atrial fibrillation in Iran
atrial fibrillation in Iran
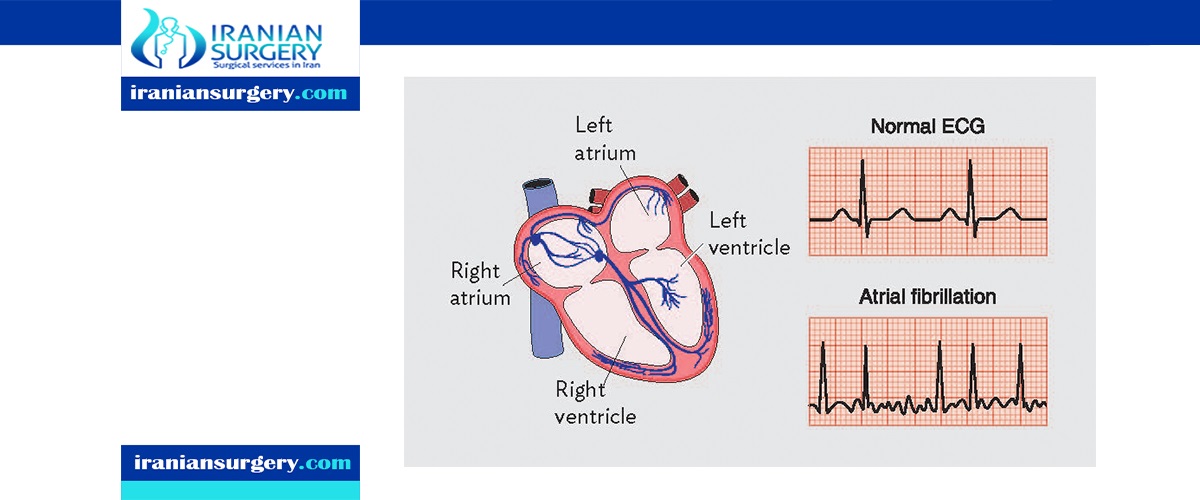
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common types of arrhythmias, which are irregular heart rhythms. Atrial fibrillation causes your heart to beat much faster than normal. Also, your heart’s upper and lower chambers do not work together as they should. When this happens, the lower chambers do not fill completely or pump enough blood to your lungs and body. This can make you feel tired or dizzy, or you may notice heart palpitations or chest pain. Blood also pools in your heart, which increases your risk of forming clots and can leads to strokes or other complications. Atrial fibrillation can also occur without any signs or symptoms. Untreated fibrillation can lead to serious and even life-threatening complications.
Sometimes atrial fibrillation goes away on its own. For some people, atrial fibrillation is an ongoing heart problem that lasts for years. Over time, it may happen more often and last longer. Treatment restores normal heart rhythms, helps control symptoms, and prevents complications. Your doctor may recommend medicines, medical procedures, and lifestyle changes to treat your atrial fibrillation.
What are the Symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
Some people with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms and are unaware of their condition until it's discovered during a physical examination. Those who do have atrial fibrillation symptoms may experience signs and symptoms such as:
- Palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heartbeat or a flip-flopping in your chest
- Weakness
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
What are the risks and causes atrial fibrillation?
AF is linked to several forms of cardiovascular disease, but may occur in otherwise normal hearts. Cardiovascular factors known to be associated with the development of AF include high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, mitral valve stenosis (e.g., due to rheumatic heart disease or mitral valve prolapse), mitral regurgitation, left atrial enlargement, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), pericarditis, congenital heart disease, and previous heart surgery. Additionally, lung diseases (such as pneumonia, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, and sarcoidosis) are thought to play a role in certain people. Disorders of breathing during sleep such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are also associated with AF. Obesity is a risk factor for AF. Hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism are associated with AF development. Caffeine consumption does not appear to be associated with AF, but excessive alcohol consumption ("binge drinking" or "holiday heart syndrome") is linked to AF. Sepsis also increases the risk of developing new-onset atrial fibrillation. Long-term endurance exercise (e.g., long-distance bicycling or marathon running) appears to be associated with a modest increase in the risk of atrial fibrillation in middle-aged and elderly people. Tobacco smoking and secondhand tobacco smoke exposure are associated with an increased risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
How to prevent from atrial fibrillation
To prevent atrial fibrillation, it's important to live a heart-healthy lifestyle to reduce your risk of heart disease. A healthy lifestyle may include:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet
- Increasing your physical activity
- Avoiding smoking
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting or avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- Reducing stress, as intense stress and anger can cause heart rhythm problems
- Using over-the-counter medications with caution, as some cold and cough medications contain stimulants that may trigger a rapid heartbeat
How to Diagnose atrial fibrillation in Iran?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). An ECG uses small sensors (electrodes) attached to your chest and arms to sense and record electrical signals as they travel through your heart. This test is a primary tool for diagnosing atrial fibrillation.
