carbon dioxide gas is inserted into the abdomen to fill the abdomen with wind. This gas can be clearly seen by removing the abdominal wall from the internal organs. The laparoscope is then inserted into the abdomen to examine the organs. Your doctor may use other tools to remove the tissue sample, treat the affected part, or remove the cyst. Laparoscopes may be equipped with a laser to make this easier.
When the operation is complete, all the tools are removed and the gas exits into the abdominal cavity. They are then sutured and bandaged for surgery. Laparoscopic wounds are very small and will heal after a while. Laparoscopic surgery can take anywhere from 2 to 5 minutes depending on the procedure, but it may take longer if an operation such as endometriosis is observed and treated. You will be in the recovery ward for two to four hours after the operation. Your daily activities can usually start the day after the operation, but you should avoid exercising for up to a week.
Necessary care after laparoscopy
How is the laparoscopy aftercare?
After laparoscopy, you will be immediately transferred to the recovery ward, where the nurses will monitor your vital signs such as body temperature, blood pressure, blood oxygen level and heart rate. You will be in recovery for two to four hours before being discharged. If you perform general anesthesia, you will fall asleep during the procedure and do not feel anything. After waking up, you will feel sleepy for a few hours and you will feel tired and painful for a few days after the laparoscopy.
You may have a little bit of a sore throat because of the breathing tube that was inserted in your throat during surgery. You can gargle lukewarm water to improve sore throat. If you are numb to surgery, you may feel pain for several days after the effect of the anesthetic has disappeared. The area around the surgery may be bruised for several days and you may feel pain. Your doctor will usually prescribe painkillers orally or suppositories for your relief. You may also be given antibiotics to prevent any infection.
After surgery you may feel bloated, it is best not to drink carbonated drinks until two days after the laparoscopy to avoid painful bloating and vomiting. The gas used in laparoscopic surgery may stimulate the diaphragm for several days. You may also feel pain in your abdomen for up to two days after the procedure. A little bit of gas injected into the abdominal cavity may penetrate under your skin and make it look like a scratch by rubbing the areas around the sutures.
This problem is not serious and disappears after a few days. You may also have vaginal bleeding a few days after surgery. It is best to follow your doctor's recommendations. Do not lift or lift heavy objects for up to a week after surgery. Keep the cut wound clean and replace the bandage regularly as directed by your doctor or nurse. After surgery there is a risk of bleeding, infection or organ damage, so contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bleeding or discharge from sutures
- Redness or swelling of the area around the surgical site
- Itching for more than a few days or worse
10 common question about Laparoscopic infertility treatment
[kkstarratings]


