Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty (literally "[re-]forming of joint") is an orthopedic surgical procedure where the articular surface of a musculoskeletal joint is replaced, remodeled, or realigned by osteotomy or some other procedure. It is an elective procedure that is done to relieve pain and restore function to the joint after damage by arthritis or some other type of trauma.
Types
Joint replacement
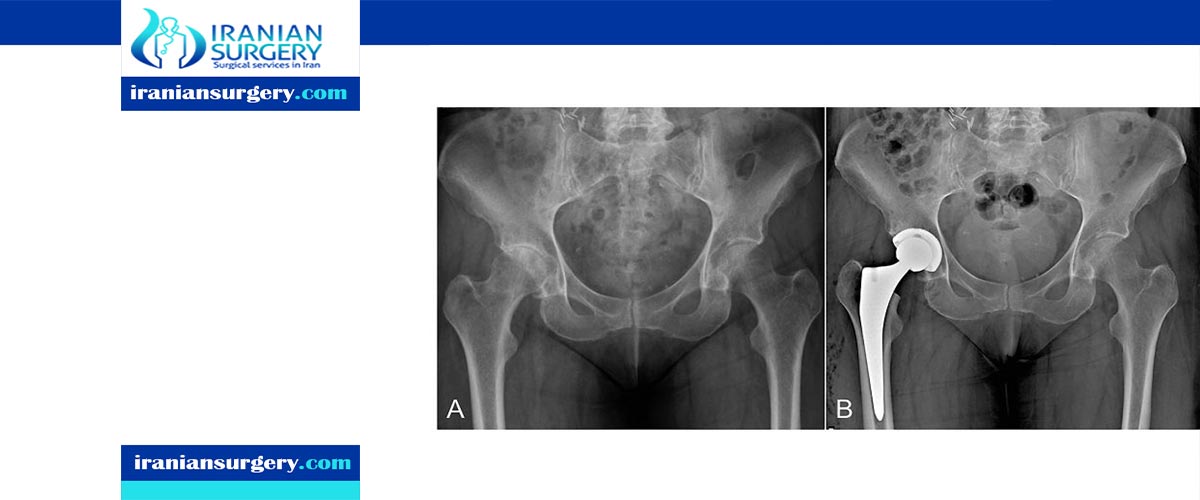
For the last 45 years the most successful and common form of arthroplasty is the surgical replacement of arthritic or destructive or necrotic joint or joint surface with a prosthesis. For example a hip joint that is affected by osteoarthritis may be replaced entirely (total hip arthroplasty) with a prosthetic hip. This would involve replacing both the acetabulum (hip socket) and the head and neck of the femur. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain, to restore range of motion and to improve walking ability, thus leading to the improvement of muscle strength.
Other types of arthroplasty
- Interpositional arthroplasty, previously a popular form of arthroplasty, with interposition of some other tissue like skin, muscle or tendon to keep inflammatorysurfaces apart
- Excisional or resection(al) arthroplasty in which joint surface and bone is removed. The remaining ends are attached, or left to give time for scar tissue to fill in the gap. One variant of is the Stainsby procedure which consists of excision of part of a proximal phalanx in a metatarsophalangeal joint, reduction of the plantar plateand kirschner wire fixation of the metacarpal bone to the remaining phalanx.
- Resurfacing arthroplasty, where one or both bone surfaces are trimmed and replaced with a smooth metal covering.
- Mold arthroplasty,
- Silicone replacement arthroplasty
- Osteotomy to restore or modify joint congruity
Complications and Improvements
Arthroplasty presents various and continuous challenges to the engineer and surgeon. The prosthesis selected must be nontoxic yet resistant, compatible and durable. Meeting all these criteria usually means that the prosthesis will not last 10–20 years. 75% of artificial knees will last 20 years and 90% will last 10 years.
In recent years the technology has been improved with a porous-coated prosthesis which allows for stronger bonding to the body, but even more notable improvements have derived from the recent explosion in computer-assisted design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM). Using X-rays and other scans of the patient as well as modern 3D printing, personally tailored prostheses are a reality for more and more individuals.
Indications
- osteoarthritis (OA)
- rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- avascular necrosis (AVN) or osteonecrosis (ON)
- congenital dislocation of the hip joint (CDH) Hip dysplasia (human)
- acetabular dysplasia (shallow hip socket)
- frozen shoulder, loose shoulder
- traumatized and malaligned joint
- joint stiffness
Complications
- Blot Clots or Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Periprosthetic fracture
- Loosening
- Mechanical wear
- Failure
10 common question about Arthroplasty
[kkstarratings]


