Endoscopy in Iran
overview
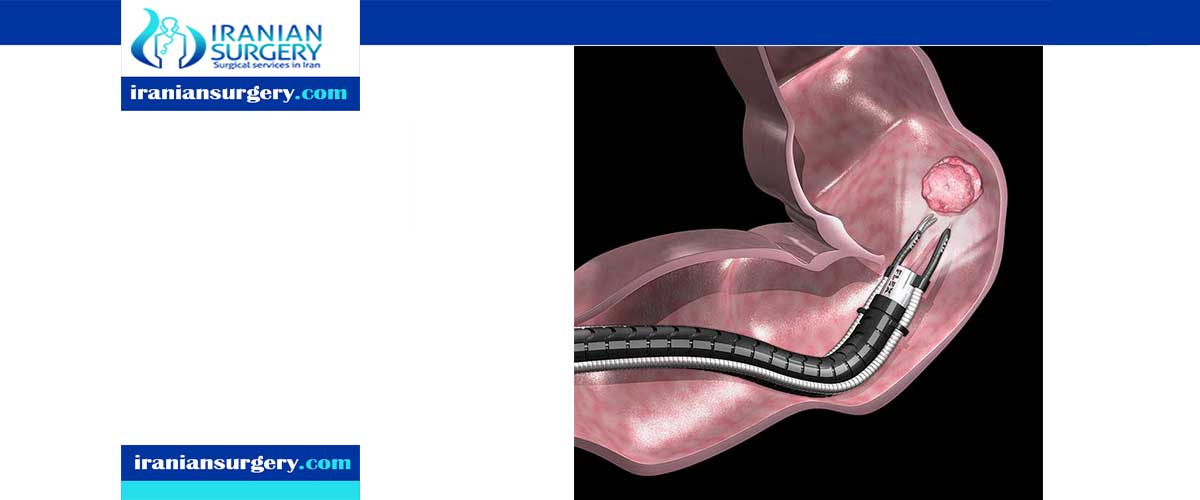
Endoscopy is a nonsurgical procedure used to examine a person's digestive tract. Using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera attached to it, your doctor can view pictures of your digestive tract on a color TV monitor.
During an upper endoscopy, an endoscope is easily passed through the mouth and throat and into the esophagus, allowing the doctor to view the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine.
Similarly, endoscopes can be passed into the large intestine (colon) through the rectum to examine this area of the intestine. This procedure is called sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy depending on how far up the colon is examined.
A special form of endoscopy called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography, or ERCP, allows pictures of the pancreas, gallbladder, and related structures to be taken. ERCP is also used for stent placement and biopsies.
Endoscopic ultrasound or EUS combines upper endoscopy and ultrasound examination to obtain images and information about various parts of the digestive tract.
Why it's done
Gastrointestinal tract
An upper endoscopy is used to diagnose and, sometimes, treat conditions that affect the upper part of your digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach and beginning of the small intestine (duodenum).
Your doctor may recommend an endoscopy procedure to:
- Investigate signs and symptoms.An endoscopy may help your doctor determine what's causing digestive signs and symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Diagnose.Your doctor may use an endoscopy to collect tissue samples (biopsy) to test for diseases and conditions, such as anemia, bleeding, inflammation, diarrhea or cancers of the digestive system.
- Your doctor can pass special tools through the endoscope to treat problems in your digestive system, such as widening a narrow esophagus, clipping off a polyp or removing a foreign object.
How do I prepare for an endoscopy?
Your doctor will give you complete instructions on how to prepare. Most types of endoscopy require you to stop eating solid foods for up to 12 hours before the procedure. Some types of clear liquids, such as water or juice, might be allowed for up to two hours before the procedure. Your doctor will clarify this with you.
Your doctor may give you laxatives or enemas to use the night before the procedure to clear your system. This is common in procedures involving the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the anus.
Prior to the endoscopy, your doctor will do a physical examination and go over your complete medical history, including any prior surgeries.
Be sure to tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and nutritional supplements. Also alert your doctor about any allergies you might have. You may need to stop taking certain medications if they might affect bleeding, especially anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
Types of Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor to view the inside of a person's body. Doctors use it to diagnose diseases in the following parts of the body:
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Colon
- Ears
- Nose
- Throat
- Heart
- Urinary tract
- Joints
During the procedure
For most endoscopic procedures, you will not need to stay in the hospital overnight.
You may receive a type of anesthesia, depending on the type of endoscopy. Anesthesia blocks the awareness of pain. You may be awake, drowsy, or asleep during the procedure depending on the type of anesthesia you have. While you receive anesthesia, your health care team will provide "anesthesia care," which includes monitoring your temperature, blood pressure, and heart rate.
During the procedure, your doctor will review and, possibly, record images from the endoscope. He or she will also perform any procedures. This could include the collecting tissue for testing.
After the procedure
After the endoscopy, you will rest in a recovery area. You may have mild side effects. Side effects depend on the type of endoscopy and may include a sore, dry throat, or bloating and gas.
Depending on the type of anesthesia you receive, you may need to have someone drive you home.
What should I expect after returning home?
Problems from an endoscopy are uncommon, but they can happen. These include a hole or tear in the examination area, bleeding, or infection.
Talk with your doctor immediately if you have any of these symptoms:
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Chest pain
- Abnormal stool
- Shortness of breath
- Severe abdominal pain or other unusual symptoms
Risks
An endoscopy is usually a safe procedure, and the risk of serious complications is very low.
Possible complications include:
an infection in a part of the body the endoscope is used to examine – this may require treatment with antibiotics
piercing or tearing (perforation) of an organ, or excessive bleeding – you may need surgery to repair tissue or organ damage; sometimes a blood transfusion may also be needed
Sedation
Sedation is usually safe, but it can occasionally cause complications, including:
feeling or being sick
a burning sensation at the site of the injection
saliva or, rarely, small particles of food falling into the lungs, triggering an infection (aspiration pneumonia)
irregular heartbeat or low blood pressure
breathing difficulties
Recovery
Recovery will depend on the type of procedure. For an upper endoscopy, which is used to enable a doctor to examine the upper gastrointestinal tract, the patient will be observed for some time after the procedure, usually around one hour, while any sedative medication wears off.
The person should not usually work or drive for the rest of the day, because of the sedative effect of the medication used to prevent the pain.
There may be some soreness. With this type of endoscopy, there may be bloating and a sore throat, but these usually resolve quickly.
10 common questions about Endoscopy in Iran
[kkstarratings]