- Holter monitor. This portable ECG device is carried in your pocket or worn on a belt or shoulder strap. It records your heart's activity for 24 hours or longer, which provides your doctor with a prolonged look at your heart rhythms.
- Event recorder. This portable ECG device is intended to monitor your heart activity over a few weeks to a few months. When you experience symptoms of a fast heart rate, you push a button, and an ECG strip of the preceding few minutes and following few minutes is recorded. This permits your doctor to determine your heart rhythm at the time of your symptoms.
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart. Usually, a wandlike device (transducer) is held on your chest. Sometimes, a flexible tube with the transducer is guided down your throat through to your esophagus. Your doctor may use an echocardiogram to diagnose structural heart disease or blood clots in the heart.
- Blood tests. These help your doctor rule out thyroid problems or other substances in your blood that may lead to atrial fibrillation.
- Stress test. Also called exercise testing, stress testing involves running tests on your heart while you're exercising.
- Chest X-ray. X-ray images help your doctor see the condition of your lungs and heart. Your doctor can also use an X-ray to diagnose conditions other than atrial fibrillation that may explain your signs and symptoms.
atrial fibrillation treatment in Iran
Your doctor will decide on the best treatment, depending on:
- how bad your symptoms are
- the cause (if known)
- how long you have had the problem
- your risk of stroke and other problems
- the risks of each treatment.
Medicines
Most people with atrial fibrillation will need to take medicines. Your doctor will decide the best ones.
They may prescribe medicines to restore or maintain a normal heart beat in the short or long term.
Most medicines usually have to be taken for the long term. It’s important to take medicines as prescribed.
Procedures
Your doctor may also recommend procedures like:
- surgery (very rare) to try to make your heart beat normally.
- electrical cardioversion
- catheter ablation
Catheter ablation is a procedure that very carefully destroys the diseased area of your heart and interrupts abnormal electrical circuits.
It's an option if medicine has not been effective or tolerated.
Catheters (thin, soft wires) are guided through 1 of your veins into your heart, where they record electrical activity.
When the source of the abnormality is found, an energy source, such as high-frequency radiowaves that generate heat, is transmitted through 1 of the catheters to destroy the tissue.
The procedure usually takes 2 to 3 hours, so it may be carried out under general anaesthetic, which means you're unconscious during the procedure.
You should make a quick recovery after having catheter ablation and be able to carry out most of your normal activities the next day.
But you should not lift anything heavy for 2 weeks, and driving should be avoided for the first 2 days.
Lifestyle changes
As with other heart conditions the best way to manage your heart health is to make sure you see your doctor regularly and reduce the risks. It’s important to manage the risk factors for heart disease to avoid more heart problems.
You may also need to reduce your caffeine intake.
What are the atrial fibrillation complications?
Sometimes atrial fibrillation can lead to the following complications:
- Stroke. In atrial fibrillation, the chaotic rhythm may cause blood to pool in your heart's upper chambers (atria) and form clots. If a blood clot forms, it could dislodge from your heart and travel to your brain
- Heart failure. Atrial fibrillation, especially if not controlled, may weaken the heart and lead to heart failure — a condition in which your heart can't circulate enough blood to meet your body's needs
10 common questions about atrial fibrillation in Iran
[kkstarratings]



