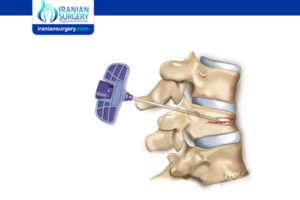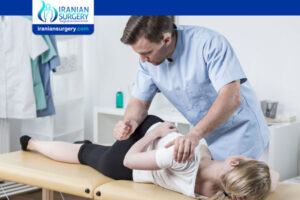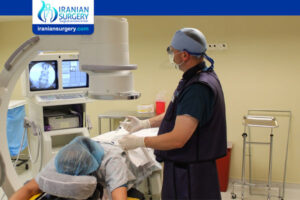
The face-lift, also known as a Rhytidectomy, is an anti-aging procedure that can provide favorable results for individuals …
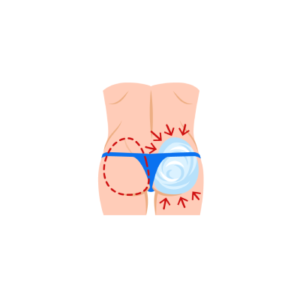
This surgery can be performed through two methods, namely fat transfer, and buttock implants …
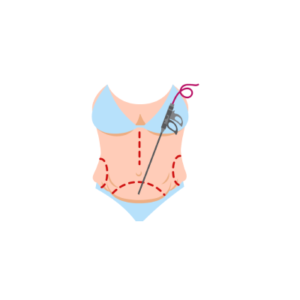
A tummy tuck procedure usually lasts between two to four hours depending on your skin type, the degree …
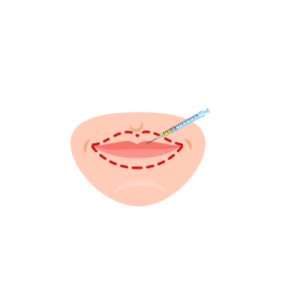
Lip augmentation is a fairly common cosmetic surgery. While some people have naturally beautiful and full lips …
This plastic surgery is done by placing implants behind the breast tissue or under the chest muscle. It is an …

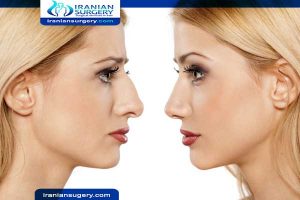
Rhinoplasty is a complex surgery that should only be performed by experienced surgeons with relevant …
You can travel to Iran by air, land or sea. Usually, our clients prefer air transportation. All cities with Iranian Surgery representative branches have international airports with many daily flights. Once you enter Iran, your airport pick-up and transportation in the city between your hotel and clinic/hospital will be covered by Iranian Surgery as a complimentary service. For getting around in the city, the client’s hotel is often in locations, which makes it easy to access everything you might need to buy or visit. Underground railway system (Metro), Personal drivers, and online taxi services are also available. If you want to travel to other cities in Iran, your options are airplanes, trains, and the Iran bus service, which works very well for traveling from city to city.
Clients must be aware that they will no longer have access to their bank accounts or credit cards while traveling in Iran. Therefore, they should bring the money they need in cash or transfer it to one of the Iranian Surgery accounts before traveling to Iran. it is recommended to bring the cash in Euro or USD as these two currencies are easier to exchange.
If you’re traveling to Iran for treatment, having a companion you’re familiar with will have a positive mental and physical impact. However, if you decide to travel alone, that will also be perfectly fine, and you won’t have any limitations. Iran is absolutely safe for solo travelers. Iranian Surgery guides/interpreters welcome you at the airport and will accompany you throughout check-ups, pre-op, administrative, post-op, recovery, nursing care, sightseeing, shopping, and more. From the moment you land in Iran, the Iranian Surgery staff and experts will be in contact with you. You will not be left alone during your stay in Iran as you are a member of the Iranian surgery family, and we will ensure everything goes well for you.
Despite what you usually read or see in the media, Iran is a perfectly safe country to travel to. The people of Iran are very hospitable towards foreigners. Iran is a suitable destination for family travel as well as solo travel. In the following links, you can find testimonies from our clients in which they talk about their experiences in Iran.
Citizens of the below list do not need a visa to travel to Iran: Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, China, Russia, Syria, Iraq, Oman, Kazakhstan, Georgia, Lebanon, Egypt, Malaysia, Venezuela Citizens of Jordan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Somalia, Colombia, the USA, the UK, and Canada must have their visas confirmed in the Iran embassy before traveling to Iran. Other nationalities can apply for e-visa online and get it issued at Iran’s airport upon arrival. Iranian Surgery can apply for your visa as the party responsible for your treatment. There are two types of visas that Iranian Surgery clients can apply for: • T-visa, which is for treatment purposes. You need Iranian Surgery to apply for it as your health care provider. • B-visa is a tourist visa; clients can apply for it themselves or ask Iranian Surgery to help. Your visa is valid for 30 days and can be extended.