Colpotomy procedure in Iran
Colpotomy procedure in Iran
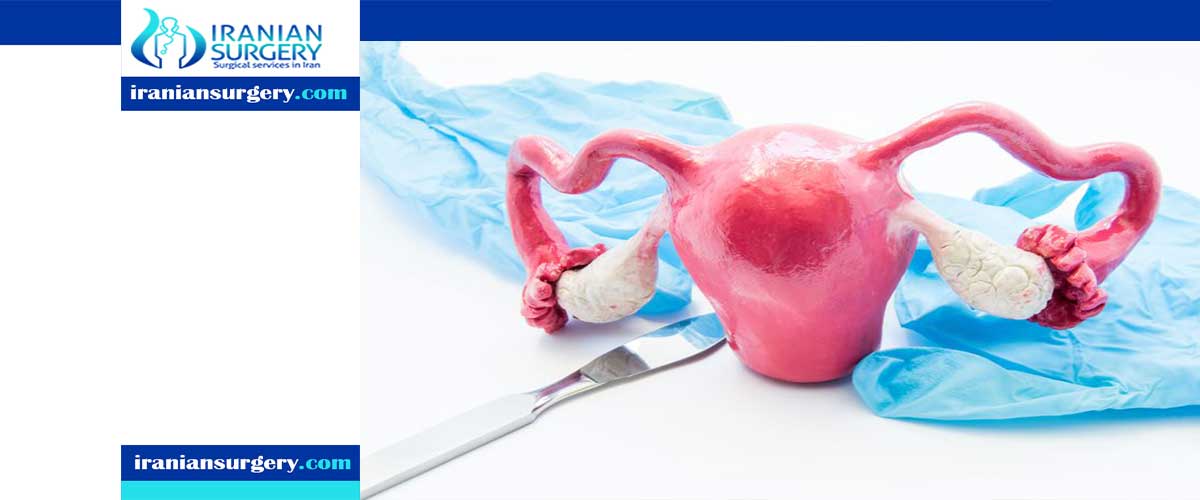
What is Colpotomy?
A colpotomy, also known as a vaginotomy, is a procedure by which an incision is made in the vagina.
A colpotomy is performed either to visualize pelvic structures or to perform surgery on the fallopian tubes or ovaries.
Role of colpotomy in gynecologic surgery
Several gynecologic surgery protocols require a colpotomy as part of the overall surgical procedure. It is performed whenever the surgeon needs to access the vagina. Several of these surgeries include:
. Tubal sterilization. Sterilization is a procedure that can be performed using either abdominal or vaginal procedures. When a vaginal procedure is selected by the surgeon, he performs a colpotomy and may also insert a culdoscope to locate the tubes (culdoscopy), and close them off.
. Removal of myomas. Myomas are fibroid tumors of the muscle tissue of the uterus and they are sometimes removed vaginally by colpotomy.
. Removal of pelvic cysts and masses. In one treatment variant, patients may undergo a laparoscopy followed by a colpotomy for the vaginal extraction of the pelvic cyst or mass.
. Hysterectomy. One technique used to surgically remove the uterus combines three steps, an initial laparoscopic stage, followed by a vaginal stage, and a final laparoscopic stage. The colpotomy is performed during the second step to deliver the uterus into the vagina.
. Dysmenorrhea. Separation of the uterosacral ligaments via colpotomy is an approach that has been used for the relief of dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation).
. Complications in pregnancy and childbirth. Colpotomy may be used in the management of difficult pregnancies and childbirths.
Description
The patient is placed in a supine position on the operating table with her legs in stirrups and the incision site is prepared. An antiseptic solution, such as chlorhexidine, is applied to the skin using highly disinfected forceps and gauze swabs. The patient is covered with surgical drapes with the window positioned directly over the incision site. Throughout the procedure, the vital signs of the patient are monitored (blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate) as well as her level of consciousness and blood loss. Pain management depends on the surgery that requires the colpotomy, and may involve local, regional, or general anesthesia. The incision is only made as large as necessary for the requirements of the overall surgery.
For example, when a decision has been made to remove a myoma by colpotomy, the procedure may proceed as follows:
. A small myoma screw is inserted into the myoma and a grasper with locking mechanism is placed on the lower edge of the wound.
. The myoma is directed toward the cul-de-sac using the myoma screw.
. A colpotomy is performed.
. The myoma is grasped and removed vaginally. During this part of the procedure, the surgeon examines whether the myoma extends into the uterine cavity.
. If it does, the uterus is guided to the colpotomy site. T-clamps are placed on the edges of the wounds and the fundus of the uterus is delivered, via the colpotomy incision, into the vagina.
. The uterus is sutured in three layers (endometrial, myometrial and serosal).
. The repaired uterus is returned to the abdominal cavity.
. The colpotomy incision is sutured.
Who performs the procedure and where is it performed?
A colpotomy is performed by a gynecological surgeon either in an outpatient clinic or in a hospital setting, depending on the overall surgical procedure of which the colpotomy is a part.
Preparation
The procedure is explained to the patient within the broader context of the surgery that includes the colpotomy. Preoperative preparation includes whatever is required for the overall surgical procedure that will be performed.
Aftercare
Aftercare for colpotomy is associated with the overall surgery that required the colpotomy.
For example, if a colpotomy is performed for tubal ligation (female sterilization), the procedure takes only 15-30 minutes and women usually go home the same day. It may take a few days at home to recover. Sexual intercourse is usually postponed until the colpotomy incision is completely healed, and as advised by the doctor. The healing process usually requires several weeks and there are no visible scars. In the case of a colpotomy performed for myoma removal, aftercare is more elaborate with the patient’s vital signs monitored in the recovery room until she regains consciousness.
Risks
Complications such as bleeding, infection, or reaction to the anesthetic, may occur as with any type of gynecological surgery.
Normal results
Colpotomy results are considered normal when the incision performed allows the surgeon to meet the goal of the overall surgical protocol.
10 common question about Colpotomy procedure
[kkstarratings]


