Dental X-ray (OPG)
What Is Orthopantomography?
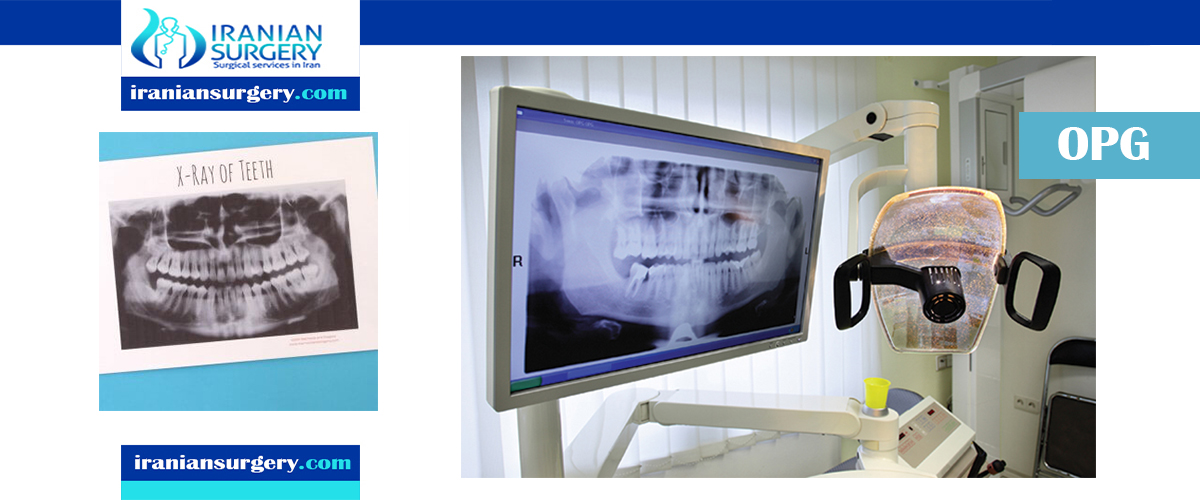
Orthopantomography, also known as an OPG X-ray (or simply OPG), panoramic radiography, or a pantogram is a type of X-ray scan that gives a panoramic or wide view of the lower face. It can display all the teeth on both jaws on one film, including those that have not surfaced or erupted yet, such as wisdom teeth. It also offers a view of the jawbone and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jaw to the rest of the skull.
Read more about : Dental implant in Iran
What Does An OPG X-Ray Involve?
An OPG is an X-ray of the lower face. Like all X-rays, it involves using short blasts of low-level radiation to create images of inside the body – in this case, of the bones and teeth.
The procedure for dental panoramic radiography consists of the patient resting their chin on a small shelf in front of the X-ray machine and bite softly on a sterile mouthpiece. This will keep the head and mouth steady while the images are taken.
The panoramic X-ray machine consists of a rotating arm with the X-ray source at one end and the film mechanism (which captures the image) at the opposite extremity. The arm rotates around the patient’s head to capture the wide view of their mouth and jaw.
The procedure is performed very quickly. As with any X-ray, the patient feels no discomfort during the procedure and can continue with their daily routine afterwards.
Read more about : Root canal trearment
Why Is an OPG X-Ray Done?
Orthopantomography is a technique used in dentistry to allow the dentist to view all their patient’s teeth and determine their number, position, and growth, including those that have not yet erupted. An OPG X-ray might be done to plan orthodontic treatment, to detect the presence or asses the development of wisdom teeth, to examine the jawbone, or for a general overview of the patient’s dental health.
What happens during a dental x-ray?
You may be asked to remove jewelry, eyeglasses, and any metal objects that may obscure the images. You will be asked to stand with your face resting on a small shelf and to bite gently on a sterile mouth piece to steady your head. It is important to stay very still while the x-ray is taken. You will not feel any discomfort during the procedure.
OPG Advances / developments
Dental X-ray technology is currently moving away from traditional film technology to digital X-ray technology, using electronic sensors and computers to create images. Digital X-rays allow instant review of the scans without having to wait to develop the film. They are also more efficient at getting high-quality images first time, reducing the number of repeat scans necessary, and therefore reducing the patient’s exposure to radiation.
Source:
https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/medical-dictionary/opg-x-ray-orthopantomography

