Ectopic pregnancy treatment
Ectopic Pregnancy
What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
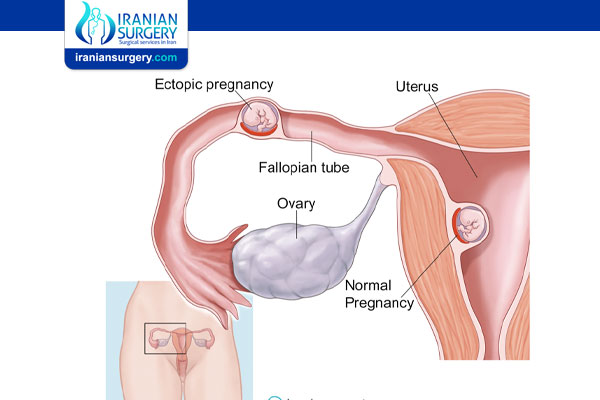
Pregnancy begins with a fertilized egg. Normally, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus.
An ectopic pregnancy most often occurs in a fallopian tube, which carries eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This type of ectopic pregnancy is called a tubal pregnancy. Sometimes, an ectopic pregnancy occurs in other areas of the body, such as the ovary, abdominal cavity or the lower part of the uterus (cervix), which connects to the vagina.
An ectopic pregnancy can't proceed normally. The fertilized egg can't survive, and the growing tissue may cause life-threatening bleeding, if left untreated.
About Iranian Surgery
Iranian surgery is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best Surgeons in Iran. The price of Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined based on photos and an in-person assessment with the doctor.
For more information about the cost of Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment in Iran and to schedule an appointment in advance, you can contact Iranian Surgery consultants via WhatsApp number 0098 901 929 0946. This service is completely free.
Before Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Symptoms
You may not notice any symptoms at first. However, some women who have an ectopic pregnancy have the usual early signs or symptoms of pregnancy — a missed period, breast tenderness and nausea.
If you take a pregnancy test, the result will be positive. Still, an ectopic pregnancy can't continue as normal.
As the fertilized egg grows in the improper place, signs and symptoms become more noticeable.
Early warning of ectopic pregnancy
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
If blood leaks from the fallopian tube, you may feel shoulder pain or an urge to have a bowel movement. Your specific symptoms depend on where the blood collects and which nerves are irritated.
Emergency symptoms
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it can cause the tube to rupture. Heavy bleeding inside the abdomen is likely. Symptoms of this life-threatening event include extreme lightheadedness, fainting and shock.
When to see a doctor
Seek emergency medical help if you have any signs or symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, including:
. Severe abdominal or pelvic pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
. Extreme lightheadedness or fainting
. Shoulder pain
Causes
A tubal pregnancy — the most common type of ectopic pregnancy — happens when a fertilized egg gets stuck on its way to the uterus, often because the fallopian tube is damaged by inflammation or is misshapen. Hormonal imbalances or abnormal development of the fertilized egg also might play a role.
Risk factors
Some things that make you more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy are:
. Previous ectopic pregnancy. If you've had this type of pregnancy before, you're more likely to have another.
. Inflammation or infection. Sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, can cause inflammation in the tubes and other nearby organs, and increase your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
. Fertility treatments. Some research suggests that women who have in vitro fertilization (IVF) or similar treatments are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Infertility itself may also raise your risk.
. Tubal surgery. Surgery to correct a closed or damaged fallopian tube can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
. Choice of birth control. The chance of getting pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) is rare. However, if you do get pregnant with an IUD in place, it's more likely to be ectopic. Tubal ligation, a permanent method of birth control commonly known as "having your tubes tied," also raises your risk, if you become pregnant after this procedure.
. Smoking. Cigarette smoking just before you get pregnant can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. The more you smoke, the greater the risk.
Complications
An ectopic pregnancy can cause your fallopian tube to burst open. Without treatment, the ruptured tube can lead to life-threatening bleeding.
