ectopic pregnancy approach
ectopic pregnancy approach
what is ectopic pregnancy?
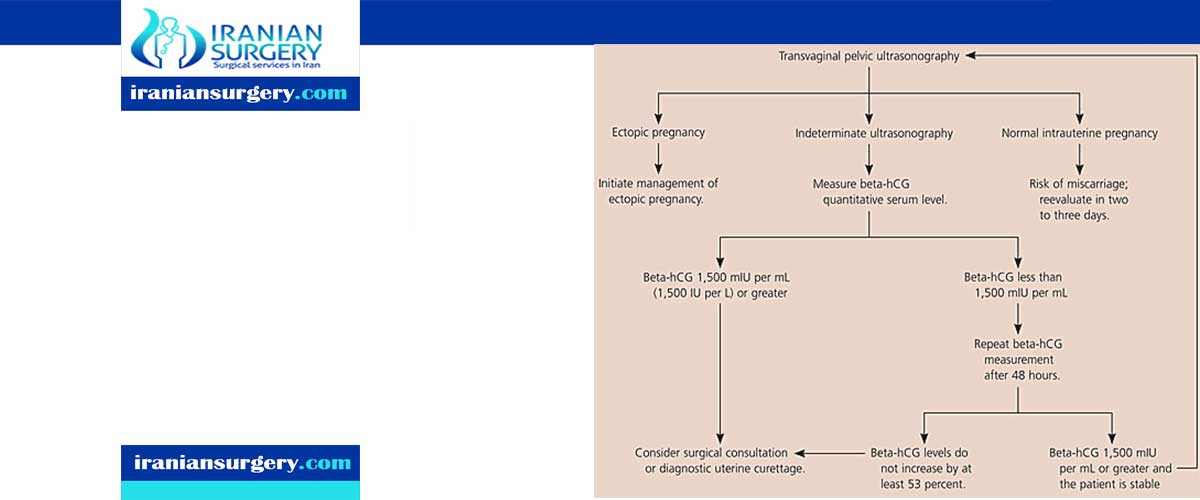
Ectopic pregnancy is a high-risk condition that occurs in 1.9 percent of reported pregnancies. The condition is the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in the first trimester. If a woman of reproductive age presents with abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, syncope, or hypotension, the physician should perform a pregnancy test. If the patient is pregnant, the physician should perform a work-up to detect possible ectopic or ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Prompt ultrasound evaluation is key in diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. Equivocal ultrasound results should be combined with quantitative beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin levels. If a patient has a beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin level of 1,500 mIU per mL or greater, but the transvaginal ultrasonography does not show an intrauterine gestational sac, ectopic pregnancy should be suspected.
Diagnostic uterine curettage may be appropriate in patients who are hemodynamically stable and whose beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin levels are not increasing as expected. Appropriate treatment for patients with nonruptured ectopic pregnancy may include expectant management, medical management with methotrexate, or surgery. Expectant management is appropriate only when beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin levels are low and declining. Initial levels determine the success of medical treatment. Surgical treatment is appropriate if ruptured ectopic pregnancy is suspected and if the patient is hemodynamically unstable.
10 common questions about ectopic pregnancy approach
[kkstarratings]


