Common Materials Used for Making Dental Crowns
Crowns are used for restoring teeth that have been damaged or diseased, and essentially they protect and extend the functionality of your challenged teeth, or to cap implants. Most dentists tell patients their dental crown(s) will last from 5 – 15 years, even though many remain functional significantly longer.
During a recent research project involving approximately 2,300 porcelain fused to metal crowns (PFM) 85% of them lasted over 25 years, and 95% were still stable after 10 years. Most insurance companies are willing to pay for replacement crowns every 8 years, which is an indicator that they must last at least that long.
Types of Dental Crown Materials
There are four different types of materials used for dental crowns:
- All ceramic (porcelain-based).
- Porcelain fused to metal.
- Gold alloys.
- Base metal alloys.
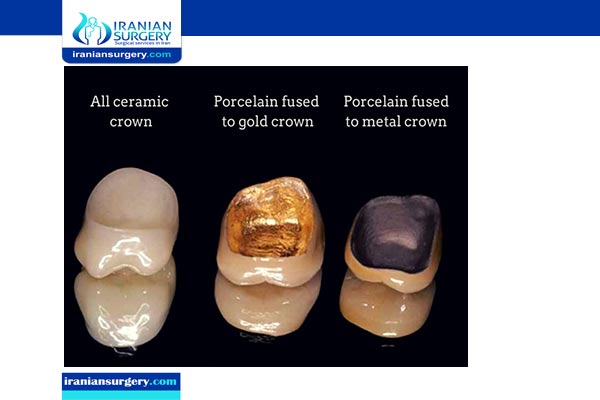
All ceramic (porcelain-based):
Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns have been considered the gold standard for the repair of damaged teeth. PFM crowns have good mechanical properties, satisfactory esthetic results, and an acceptable biological quality needed for periodontal health. However, PFM crowns have some limitations that may limit their use. For example, the esthetic of PFM crowns is limited by the metal framework and the layer of opaque porcelain needed for masking the underlying metal grayish shade. Recently the cost of precious metals has risen markedly making PFM relatively unattractive from an economic standpoint.
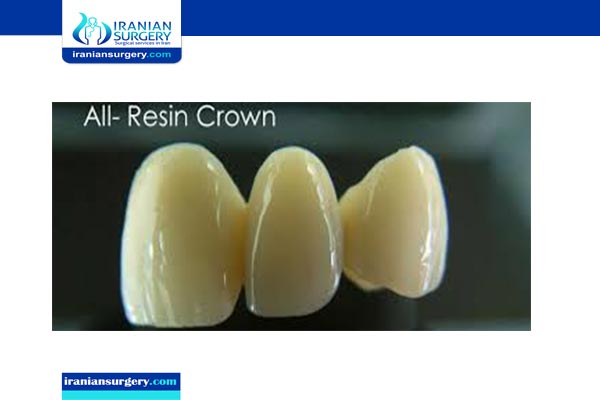
All-ceramic crowns have been used over the last four decades as an alternative for PFM crowns to overcome their esthetic limitations. All-ceramic crowns can be made from different types of ceramic, and not all ceramic types have the same physical and esthetic proprieties. Historically, resin-based crowns were the first metal-free crowns to be used, but they were abandoned because of their low fracture resistance. Newer metal-free crowns are increasingly being used in dental practice; these crowns are made from different ceramic materials such as lithium disilicate, zirconia, leucite-reinforced glass, and glass-infiltrated alumina.
Policy makers require information on the relative benefits and costs associated with different types of crown materials in order to support reimbursement decisions. The objective of this review is to evaluate the clinical and cost-effectiveness of dental PFM and all-ceramic crowns.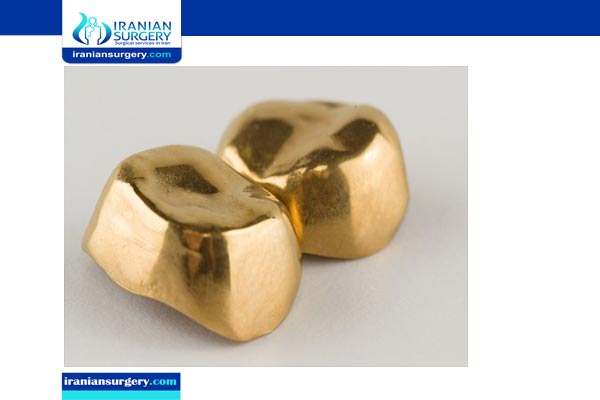
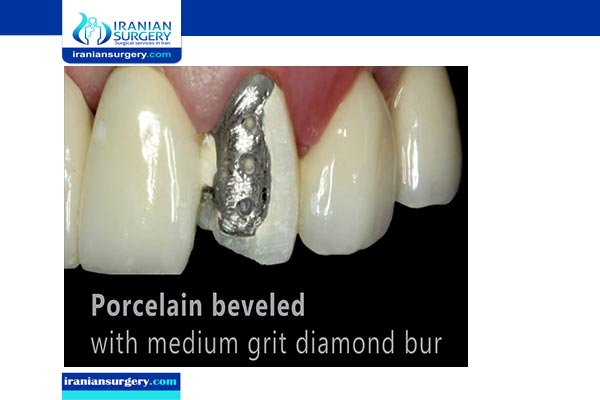
Porcelain fused to metal.
Porcelain fused to metal crowns (or PFM crowns) can be referred to as full-cast crowns which has porcelain fused on most or all parts of the tooth. They are a hybrid between porcelain and metal crowns. The entire crown has a metal layer underlying and porcelain / ceramic on top of it.
Gold alloys.
Although common several years ago, gold crowns are not typically used due to lack of cosmetic appeal and cost (i.e. gold is valued at $1,300 per ounce at time of this writing). This type of crown has a long track record of success in the mouth as they are durable, produce fewer reactions than other metal materials, and they do not wear the opposing teeth. The biggest con for most people is that they are not cosmetically appealing. Gold crowns tend to be a great option for upper back teeth where nobody will see them and where the crown provides the most durability against strong bite forces. Finally, gold crowns require less tooth preparation, which can help for a tooth to be less sensitive, and they can last upwards of 40 years if well maintained! It’s safe to say that gold is a pretty amazing material in the mouth, it just comes at a cost.
A more esthetic option which still takes advantage of gold’s strength is porcelain fused to metal crowns, or PFMs. The substructure of the crown consists of gold/platinum/palladium and other semi-precious metals, while the exterior of the crown is covered in porcelain. Most of the time, there is a small rim of the metal that exists on the inside of the crown where nobody but your dentist/hygienist can see; however, when the gums recede, patients often notice a darkening around the gum line area, making the crown look less life-like because of the undertone. These crowns are fabricated in a dental lab over 2 weeks and are great for all areas of the mouth but play a more integral role restoring the back teeth. These crowns typically last 7-12 years.
Base metal alloys
Base metal alloys contain non-noble metals which provide great strength to the crown and tooth and provide high resistance to corrosion. When preparing the tooth using base metal alloys, the dentist or prosthodontist would remove the least amount of healthy tooth structure. This material is resistant to wear and gentle to opposing teeth.
10 common question about Materials Used for Making Dental Crowns
[kkstarratings]