Prevention
There's no way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but here are some ways to decrease your risk:
. Limiting the number of sexual partners and using a condom during sex helps to prevent sexually transmitted infections and may reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
. Don't smoke. If you do, quit before you try to get pregnant.
Diagnosis
A pelvic exam can help your doctor identify areas of pain, tenderness, or a mass in the fallopian tube or ovary. However, your doctor can't diagnose an ectopic pregnancy by examining you. You'll need blood tests and an ultrasound.
Pregnancy test
Your doctor will order the human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) blood test to confirm that you're pregnant. Levels of this hormone increase during pregnancy. This blood test may be repeated every few days until ultrasound testing can confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy — usually about five to six weeks after conception.
Ultrasound
A transvaginal ultrasound allows your doctor to see the exact location of your pregnancy. For this test, a wandlike device is placed into your vagina. It uses sound waves to create images of your uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, and sends the pictures to a nearby monitor.
Abdominal ultrasound, in which an ultrasound wand is moved over your belly, may be used to confirm your pregnancy or evaluate for internal bleeding.
Other blood tests
A complete blood count will be done to check for anemia or other signs of blood loss. If you're diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor may also order tests to check your blood type in case you need a transfusion.
During Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Treatment
A fertilized egg can't develop normally outside the uterus. To prevent life-threatening complications, the ectopic tissue needs to be removed. Depending on your symptoms and when the ectopic pregnancy is discovered, this may be done using medication, laparoscopic surgery or abdominal surgery.
Medication
An early ectopic pregnancy without unstable bleeding is most often treated with a medication called methotrexate, which stops cell growth and dissolves existing cells. The medication is given by injection. It's very important that the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is certain before receiving this treatment.
After the injection, your doctor will order another HCG test to determine how well treatment is working, and if you need more medication.
Laparoscopic procedures
Salpingostomy and salpingectomy are two laparoscopic surgeries used to treat some ectopic pregnancies. In these procedure, a small incision is made in the abdomen, near or in the navel. Next, your doctor uses a thin tube equipped with a camera lens and light (laparoscope) to view the tubal area.
In a salpingostomy, the ectopic pregnancy is removed and the tube left to heal on its own. In a salpingectomy, the ectopic pregnancy and the tube are both removed.
Which procedure you have depends on the amount of bleeding and damage and whether the tube has ruptured. Also a factor is whether your other fallopian tube is normal or shows signs of prior damage.
Emergency surgery
If the ectopic pregnancy is causing heavy bleeding, you might need emergency surgery. This can be done laparoscopically or through an abdominal incision (laparotomy). In some cases, the fallopian tube can be saved. Typically, however, a ruptured tube must be removed.
After Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Can I get pregnant again after an ectopic pregnancy?
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can go on to have future successful pregnancies. There is a higher risk of having future ectopic pregnancies after you have had one. It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about the causes of your ectopic pregnancy and what risk factors you may have that could cause a future ectopic pregnancy.
How long should I wait before becoming pregnant again after an ectopic pregnancy?
You should talk to your healthcare provider about future pregnancies after being treated for an ectopic pregnancy. Although pregnancy may happen quickly after treatment, it’s often best to wait about three months. This allows your fallopian tube time to heal and decreases the risk of another ectopic pregnancy.
If my fallopian tube is removed, can I still have a baby?
In most cases, you can still have a baby if you have had one of your fallopian tubes removed. You have a pair of fallopian tubes and eggs can still travel down your remaining tube. There are also assisted fertility procedures where the egg is extracted from the ovary, fertilized outside of the body and placed in the uterus for implantation. This is called in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Have an open conversation about your thoughts on future pregnancies with your healthcare provider. Together, you can form a plan and discuss ways to decrease any risk factors you may have.
Sources:
. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9687-ectopic-pregnancy
. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ectopic-pregnancy/symptoms-causes/syc-20372088
10 common questions about Ectopic pregnancy treatment
[kkstarratings]